2297
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Prediction of Prognosis in Intermediate Risk Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Jianting Li1, Jinliang Niu1, Wenjin Bian2, and Wenqi Wu1
1The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China, 2Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
1The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China, 2Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
Synopsis
The mortality rate for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is still high. Cytogenetic features are the most important prognostic parameter, and the most appropriate treatment of intermediate risk AML (IR-AML), which accounts for about 60% of AML, is controversial. Our study suggested that the D value obtained from intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) could play a potential role in predicting treatment response of IR-AML patients. Moreover, f value and D* value in an IVIM model can independently predict OS of patients with IR-AML. These findings suggest that IVIM parameters can be useful imaging markers to predict prognosis for IR-AML.
Introduction
The mortality rate for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is still high1. Cytogenetic and molecular features are the most important prognostic parameters and separate patients into favorable-, intermediate- and unfavorable- risk groups2. However, prognostic factors for AML do not accurately predict treatment response in IR-AML, which accounts for about 60% of AML2. Diffusion and perfusion are important biological characteristics of tumor tissue and are of great significance for prognosis evaluation. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) can provide these two characteristics simultaneously3. The aim of this study was to investigate whether IVIM parameters of bone marrow could predict the outcome in patients with untreated IR-AML.Materials and Methods
This prospective study enrolled participants with newly diagnosed IR-AML between June 2014 and November 2015 consecutively. Participants underwent MRI of the lumbar spine using an IVIM sequence. Participant clinical characteristics and OS were collected. The median follow-up was 17.5 months (range, 1-56 months). The IVIM parameters (f, D, and D*) were obtained. A nonparametric log-rank test was used to identify the threshold of IVIM parameters for OS. Univariable Kaplan-Meier and multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression analyses were performed to investigate prognostic significance of possible indicators.Results
The D value differed significantly between CR and NR group (P=.043). AUC of D was 0.717 (P=.042), with a sensitivity of 83.3% and a specificity of 50.0% were achieved. Univariate analysis results showed that high value of f (>30.1%) and low value of D* (≤80.0×10-3mm2/s) were associated with shorter OS (P=.015, 023, respectively). When IVIM DWI parameters, age and WBC count were included in the multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis, the results showed that f value (hazard ratio [HR]: 3.346, P=.018) and D* value (HR: 0.357, P=.025) were independent factors for OS.Discussion
The f value of IVIM DWI, reflecting the fractional volume of capillary blood flow in each voxel, relate to bone marrow perfusion4. The f value was mentioned in several studies as biomarkers for tumor angiogenesis assessment and evidence suggested that the levels of microvessel density (MVD) are useful to evaluate the status of AML5. The MVD is the gold standard to assess angiogenesis in the bone marrow, but it is invasive and cannot represent the overall and dynamic changes of the bone marrow of IR-AML patients5. IVIM DWI may be used as an alternative method for perfusion MR imaging in these patients.D was used for evaluating the cellularity4. Previous work suggested D value was statistically different between CR group and NR group in patients with AML before treatment6. The results of this time further suggested that lower D value tend to achieve NR in untreated IR-AML patients. The possible reason was lower D value reflects hypercellularity and higher tumor burden, leading to the intercellular space and restriction of water diffusion. Therefore, we believe that D value could assess bone marrow cellularity before induction chemotherapy in patients with IR-AML, which is an important predictive factor of potential utility into clinical practice.
The D* value was another perfusion parameter of IVIM. D* value reflects the rate of micro-capillary blood flow. Our result showed that D* value could independently predict the OS of patients with IR-AML. Given the fact that D* maps had lower signal-to-noise ratio compare with the other maps and its poor reproducibility, we need further study to prove this result7.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the D value obtained from IVIM could play a potential role in predicting treatment response of patients with IR-AML. Moreover, f value and D* value in an IVIM model can independently predict OS of patients with IR-AML. These findings suggest that IVIM parameters can be useful imaging markers to predict prognosis for IR-AML.Acknowledgements
There are no acknowledgments.References
- Lowenberg B, Downing JR, Burnett A. Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1051-1062.
- Lowenberg G. Strategies in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2004;89:1029-1032.
- Li J, Li W, Niu J, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI of infiltrated marrow for predicting overall survival in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia. Radiology. 2020;295:155-161.
- Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, et al. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 1988;168:497–505.
- Kuzu I, Beksac M, Arat M, et al. Bone marrow microvessel density (MVD) in adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML): therapy induced changes and effects on survival. Leuk Lymphoma 2004;45:1185-1190.
- Niu J, Li W, Wang H, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging of bone marrow in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a pilot study of prognostic value. J Magn Reson Imaging 2017;46:476-482.
- Lima M, Le Bihan D. Clinical intravoxel incoherent motion and diffusion MR imaging: past, present, and future. Radiology 2016;278:13-32.
Figures
Comparison of
IVIM Parameters Between CR and NR Groups of 40 Patients with IR-AML.
Univariate and
Multivariate Cox Proportional Hazards Regression Analyses of Variables
Associated with Overall Survival of 40 Patients with IR-AML.
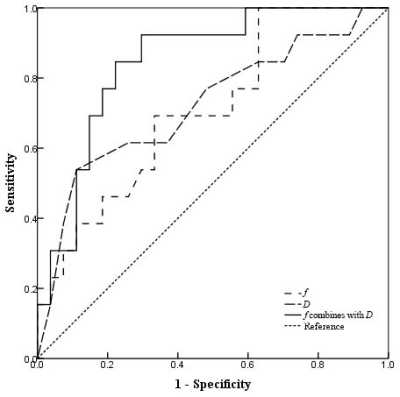
ROC Analysis to Evaluate the Treatment Response of Patients with IR-AML.
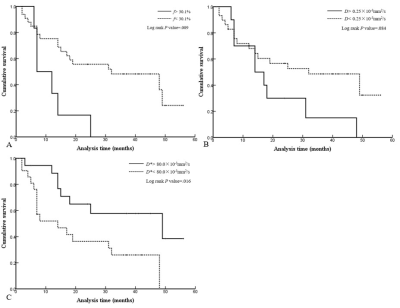
Kaplan-Meier Survival Curves of Overall Survival Stratified by Different Independent Variable.
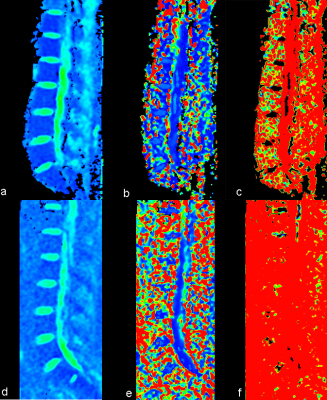
Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI parametric maps of the D (a, d), D* (b, e), and f (c, f) from two patients with IR-AML, whose overall survival showed significant differences. Color bars are the same for both participants.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2022/2297