2582
Combination of IVIM with DCE-MRI in diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of breast cancer1Department of Magnetic Resonance, LanZhou University Second Hospital, Lanzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Xi’an, China
Synopsis
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) combined with Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) are meaningful MRI techniques applied to breast cancer. This study uses DCE-derived parameters (voiume translocation constant, Ktrans and rate constant, Kep) and IVIM-derived parameters (diffusion coefficient, D and perfusion fraction, f) to perform correlation analysis with prognosis of breast cancer indexes (ER, PR, her-2, Ki-67). The results show that IVIM and DCE-MRI can distinguish benign and malignant breast lesions. Therefore, there are correlation between Ktrans, Kep, D and prognostic factors of breast cancer. Our research may provide more important clinical evidence for the treatment and prognosis of breast cancer.
Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy among females with high heterogeneous characterized by variant biological features. Its diagnosis, treatment and prognosis are affected by many factors, including the size and shape of breast cancer, pathological grade, receptor expression, the status of axillary lymph node metastasis, Ki-67. Scholars1,2 have been committed to studying the characteristics of breast cancer with different prognosis, predicting its biological behavior, and seeking the best treatment to improve the prognosis of patients, and trying to explore the relationship between MRI functional imaging parameters and prognostic factors of breast cancer. As a non-invasive and non-radiation method, MRI can not only evaluate the lesions from the macroscopic point of view of gross morphology, but also provide tumor micro-molecular level information through a variety of functional imaging methods (including DCE-MRI and IVIM)3,4. The prognosis of the tumor is closely related to the microscopic characteristics of the tumor5. Previous studies focused on the correlation between the microcosmic characteristics and prognosis factors, but very little was known on the multiparameter application. Therefore, in this study, we compared the application of DCE-MRI and IVIM in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions, and analyzed the correlation between various parameters and prognostic factors of breast cancer.Methods
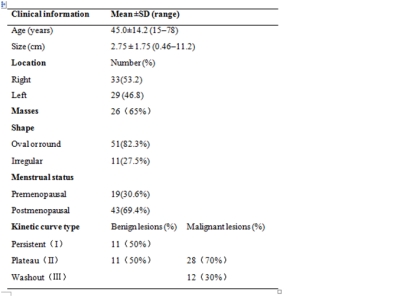
A total of 157 female patients with breast lesions were selected for breast MR imaging. 98 patients were excluded for the following reasons: 1) radiotherapy, chemotherapy, needle biopsy (47 patients); 2) failure to obtain clear immunohistochemistry and pathological results after scanning (36 patients); and 3) missed scanning sequence or showed poor lesion visibility on DCE and IVIM parameter maps for analysis (15 patients). Finally, a total of 62 lesions from 59 patients were included in the study. In all, including 22 benign lesions and 40 malignant lesions were recruited from the LanZhou University Second Hospital and underwent T1WI, T2WI, DCE-MRI, IVIM-MRI with a 3.0T scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, the Netherlands). The clinical and the patient’s populations are shown in Table 1. The DCE-MRI related parameters including Ktrans, Kep were extracted by IntelliSpace Portal workstation. IVIM related D, and f were obtained by MITK-Diffusion software (https://www.mikt.org/wiki/Downloads). Then, these multiple parameters were compared between the benign and malignant groups and between groups with different expression levels of prognostic factors. The software SPSS 22.0 was used for the statistical analysis. The measurement data using mean ± standard deviation (x±s); The independent-sample t-test, χ2 test exact probability analysis were used to compare the differences of parameters. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of different parameters. The Pearson correlation coefficient was used to analyze the correlation. For multi-index combined diagnosis, we constructed a binomial logistic regression model to estimate the corresponding performance.Results
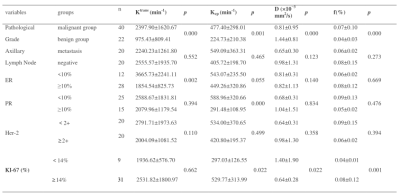
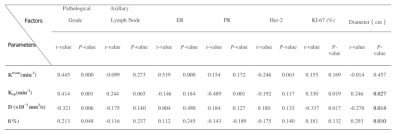
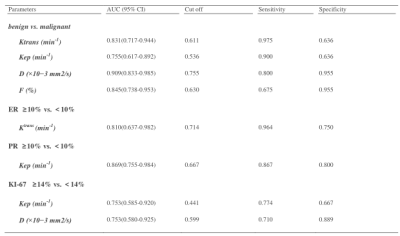
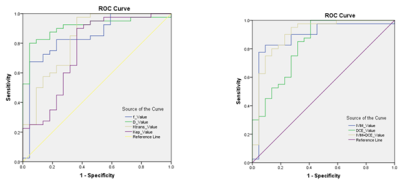
The D value of the malignant group were lower, Ktrans, Kep and f were higher than those of the benign group (p < 0.05) (Table 2). The areas under the curve (AUCs) of DCE, IVIM, DCE + IVIM were 0.828, 0.882, 0.901 respectively (Fig. 1). The Ktrans, Kep, D, f value showed correlated with the pathological grade (r = 0.445, 0.414, -0.321, 0.213, p<0.05). The Ktrans showed negatively correlated with the ER (r = -0.519, p<0.05); The Kep showed correlated with the PR, Ki-67 (r = -0.489, 0.330, p<0.05); Her-2, the status of axillary lymph node metastasis showed no significant correlation with DCE and IVIM (P>0.05, Table 3 and 4). Tumor diameter showed correlated with the Kep, D, f (r = 0.246, -0.278, 0.293, p<0.05).Discussion
DCE-MRI and IVIM can distinguish benign and malignant breast lesions. Malignant breast tumors have numbers of nourishing blood vessels, resulting in vascular endothelial structure disorder and immature development, increased permeability, and perfusion increase. This tumor expansion process causes tumor cell spreading limitation, D value decreases, f, Ktrans, Kep increase. The Ktrans showed negatively correlated with the ER. These findings are consistent with previous study6 suggesting that the Ktrans could be used to preliminarily assess ER expression in breast cancer patients, possibly because ER down regulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and thus inhibits tumor angiogenesis7.The Kep showed negatively correlated with the PR, as far as we known, there was no similar report in the previous literature. Some scholars8 observed that Kep might provide a better depiction of actual tumor capillary permeability than Ktrans, as any conditions influencing blood perfusion may potentially confound measurements of Ktrans. At the same time, Ki-67 can induce the production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which promotes tumor vascular perfusion . Tumor diameter can also affect the treatment and prognosis of breast cancer, indicating that IVIM and DCE have the capability to comprehensively evaluate the prognostic factors of breast cancer.Conclusion
This research shows that IVIM and DCE-MRI can distinguish benign and malignant breast lesions. DCE-derived Ktrans, Kep and IVIM-derived D and f are associated with prognostic factors of breast cancer. These results suggest that our method may provide complementary information to breast cancer imaging biomarkers, which potentially leading to earlier diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgment found.References
1. Makkat Smitha, Luypaert Robert,Stadnik Tadeusz et al. Deconvolution-based dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging of breast tumors: correlation of tumor blood flow with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status and clinicopathologic findings--preliminary results.[J] .Radiology, 2008, 249: 471-82.
2. Tudorica Alina, Oh Karen Y, Chui Stephen Y-C et al. Early Prediction and Evaluation of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Using Quantitative DCE-MRI. Transl Oncol, 2016, 9: 8-17. 3. El Khouli Riham H,Macura Katarzyna J,Kamel Ihab R et al.
3-T dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast: pharmacokinetic parameters versus conventional kinetic curve analysis.AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2011, 197: 1498-505.
4. Cho Gene Young, Moy Linda, Kim Sungheon G et al. Evaluation of breast cancer using intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) histogram analysis: comparison with malignant status, histological subtype, and molecular prognostic factors. Eur Radiol, 2016, 26: 2547-58.
5. Iima Mami, Kataoka Masako, Kanao Shotaro et al. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion and Quantitative Non-Gaussian Diffusion MR Imaging: Evaluation of the Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Several Markers of Malignant and Benign Breast Lesions.Radiology, 2018, 287: 432-441.
6. Koo Hye Ryoung,Cho Nariya,Song In Chan et al. Correlation of perfusion parameters on dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI with prognostic factors and subtypes of breast cancers.[J] .J Magn Reson Imaging, 2012, 36: 145-51.
7. Li Sonia P, Padhani Anwar R, Taylor N Jane et al. Vascular characterisation of triple negative breast carcinomas using dynamic MRI.[J] .Eur Radiol, 2011, 21: 1364-73.
8. Kim Sung Hun,Cha Eun Suk,Kim Hyeon Sook et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of breast cancer: correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficient value with prognostic factors.[J] .J Magn Reson Imaging, 2009, 30: 615-20.
Figures