2454
Compression sensing based uterine 3D-T2WI isotropic imaging: Optimization of the optimal accelerator1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian,China, China, 2Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
3D-ISO-T2WI can obtain ISO volume images compared with traditional 2D-T2WI imaging, reducing partial volume effects, and volume data post-processing can be omni-directional, Three-dimensional, multi-angle display of the overall picture of the uterine structure and the scope of the lesion, but its scanning time is longer [1], the peristalsis of the subject's uterus, bladder and intestine during the scanning time may affect the image quality, and the scanning time The long-term reduction of the patient’s coordination and examination circulation.In this study, different AF will be selected to optimize the best AF based on the CS-based 3D-ISO-T2WI sequence of the uterus.
Introduction
Three-dimensional T2-weighted imaging (3D T2WI) can be used for isotropic (ISO) volume images with reduced partial volume effects in comparison to traditional 2D-T2WI imaging. And the 3D volume data allow for 3D omni-directional, multi-angle reconstruction thus more comprehensive representation of the uterine structure and the scope of the lesion. However, its scan time is much longer than 2D acquisitions, and the peristalsis of uterus, bladder and intestine during the data acquisition may affect the image quality. The long-term reduction of the patient’s coordination and examination circulation, the emergence of compressed sensing (compressed SENSE, CS) technology greatly shortens the scan time. In this study, the 3D-ISO-T2WI for the uterus will be scanned with different acceleration factors (AF) on healthy volunteers, and an optimal AF will be recommended based on subjective and objective image evaluations.Materials and Methods
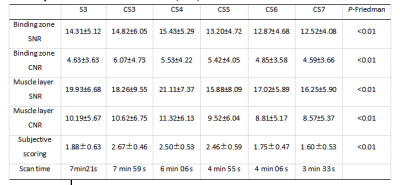
Twenty-four healthy female volunteers aged 21-40 years, with an average age of (29.48±7.69) years, were recruited to perform sagittal scanning of uterus 3D-ISO-T2WI sequence (FOV: 300 * 300 * 120 mm3; voxel: 1.00×1.00×1.00 mm3; TR/TE: 1250/147ms) using 6 different AF (Including SENSE 3, CS3, CS4, CS5, CS6 and CS7) on a 3.0T MRI scanner. The SENSE3 was used as a reference scan. And the image quality was analyzed and evaluated by two observers on the workstation using a double-blind method. An three-point system was used for subjective image evaluation, and the objective measurements included the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) and Contrast to Noise Ratio (CNR) of the uterine binding zone and muscular layer. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were used to analyze the consistency of their measurement results, and the Friedman rank-sum test was used to compare the differences between SNR and CNR under different AF conditions .Results
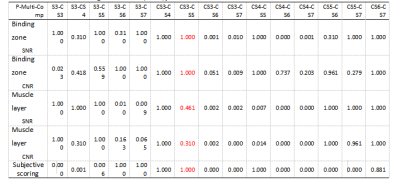
There was a good agreement between objective measurements by the two observers (ICC >0.75). The scan time of six different AFs (including SENSE 3, CS3, CS4, CS5, CS6 and CS7) was 7min21s, 7min51s, 6min06s, 4min55s, 4min06s and 3min33s, respectively. The results showed that the SNR (14.82±6.05, 18.26±9.55) and CNR (6.07±4.73, 10.62±6.75) were the highest in CS3. The scan time of CS5 and CS3 was reduced from about 8 mins to about 5 mins (reduced by 37.5%) without significant difference in SNR and CNR (P > 0.05). CS6 and CS7 could further shorten the scan time, but their SNR and CNR were significantly lower than those of CS3 (P < 0.05). In addition, the subjective scores by the two observers were also in good agreement (ICC >0.75). CS3 had the highest and CS7 had the lowest subjective score. There was statistically significant difference in scores among all groups (P< 0.05).Discussion and Conclusion
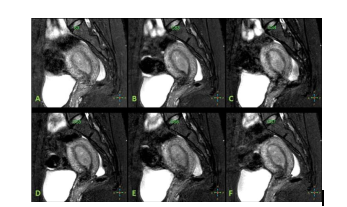
In female pelvic MRI examination, conventional T2WI can better display the anatomical structure of the uterus than T1WI [2], which is of great value for the identification of uterine MRI anatomy and lesions. In order to make a clear diagnosis and accurately assess the staging of uterine tumors, it is usually necessary to comprehensively observe the uterus, cervix and vagina (fornix), parauterine and lymph nodes. Therefore, when routine multi-layer 2D-T2WI scanning is used in clinical practice, three azimuth imaging (oblique) axial, (oblique) coronal, and sagittal are required. The cumulative scanning time is longer, and due to the anterior and posterior inclination of the uterus, etc. , It is difficult to show the whole picture on a single level. 3D-ISO-T2WI imaging can obtain volumetric images, which is conducive to omni-directional and multi-angle display of the uterine body, cervix, vagina and other anatomical structures and the scope of lesion involvement, providing reliable information for accurate diagnosis and clear staging. It has been used in the uterus Diagnosis of malformation [3-6].Results by this study indicated that images by CS5 were evaluated with the highest subjective score and the best display of the three-layer structure of the uterus. In terms of objective measurements, images by CS5 shows slightly lower SNR and CNR than those by CS3 by without significant difference. Considering with the significantly redeced scan time, , CS5 is selected as the optimal AF for routine uterine high-resolution 3D-ISO-T2WI.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]Zhu Ying, Zhu Tianzhao, Wang Yue, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of 3D T2WI in staging endometrial cancer. Journal of Practical Radiology, 2012, 28(12):1827-1830.
[2] FENG R M, z0NG Y N, cA0 s M, et a1. current cancer situation in China: Good or bad news from the 2018 Global Cancer statistics?口]. Cancer commun(Lond), 2019, 29; 39(1): 22.
[3] Wang Xuezhen, Tian Xiaomei, et al. Application value of 3D MRI in the diagnosis of congenital uterine malformations. Chinese Journal of Medical Computer Imaging, 2012, 18:395-397.
[4]Bertrand MM, Macri F, Mazars R, et al. The 3D reconstructions of female pelvic autonomic nerves and their related organs based on MRI: a first step towards neuronavigation during nerve-sparing radical hysterectomy. EurRadiol, 2018, 28(11 ):4561-4569.
[5] Gu Shouxin, Li Ke, Zhang Guofu, et al. Value analysis of 3D-SPACE sequence in deep invasive endometriosis. Chinese Journal of Medical Computer Imaging, 2017, 23:347-351.
[6]Ota T, Hori M, Onishi H, et al. Feasibility of a reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted (rFOV) sequence in assessment of myometrial invasion in patients with clinical FIGO stage I endometrial cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging , 2016, 43(2):316-324.
Figures