2756
MRI Monitoring of Therapeutic Efficacy of Novel Heme targeting drugs in Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Orthotopic Tumors in Mice1Radiology, The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States, 2Biological Sciences, University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, TX, United States
Synopsis
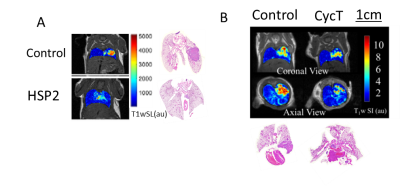
The goal was to evaluate the activity of two novel heme targeting drugs in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer models using multi-modality imaging. We found that the novel heme targeting drugs CycT (cyclopamine tartrate) and HSP2 (heme-sequestering peptide 2) were effective in suppressing NSCLC lung tumor growth as assessed by multimodality imaging and confirmed by pathology/histology. MRI detected the H1395 and H1299 orthotopic xenografts and was correlated with PET studies and histology.
We aimed to evaluate and optimize novel, heme targeting drugs in NSCLC therapeutic strategies with the aid of multi-modality imaging. Previous studies have demonstrated that NSCLC cells exhibit elevated mitochondrial respiration, increased heme synthesis and uptake compared to normal cells[3][4]. Here, we examined response of orthotopically implanted lung tumors to CycT (an inhibitor of heme synthesis) and HSP2 (inhibitor of heme uptake) in terms of vascular function, oxygenation and metabolism in mice using MRI and PET.
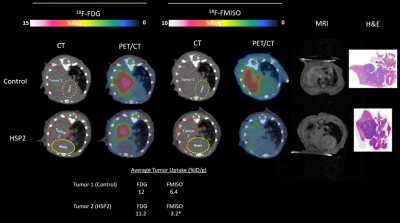
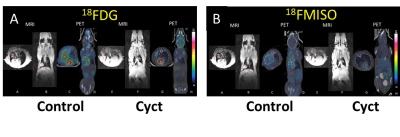
Methods: Briefly, 1-3 x106 H1299-Luc or H1395-Luc cells in serum-free medium containing 50% Matrigel were implanted surgically in orthotopically in 6-8 week-old NOD/SCID mice (n=6 for each cell line). Starting after two weeks implantation, BLI and anatomical T1-weighted MRI were carried out weekly to monitor tumor growth and metastasis. MRI was performed with a 4.7 T or 9.4 T small animal MRI system. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane (1.5%) in air (2 L/min) and kept warm using a circulating warm water blanket. Mouse body temperature and respiration were monitored with a small animal physiological monitoring system. High-resolution T1-weighted images were acquired using fast spin echo sequence with respiratory gating to reduce motion artifacts. Treatments with CycT (7.5 mg/kg) or HSP2 (25 mg/kg) started 2-3 weeks after tumor implantation. After treatment with these two drugs for five weeks, radiolabeled 18FDG and 18F-misonidazole (FMISO) were also applied using about 100 µCi for PET-CT and finally histology was performed after sacrifice.
Results: Our data showed that CycT and HSP2 were effective in suppressing lung tumor growth (figs. 1-3). MRI clearly showed the orthotopic lung tumors with features consistent with histology. As expected MRI showed better spatial resolution for localizing and monitoring tumor growth than BLI or PET and CT.
Conclusion: MR imaging and PET helped to monitor and evaluate the effects of two novel heme targeting drugs CycT or HSP2, which significantly suppress orthotopic lung tumor H1299 and H1395 tumor growth. While we successfully co-registered the separate MRI and PET/CT images combined PET-MR would be particularly attractive for future studies.
Acknowledgements
CPRIT RP200021 & RP160617 and infrastructure provided by small animal imaging resource of the Cancer Center via 2P30CA142543 and S10 OD018094.References
[1] Riaz, S. P. et al. Trends in incidence of small cell lung cancer and all lung cancer. Lung Cancer 75, 280-284.
[2] R.L. Siegel, K.D. Miller, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2016, CA Cancer J Clin, 66 (2016) 7-30.
[3] S. Sohoni, P. Ghosh, T. Wang, S.P. Kalainayakan, C. Vidal, S. Dey, P.C. Konduri, L. Zhang, Elevated Heme Synthesis and Uptake Underpin Intensified Oxidative Metabolism and Tumorigenic Functions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells, Cancer Res, 79 (2019) 2511-2525.
[4] P. Ghosh, Y. Guo, A. Ashrafi, J. Chen, S. Dey, S. Zhong, J. Liu, J. Campbell, P.C. Konduri, J. Gerberich, M. Garrossian, R.P. Mason, L. Zhang, L. Liu, Oxygen-Enhanced Optoacoustic Tomography Reveals the Effectiveness of Targeting Heme and Oxidative Phosphorylation at Normalizing Tumor Vascular Oxygenation, Cancer Research, 80 (2020) 3542.
Figures