2742
Qualitative and Quantitative Imaging Phenotypes can Predict CDKN2A/B Homozygous Deletion Status in IDH-mutant Astrocytomas1Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Pohang University of Science and Technology, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Synopsis
CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion is a key molecular marker in the 2021 WHO classification of IDH-mutant astrocytomas; presence of CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion results in a grade of 4. On multivariable analysis, infiltrative pattern, larger tumor volume, and higher 95th percentile of nCBV were independent predictors of CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion. The infiltrative pattern and larger volume may be reflected from the increased tumor cell proliferation, whereas the higher 95th percentile of nCBV may reflect the increased angiogenesis due to CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion.
Objectives
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CDKN)2A/B homozygous deletion is a key molecular marker in the 2021 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH)-mutant astrocytomas; the presence CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion in IDH-mutant histological grade 2 or 3 astrocytomas lead to designation to grade 4, even in the absence of microvascular proliferation or necrosis. The purpose of this study was to assess whether qualitative and quantitative imaging parameters can noninvasively predict the CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion status of IDH-mutant astrocytomas.Methods
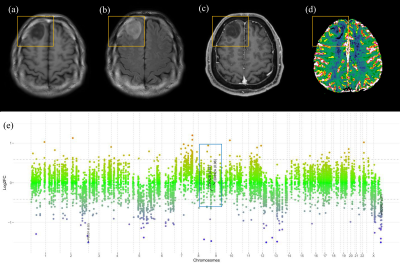
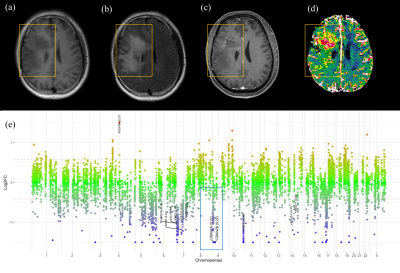
Preoperative MRI data of 34 patients with IDH-mutant astrocytomas (29 without and 5 with CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion, respectively) from our institution were included. Qualitative imaging assessment was performed. The mean ADC, 5th percentile of ADC, mean normalized cerebral blood volume (nCBV), and 95th percentile of nCBV were also assessed via automatic tumor segmentation. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression models were constructed.Results
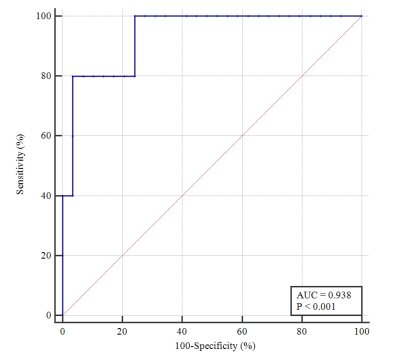
On univariable analysis, corpus callosum involvement (Odds ratio [OR] = 20.25, P = 0.010), ependymal extension (OR = 15.33, P = 0.024), proportion of necrosis > 5% (OR = 13.00, P = 0.019), infiltrative pattern (OR = 54.00, P = 0.003), and 95th percentile of nCBV (OR = 2.32, P = 0.28) were predictors of CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion. On multivariable analysis, tumor volume (OR = 1.01, P = 0.027), infiltrative pattern (OR = 38.02, P = 0.028), the volume (OR = 1.01, P = 0.027), and 95th percentile of nCBV (OR = 2.83, P = 0.043) were independent predictors of CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion. The area under the curve, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the multivariable model were 0.94 (95% confidence interval 0.80-0.99), 94.1%, 80.0, and 96.6%, respectively.Conclusion
Presence of infiltrative pattern, larger tumor volume, and higher 95th percentile of nCBV may be useful imaging biomarkers for CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion in IDH-mutant astrocytomas.Acknowledgements
None.References
Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P et al (2021) The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Neuro Oncol. 10.1093/neuonc/noab106
Louis DN, Wesseling P, Aldape K et al (2020) cIMPACT-NOW update 6: new entity and diagnostic principle recommendations of the cIMPACT-Utrecht meeting on future CNS tumor classification and grading. Brain Pathol 30:844-856
Shirahata M, Ono T, Stichel D et al (2018) Novel, improved grading system(s) for IDH-mutant astrocytic gliomas. Acta Neuropathol 136:153-16
Figures