2764
Low Resolution Diffusion Weighted Imaging for the Assessment of Diffuse Liver Disease1Radiology, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States
Synopsis
We evaluated the reproducibility of liver ADC measurements across acquisition parameters using low spatial resolution DWI with M1 optimized diffusion imaging waveforms (MODI) and the routinely clinically utilized monopolar (MONO) waveforms. We also evaluated the effects of various M1 values as well as those of breath-hold and respiratory-triggering on MODI-DWI liver ADC measurements at lower resolutions than utilized in clinical practice. MONO-DWI liver ADC suffered from bias and resolution-dependence in the left lobe while MODI-DWI liver ADC did not demonstrate this effect. MODI-DWI liver ADC did not demonstrate bias with respect to resolution, M1, or breathing technique.
Introduction
Liver fibrosis is the consequence of chronic liver injury of any etiology, and end-stage liver fibrosis (i.e., cirrhosis) is the leading cause of liver-disease-related deaths and the most important factor for liver cancer.1-3 The current gold standard for detection and evaluation of liver fibrosis is biopsy, which suffers from sampling/interpretation variability and potential complications.4-14 MR elastography (MRE) is validated to noninvasively estimate liver stiffness as an indirect surrogate for fibrosis.9,15-23 However, MRE limitations include lower sensitivity for detection of early stages of fibrosis and inability to differentiate fibrosis from concurrent liver inflammation as both processes increase liver stiffness.24-26Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) obtained through diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) has been proposed as a promising marker for assessment of liver fibrosis. However, variabilities in ADC measurements, which are in part due to low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), motion, and nonuniform acquisition parameters have precluded its widespread clinical utilization.27-30 M1-optimized diffusion imaging (MODI) waveforms have been reported to improve the accuracy and reproducibility of ADC measurements.31 Furthermore, lower-resolution images with subsequently higher SNR may improve ADC reproducibility. Hence, a combination of lower resolution and MODI waveforms may yield more reproducible liver ADC in shorter acquisition times than previously achievable; this approach is tailored for evaluation of diffuse liver disease and not lesion detection. However, the potential impacts of lower resolution and different M1 values on liver ADC obtained through MODI- and MONO-DWI are unknown. Hence, the goal of this study is to evaluate the impact of different spatial resolutions, M1 values, and breath-hold versus respiratory triggering acquisitions on MODI- and MONO-DWI liver ADC in healthy volunteers.
Methods
Images were acquired on a 3.0T MRI scanner(Signa Premier, GE Healthcare) using an anterior array coil (Air Coil, GE Healthcare) and a posterior embedded table coil. Seven healthy volunteers were recruited. Table 1 summarizes the image acquisition parameters. DWI sequences were acquired at b=50 and 500s/mm2. MODI-DWI was acquired using three M1-values: 0.0, 0.06, and 0.1s/mm. M1 was fixed across b-values for MODI-DWI. Breath-held and respiratory-triggered images were acquired for all waveforms. For MODI-DWI, images at 2.8x2.8x6mm3 were not acquired due to scan time limitations. Furthermore, the MODI waveform of breath-hold acquisitions was limited to one diffusion direction to accommodate realistic breath-hold times.ADC maps were generated in MATLAB (R2020a) using the b=50 and 500s/mm2 images and were reviewed/analyzed in Horos (v3.3.6). For each subject, three circular regions of interest (ROIs) measuring 2cm in diameter were placed on the b=50 s/mm2 image to avoid bias: one in each liver lobe and one in the spleen, avoiding major vessels and artifacts. ROIs were copied onto the corresponding ADC maps. Paired t-tests were used for comparison of ADC measurements across resolutions, M1, and breath-held versus respiratory-triggered exams.
Results
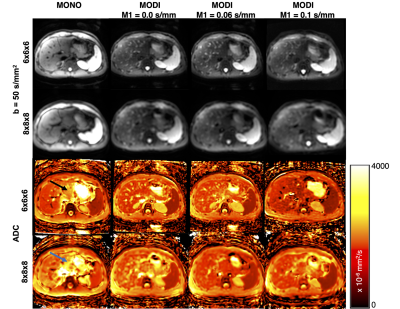
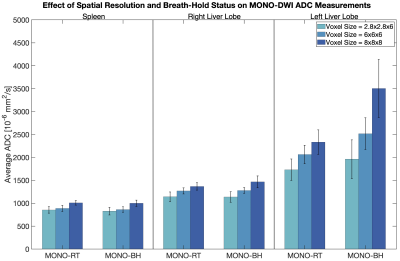
Figure 1 demonstrates sample DWI and ADC maps from a single subject, providing an example of the image resolution/subjective quality across different techniques.Figure 2 suggests an appreciable progressive increase in MONO-DWI liver ADC as a function of increasing voxel size (P=0.04). Bias is further amplified in the left lobe due to cardiac motion. While a similar pattern is noted in the spleen, it is less tangible and not statistically significant (P=0.054). While no difference was noted in the spleen and right liver lobe ADC between breath-held and respiratory-triggered acquisitions (P=0.61 and P=0.92, respectively), in the left liver lobe, breath-held MONO-DWI demonstrated even more bias and higher ADC values than the respiratory-triggered acquisition (P=0.01).
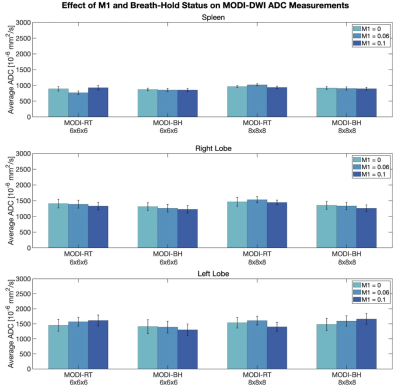
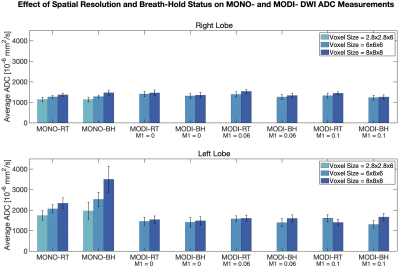
In contrast to MONO-DWI, MODI-DWI ADC was reproducible in both liver lobes and the spleen, across the tested M1 values (P=0.63), resolutions (P=0.32), and breath-hold versus respiratory-triggered acquisitions (P=0.92) (Figure 3). In the right liver lobe, where MONO-DWI ADC was most reproducible, MODI-DWI ADC demonstrates comparable values (Figure 4). Figure 4 also demonstrates the favorable reproducibility of MODI-DWI ADC in the left lobe compared to MONO-DWI ADC.
Discussion and Conclusions
We demonstrated that low-resolution MODI-DWI liver ADC is reproducible across the examined resolutions, different M1 values, and breath-held and respiratory-triggered acquisitions among healthy volunteers. Average liver ADC measurements are also similar to those reported in the literature.31-33 To our knowledge, the reproducibility of ADC at lower resolutions has not been demonstrated previously and is novel. Hence, this low-resolution approach is promising to achieve reproducible and rapid whole-liver evaluation in the setting of diffuse liver disease.We demonstrated more reproducible assessment of the left lobe by MODI-DWI ADC compared to MONO-DWI, which is a known limitation of MONO-DWI due to cardiac motion. We noted that this bias of MONO-DWI ADC is amplified at lower-resolutions and in breath-hold acquisitions, a phenomenon not observed in MODI-DWI ADC. Hence, low-resolution MODI-DWI can better assess the extent of disease heterogeneity in very short scan times.
Limitations of this study include its small sample size and absence of pathology in healthy volunteers. Furthermore, this study lacked correlation of ADC measurements with other reference standards, such as MRE or liver biopsy. Repeatability was not studied due to scan time constraints dictated by the number of parameters examined. Motivated by these promising preliminary results, we aim to further investigate the performance of low-resolution MODI-DWI in assessment of liver fibrosis among patients and in comparison to the current reference standards.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge support from the NIH (R01 EB030497), from the University of Wisconsin-Madison Office of the Vice Chancellor for Research and Graduate Education with funding from the Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation, as well as from the UW Departments of Radiology and Medical Physics. Also, GE Healthcare provides research support to the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
References
1. Ge PS, Runyon BA. Treatment of Patients with Cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(8):767-777.Figures
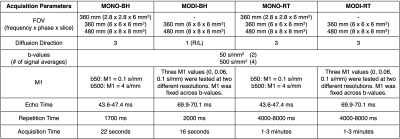
Table 1: Summary of image acquisition parameters.