2726
Large-scale simulations to create large collections of realistic white matter samples using MEDUSA1BAOBAB/NeuroSpin, Université Paris-Saclay, CNRS, CEA, Gif-sur-Yvette, France, 2iBrain U1253, Université de Tours, CHU Bretonneau, INSERM, Tours, France, 3DSSI, DIF, DAM, CEA, Bruyères-le-Châtel, France, 4LMN, MIRCen, Université Paris-Saclay, CNRS, CEA, Fontenay-aux-Roses, France
Synopsis
In this work, we demonstrate that the MEDUSA simulator can be used to create huge collections of brain white matter tissue microstructure samples in the frame of large-scale HPC simulation campaigns and how these Big Data could serve the design of novel computational models able to decode white matter microstructure.
Introduction
Diffusion MRI simulations have become a key tool to understand the impact of the various microstructural features on the diffusion MRI signal and choose the best diffusion scheme and sequence parameters to quantify them1-4. The learning of computational models require large quantities of samples associating their microstructural characteristics and their diffusion MRI signatures, which will be derived either from histological studies or from simulation campaigns of realistic geometries of cellular environments similar to those found in brain tissue. Several approaches have been proposed recently to create realistic membrane geometry mimicking white matter cellular environments5-10. In this work, we propose to exploit the MEDUSA tool5,11, within the frame of a large-scale simulation campaign, to create a large collection of white matter virtual samples embedding axonal populations with various degrees of realism.Materials/Methods
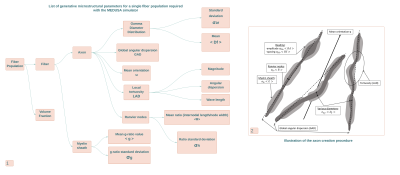
MEDUSA5 is an open source software11 embedding 1) a geometry simulator to create the virtual membranes of cell populations mimicking real brain tissues, 2) a Monte-Carlo simulator of the diffusion process of water molecules within membranes geometries 3) a simulator of the diffusion MRI signal attenuation for any type of diffusion pulse sequence. This study was focused on the use of the geometry simulator to create large dictionaries of virtual white matter membrane geometries. The generative microstructural parameters of each fiber population were drawn randomly to sample the space of plausible configurations encountered within the white matter. For a given population, a specific set of generative hyper-parameters is chosen that correspond to the parameters of distribution functions from which some individual axonal fiber characteristics described in Figure 3 are randomly drawn.The creation of a single virtual white matter tissue sample consists in selecting the number of fiber populations present in the virtual sample and then for each population in drawing its generative hyper-parameters. The MEDUSA tool was highly parallelized using the Kokkos toolbox12 to be able to run on both CPU-based and GPU-based architectures. The process to create a complex sample of mesoscopic size takes less than a minute on a conventional desktop workstation with the CPU architecture. The creation of a large dictionary including several millions of samples required the use of a high performance computing (HPC) facility (TGCC, French GENCI Large Scale Instrument, Bruyères-le-Châtel). A dedicated MEDUSA container was built and deployed on an architecture with 2292 nodes equipped with 2 AMD CPUs (AVX2, 64 cores/CPU) and 256GB RAM/node, yielding a total of 293376 cores. Several large-scale simulation campaigns summarized in Figure 4 were launched with the MEDUSA container targeting 2 complementary objectives: 1) providing large sets of single fiber population geometries with increasing levels of microstructural details to study the impact of their degree of realism on the design of diffusion MRI computation models of microstructure, 2) providing large sets of realistic 1/2/3 fiber population geometries to train new diffusion MRI of microstructure.Results
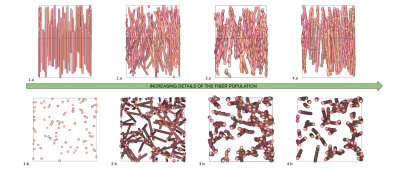
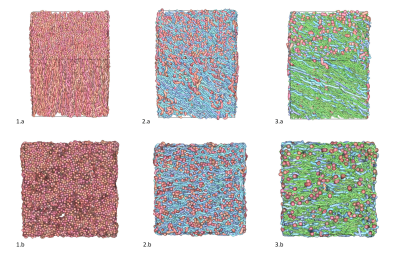
The first simulation campaign aimed at generating 100,000 membrane geometries of simple fiber populations, produced with an increasing degree of realism corresponding to: rectilinear and parallel fiber populations, rectilinear with angular dispersion, tortuous with angular dispersion, with a myelin sheath, with Ranvier nodes. The following 3 simulation campaigns aimed to generate 3 collections of virtual white matter samples with respectively 1, 2 or 3 fiber populations whose spatial mean directional distribution and microstructural characteristics were sampled to provide a wide spectrum of plausible configurations. Figure 4 gives an overview of different samples that make up these 3 collections, illustrating the variability of different microstructural parameters within populations and between populations of the same sample. Figure 5 provides histograms of the computation time for the 3 types of virtual white matter samples including 1/2/3 fiber population(s) in order to evaluate the influence of the complexity of their geometry on their computation time.Discussion
Lee et al13 used a reciprocal approach to that proposed in this work by starting from the physical reality of an axon scanned in electron microscopy and progressively deleting the microstructural features of the axon and studying the effect of its deletions on the diffusion MRI signal . One difficulty of this study is reproducing this work at the scale of the population of axons and the limited number of samples available to generalize the study to all geometric configurations encountered within the white matter. Collection 1 responds to this need through the extensive use of the generative approach available in the MEDUSA simulator by providing a large quantity of samples covering a wide spectrum of geometries of a homogeneous population of axonal fibers with an increasing degree of realism. Figure 5 illustrates the computational efficiency of the MEDUSA container to deliver collections of white matter virtual samples in a limited time, and shows the computation time increasing with the complexity of the membrane geometry.
Conclusion
In this study, the use of the MEDUSA simulator in a high-performance computing environment allowed the creation of large synthetic samples representing the diversity of geometric configurations of axonal fiber membranes in the cerebral white matter, with a high degree of realism. These Big Data are intended to explore the impact of the white matter microstructure on the diffusion MRI signal to establish new computational models to decode it.Acknowledgements
This project/research has received funding from the CEA PTC Simulation Numerical Program, from the French-German AIDAS2 Joint Institute, and from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Framework Program for Research and Innovation under the Specific Grant Agreement No. 945539 (Human Brain Project SGA3).References
1. Hall, M. G., & Alexander, D. C. (2009). Convergence and parameter choice for Monte-Carlo simulations of diffusion MRI. IEEE transactions on medical imaging,28(9), 1354-1364.
2. Yeh, C. H., Schmitt, B., Le Bihan, D., Li-Schlittgen, J. R., Lin, C. P., & Poupon, C.(2013). Diffusion microscopist simulator: a general Monte Carlo simulation system fordiffusion magnetic resonance imaging. PloS one, 8(10), e76626.
3. Neher, P. F., Laun, F. B., Stieltjes, B., & Maier‐Hein, K. H. (2014). Fiberfox: facilitating the creation of realistic white matter software phantoms. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 72(5), 1460-1470.
4. Ginsburger, K., Poupon, F., Beaujoin, J., Estournet, D., Matuschke, F., Mangin, J. F.,... & Poupon, C. (2018). Improving the realism of white matter numerical phantoms: astep toward a better understanding of the influence of structural disorders in diffusion MRI. Frontiers in Physics, 6, 12.
5. Ginsburger, K., Matuschke, F., Poupon, F., Mangin, J. F., Axer, M., & Poupon, C.(2019). MEDUSA: A GPU-based tool to create realistic phantoms of the brainmicrostructure using tiny spheres. NeuroImage, 193, 10-24.
6. Rensonnet, G., Scherrer, B., Girard, G., Jankovski, A., Warfield, S. K., Macq, B., ... &Taquet, M. (2019). Towards microstructure fingerprinting: estimation of tissueproperties from a dictionary of Monte Carlo diffusion MRI simulations. NeuroImage,184, 964-980.
7. Rafael-Patino, J., Romascano, D., Ramirez-Manzanares, A., Canales-Rodríguez, E.J., Girard, G., & Thiran, J. P. (2020). Robust Monte-Carlo simulations indiffusion-MRI: Effect of the substrate complexity and parameter choice on the reproducibility of results. Frontiers in neuroinformatics, 14, 8.
8. Kerkelä, L., Nery, F., Hall, M. G., & Clark, C. A. (2020). Disimpy: A massively parallel Monte Carlo simulator for generating diffusion-weighted MRI data in Python. Journalof Open Source Software, 5(52), 2527.
9. Reuter, J. A., Matuschke, F., Menzel, M., Schubert, N., Ginsburger, K., Poupon, C., ...& Axer, M. (2019). FAConstructor: an interactive tool for geometric modeling of nervefiber architectures in the brain. International journal of computer assisted radiologyand surgery, 14(11), 1881-1889.
10. Callaghan, R., Alexander, D. C., Palombo, M., & Zhang, H. (2020). ConFiG:Contextual Fibre Growth to generate realistic axonal packing for diffusion MRIsimulation. Neuroimage, 220, 117107.
11. MEDUSA:https://framagit.org/cpoupon/gkg/-/tree/master/simulation/src/plugin/gkg-simulation-plugin-functors/Medusa12. Edwards, H. C., & Trott, C. R. (2013, August). Kokkos: Enabling performance portability across many core architectures. In 2013 Extreme Scaling Workshop (xsw2013) (pp. 18-24). IEEE.
13. Lee, H. H., Jespersen, S. N., Fieremans, E., & Novikov, D. S. (2020). The impact of realistic axonal shape on axon diameter estimation using diffusion MRI. NeuroImage,223, 117228.
Figures