2575
Exploring the reproducibility of APT imaging technology in healthy adult kidneys based on breathing patterns1Xi'an Gaoxin Hospital, Xi'an, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
The current amide proton transfer weighted (APTw) imaging cannot control the effect of respiratory motion artifacts effectively during image acquisition. Respiratory motion artifacts are a major factor affecting the quality of APTw imaging of the liver [1].In this study, according to the characteristics of APTw imaging acquisition, the healthy adult volunteers were divided into free-breathing (FB) group and intermittent breath-holding (IBH) group. The the right renal axial plane APTw imaging acquisition with the same parameters was performed. The analysis results showed that the success rate and repeatability of APTw imaging in the IBH group were better than FB group.
Introduction
The amide proton transfer (APT) technology can indirectly reflect the content of free proteins and peptides in tissues and lesions, which was mature in the diagnosis of central nervous system diseases. However, there is still locking a effective method to control respiratory motion artifacts for APT-weighted (APTw) imaging methods, such as respiratory gating and diaphragm navigation. They have been initially used in tumors of the prostate [2], cervix [3] and other organs [4] of the body to reduce artifacts by respiratory motion. According to reports, breathing exercise is the main factor affecting the success rate of liver APTw imaging [1]. APT technology has achieved good diagnostic value in animal experiments of acute and chronic kidney diseases [5], but there are few reports on the application of clinical renal APT technology. The purpose of this study was to find an available intermittent breathing pattern to improve success rate of renal APTw imaging acquisition. (Acquisition and interval time ratio is about 1:2, about 4s interval acquisition 2s), take "inhalation - end expiration breath hold (RF pulse acquisition sound start to end about 2s) - inhalation (RF pulse sound disappears after the start)" mode training volunteers. Compare and analyze the difference in the reproducibility of the APTw values of healthy adult right kidney under the two breathing patterns: free breathing (FB) and intermittent breath-holding (IBH).Methods
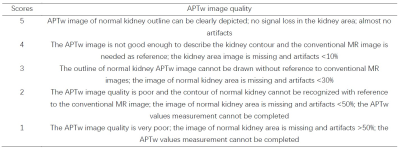
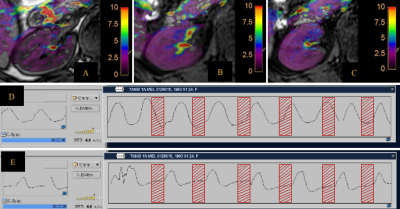
From May 2021 to October 2021, 81 healthy adult volunteers were recruited. They were divided into two groups according to the order of enrollment and breathing patterns. One group was the FB group with 54 patients (age range from 26 to 70 years, 49.56±10.34, 25 males). The other group was the IBH group with 27 cases (age range from 24 to 46 years, 30±8.9, 10 males). Both groups used Philips 3.0T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare) to acquire 3D-APTw imaging of the right kidney with the same parameters under fasting conditions . 13 patients in the IBH group were randomly selected for repeated scanning (intermittent 1 or 2 days). t. Axial position:FOV=110x102x21mm3,TR/TE=5778.0/8.3ms,Matrix=64×60; coronal position FOV=163×127×21mm3,TR/TE=5778.0/8.8ms,Matrix=96×75.According to the Likert Scale scoring method for the evaluation of the quality of APTw imaging (Table1), lower scores (1 or 2) were not included in the measurement of APTw values. A region of interest (ROI) was manually placed by three radiologists with 3-, 6- and 10-years’ experience on the location of the anterior, middle and posterior parts of axial APTw imaging. Three ROIs were placed on every part (Table 3) in right kidney, and the averaged APTw value in each part was measured. All ROIs avoid blood vessels and artifacts. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and Bland-Altman method were used to evaluate the consistency. One-way analysis of variance was used to analyze the data between different parts of APTw imaging in two groups. The two independents sample t-tests were used to assess the difference between two groups.Results
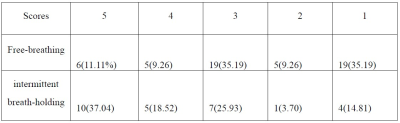
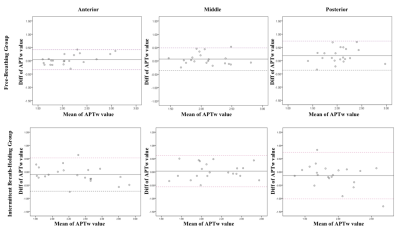
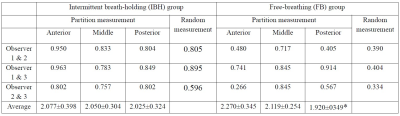
The APTw imaging quality of IBH group was better than that of FB group (table2). 22 cases (81.48%) of IBH group and 31 cases (57.41%) of FB group were included in analysis. The reproducibility of random measurement and partition measurement in the IBH group was better than that of the FB group. The reproducibility of the partition measurement is obviously better than that of the random measurement in IBH group (Table 2). The Bland-Altman analysis is shown in Figure 2. In addition, in the IBH group, the intro-observer and the repeated scan APTw values had better reproducibility (Table 3). There was no statistical difference between the APTw values in 3 parts in IBH group (P=0.838), the APTw values between three parts of FB group had statistically different (P=0.009). Further analysis shows that the difference between the anterior and posterior parts (P=0.002), and the others were no statistical difference (Table 3).Discussion
The 3D-APT sequence originated from the central nervous system, while there is lacking a effective techniques to control breathing movement. Hence, we propose an available intermittent breathing patterns to train patients for improving success rate of APTw images. Through comparative analysis, it was found that the APTw imaging quality and repeatability of the IBH group was significantly higher than that of FB group. The respiratory group revealed that respiratory movement was an important factor affecting the image quality of kidney APTw imaging. In the IBH group, the scan was repeated at intervals of 1 or 2 days. The first and second IBH of the two volunteers were good, and the quality of the two APTw imageing was poor, indicating that other factors interfered with the APTw imageing of the two volunteers’ kidneys. The quality of APTw imagings remains to be further studied, such as increasing the collection of B0 field maps to understand the uniformity of the magnetic field.Conclusion
It is speculated through comparative analysis that breathing exercise is an important factor affecting the image quality of renal APTw imaging. The current 3D-APTw IBH scan of healthy adult kidneys has good reproducibility. If the 3D-APTw technology is going to be widely used in body, and it is still necessary to effectively solve the problem of breathing movement.Acknowledgements
NOReferences
[1] Seo N, Jeong HK, Choi JY, et al. Liver MRI with amide proton transfer imaging: feasibility and accuracy for the characterization of focal liver lesions[J]. European Radiology, 2020.
[2] Jia G, Abaza R, Williams JD, et al. Amide proton transfer MR imaging of prostate cancer: a preliminary study[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2011, 33(3): 647-654.
[3] Meng N, Wang X, Sun J, et al. Application of the amide proton transfer-weighted imaging and diffusion kurtosis imaging in the study of cervical cancer[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(10): 5758-5767.
[4] Ishimatsu K, Nishie A, Takayama Y, et al. Amide proton transfer imaging for differentiating benign ovarian cystic lesions: Potential of first time right[J]. European Journal of Radiology, 2019, 120: 108656.
[5] Jing L, Zheng H, Guoli C, et al. CEST MRI of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury[J]. NMR in Biomedicine, 2018, 31: e3942.
Figures