2175
Fluorinated Tm3+-complexes as molecular temperature sensors1Institut für Organische und Analytische Chemie, University of Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 2Institute of Biometry and Medical Informatics, Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg, Medical Faculty, Magdeburg, Germany
Synopsis
Temperature is an important factor for various physiological phenomena. Hyperthermia and hypothermia are only two examples in clinical application. As the resolution of MR data increases, so does interest in the exact determination of the temperature. Molecular sensors offer the opportunity to determine temperature in living organisms. Based on the preliminary investigations of our working group using Ce3+ complexes, the more detailed characterization of Tm3+ complexes was carried out with regard to the temperature sensitivity of the 19F MR signals and, for the first time, also to the toxicity using the example of fibroblasts.
INTRODUCTION
Temperature is an important factor for various physiological phenomena.1 For example hyperthermia and hypothermia are two clinical application.2,3 Molecular sensors offer the opportunity to determine temperature i.e. in tissue in a living organism.4 To minimize to minimize interference from background or interference signals5, new fluorinated complexes were synthesized and characterized. Based on the preliminary investigations of our working group using Ce3+ complexes6, the more detailed characterization of Tm3+ complexes was carried out with regard to the temperature sensitivity of the 19F MR signals and, for the first time, also to the toxicity using the example of fibroblasts.METHODS
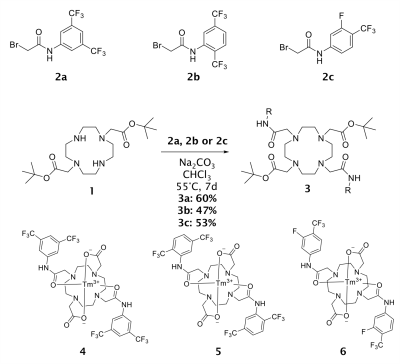
SynthesisThe first step is the alkylation of DO2A-tBu2 (1) with a bromoacet-amide derivative (2) in presence of Na2CO3 in CHCl3 for seven days at 55°C. Yet, the temperature and the reaction time are crucial parts for the yield. A decrease in one of these parameters leads to significantly lower yields of the reaction. The deprotection of the ligand ensue through hydrolysis using formic acid. Metal complexation is carried out in water at 45°C and pH 7 with 1.1 eq. of corresponding metal salt. After stirring complexations of Tm3+-complexes are completed (see Figure 1).
Temperature measurements
Variable-temperature 19F NMR spectra (ns = 16) were recorded with a Bruker Avance NEO spectrometer in the temperature range of 298.15 K (25 °C) to 323.15 K (50 °C). The Tm3+-complexes were dissolved in 0.5 mL D2O. After reaching the set temperature, a delay of 10 minutes was waited for the complete temperature adjustment.
Cell viability tests
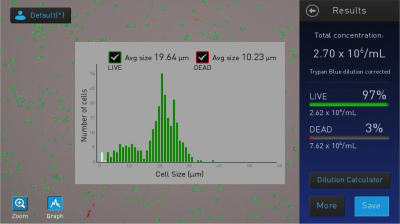
Viability tests were carried out with fibroblasts (L929). For this purpose, the cells were incubated in a 12-well plate for 24 h or 48 h. After preparation and staining with trypan blue, the cells were counted with the Countess™ II Automated Cell Counter (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
RESULTS
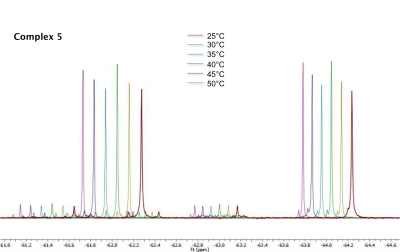
Temperature measurementsThe NMR temperature measurements has shown a maximum 19F chemical shift change of -0.197 ppm/K (-111.72 Hz/K) in case of complex 5 measurement (Figure 2). This thulium complex with CF3 groups in 2,5 position has a further advantage: Molecules with two chemically non-equivalent groups (two MR signals) can be used without further adition of standards. The distance between the two signals can be used for temperature determination. The change in chemical shift of the other two complexes differs significantly from this. The one 19F MR signal of complex 4 shows a shift of only -0.012 ppm/K (-6.761 Hz/K).
Cell viability tests
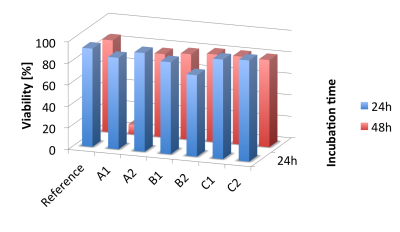
The viability studies (Figure 3) show no significant toxicity of the three water-soluble complexes. After both 24 and 48 hours of incubation, the viability was between 70% and >90% and was thus in the range of the references. A control sample to which complex and trifluoroacetic acid were added showed a viability of about 12% for comparison (see Figure 4).
DISCUSSION
Three new Tm3+ complexes were synthesized as part of this work. The fluorinated compounds used were selected so that future MR imaging is possible. Aromatic CF3 groups show a very sharp signal without splitting in most cases. The presence of at least two 19F signals allows measurements without adding a standard. This is helpful, among other things, when investigating changes in the chemical environment of the nuclei. In addition to the temperature, the gas content or pH value also have an influence on the position of the 19F signals. Initial statements on the influence of temperature were examined in this study.CONCLUSION
Three newly synthesized fluorinated Tm3+ complexes were examined for their toxicity. Fortunately, there is no increased toxicity when using fibroblasts. One of the three complexes 5 also arouses interest in future potential use in the field of MR-based temperature detection. Further investigations into the stability (transmetalation) will follow.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Umegawa Y, Tanaka Y, Nobuaki M, Murata M, 13C-TmDOTA as versatile thermometer compound for solid-state NMR of hydrated lipid bilayer membranes. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2016;54(3):227-233.
2. Wust P, Hildebrandt B, Sreenivasa G, Rau B, et al., Hyperthermia in combined treatment of cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3:487.
3. Milne M, Hudson RHE, Contrast agents possessing high temperature sensitivity. Chem. Commun. 2011;47:9194.
4. Pakin SK, Hekmatyar SK, Hopewell P, et al., Non-invasive temperature imaging with thulium 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetramethyl-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (TmDOTMA-). NMR Biomed 2006;19:116.
5. Thorarinsdottir AE, Gaudette AI, Harris TD, Spin-crossover and high-spin iron(ii) complexes as chemical shift 19F magnetic resonance thermometers. Chem. Sci. 2017;8:2448.
6. Mysegaes F, Plaumann M, Temperature determination based on chemical shift difference between two 19F signals in the case of a Ce3+ and a Tm3+-complex 42nd FGMR Annual Discussion Meeting (GDCH) 2021.
Figures