1956
Prospective motion correction in multi-inversion EPI using volumetric navigators for robust T1 map estimation1Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 3Division of Health Sciences and Technology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, United States, 4Department of Radiology, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 5Department of Biomedical Engineering, Department of Neurology & Neurosurgery, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 6McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological Institute, Montreal, QC, Canada
Synopsis
In multi-inversion EPI (MI-EPI), each slice samples a distinct inversion time during each inversion recovery, providing an efficient method for estimating T1. MI-EPI is vulnerable to through-plane motion, which results in slices sampling a subset of the desired inversion times and wrong TIs will be attributed to the slices. This cannot be corrected retrospectively. We introduce prospective motion correction in MI-EPI using volumetric navigators (vNavs). vNavs are acquired at the beginning of the inversion recovery thus the effects of their excitation pulses must be modeled for T1 estimation. This provides improved T1 estimation accuracy in the presence of subject motion.
Introduction
Inversion recovery (IR) EPI is a fast approach for quantitative T1 estimation and is increasingly used in neuroimaging applications ranging from anatomical to diffusion to functional imaging[1–6]. One variant of this approach, termed multi-inversion EPI (MI-EPI), uses non-selective inversion followed by the acquisition of multiple EPI slices, each acquired at a distinct inversion time (TI); on every sequence repetition the slice acquisition order is permuted or “shuffled” such that after N repetitions every slice is sampled at N distinct times along the IR yielding N distinct TI values for each slice[7–11]. While efficient, this method is vulnerable to through-plane motion, which will cause some brain regions to be sampled with different subsets of the desired TI values, leading to regional differences in T1 estimation accuracy. This motion-induced artifact can thus not be fully corrected with retrospective motion correction. To address this, we implemented a prospective motion correction method based on volumetric navigators (vNavs)[12]. This approach has been widely used for motion-robust imaging with multiple sequence types, especially 3D sequences, most prominently MPRAGE and T2-SPACE[13–15]. The approach is less commonly applied in 2D sequences or where navigator contrast may vary such as CEST[16]. Here we evaluate this method and its ability to provide accurate T1 maps in the presence of subject motion.Methods
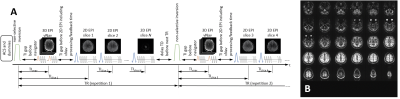
Two volunteers participated after providing informed consent, following institutional guidelines. Volunteers were imaged at 3T using either a Skyra or Prisma scanner (Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) using the vendor-supplied 32-channel head coil.The MI-EPI sequence diagram is presented in Fig. 1. The vNav consists of a low-resolution 3D-EPI readout acquired immediately after the inversion pulse and before the MI-EPI readout, therefore a small delay between the inversion pulse and the MI-EPI readout is needed. Changes in head position were estimated from the vNavs online and fed back to the pulse sequence, as described previously[12], to update the prescription of both the MI-EPI data and the vNavs themselves of the subsequent IR.
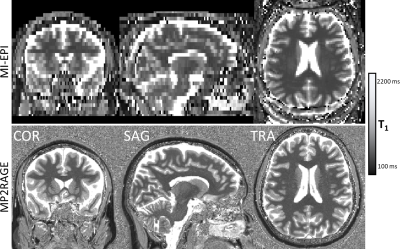
In each session, MP2RAGE data[18] were acquired to provide a reference T1 map, estimated offline[19]. Next, we acquired several runs of MI-EPI data using the following protocol: time between inversions (TR) = 5000 ms, TE = 21 ms, TI = 295 ms, voxel size 2×2×4 mm3, 30 slices, slice-permutation factor[1] = 1, 59 repetitions (2 repetitions of each TI) for a total scan time of 313 s. vNavs were acquired with the following protocol: TR = 11 ms, TE = 5.1 ms, non-selective excitation flip angle = 2°, voxel size 8×8×8 mm3, 24 partitions (with 6/8 partial Fourier), for an acquisition time of 275 ms.
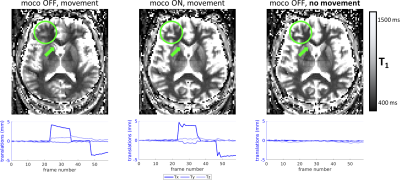
Subjects were asked to remain still for half of the runs, and in the other half instructed to move their head three times during the run. These data were acquired both with and without prospective motion correction, for a total of four MI-EPI runs per session. To quantify spin-history-artifact effects on the vNavs, an additional protocol with a reduced TR of 2000 ms was acquired while the subject was instructed to remain still.
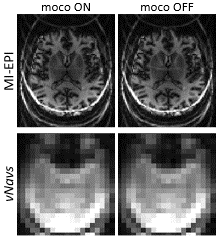
T1 estimation from the MI-EPI data was performed using a dictionary approach as described previously[1] but with two modifications. First, the effects of the vNav acquisition at the beginning of the IR on the Mz of the EPI slices were modeled, accounting for the vNav excitation flip angle, time between shots, and total number of shots. Second, because prospective correction only corrects at the start of each TR, we performed T1 fitting using motion censoring by omitting those individual volumes corrupted by motion.
Results
Figure 2 shows the resulting T1 maps estimated from MI-EPI data acquired with vNavs. Accounting for the non-selective low-flip excitation of the vNav improves the accuracy of the T1 estimates. Figure 3 demonstrates the improvement in T1 mapping with prospective motion correction in the presence of head movement.Discussion
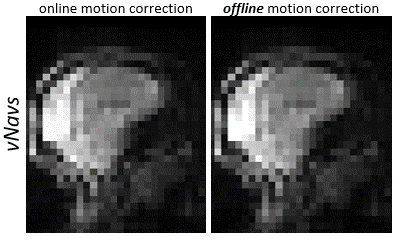
There are two main limitations of this technique. The vNav acquisition currently lasts approximately 275 ms and this duration constrains the minimal TI available for the MI-EPI acquisition, however newer approaches that speed up the vNav are available[20,21]. The spin-history artifact in the vNav data, that varies in its position from IR to IR due to slice shuffling, interferes with online motion correction. Here we attempt to minimize this effect by adding a time interval at the end of the IR, and this results in a loss of temporal efficiency. More sophisticated motion estimation algorithms (e.g., based on more robust cost functions) can alleviate this (see Fig. 5) provided that the motion estimates can be calculated with low latency on the scanner.Conclusion
Prospective correction based on vNavs is applicable to sequences with sufficient dead time where the vNav excitation minimally impacts the parent sequence, and here we have extended this approach for the first time to inversion-prepared EPI. This approach can be readily extended to inversion recovery using SMS MI-EPI[10,22,23] readouts as well as to sequences using 3D-EPI readouts[3] proposed for anatomical imaging. By extension, this approach may be compatible with non-BOLD fMRI methods based on inversion recovery[24,25], including the SS-SI-VASO approach used for CBV fMRI[26,27].Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the NIH NIBIB (grants P41-EB030006 and R01-EB019437), by the NCCIH (grant R01-AT011429), by the NICHD (grants R01-HD085813, R01-HD093578 and R01-HD099846), by the BRAIN Initiative (NIH NIMH grant R01-MH111419 and NINDS grant U19-NS123717), by FRQ-S (Fonds de Recherche du Québec -Santé) and NSERC (National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada), and by the MGH/HST Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging. We thank Mr. Kyle Droppa for help with MRI scanning, and Dr. Ville Renvall for providing his MI-EPI T1 estimation software. We also thank Dr. Jose Marques for making his MP2RAGE T1 estimation software available online. Thanks also to our volunteers.References
1. Renvall V, Witzel T, Wald LL, Polimeni JR. Automatic cortical surface reconstruction of high-resolution T1 echo planar imaging data. Neuroimage. 2016;134:338-354. PMID: 27079529.
2. Kashyap S, Ivanov D, Havlíček M, Poser BA, Uludağ K. Impact of acquisition and analysis strategies on cortical depth-dependent fMRI. Neuroimage. 2018;168:332-344. PMID: 28506874.
3. van der Zwaag W, Buur PF, Fracasso A, van Doesum T, Uludağ K, Versluis MJ, Marques JP. Distortion-matched T1 maps and unbiased T1-weighted images as anatomical reference for high-resolution fMRI. Neuroimage. 2018;176:41-55. PMID: 29665420.
4. Leppert IR, Andrews DA, Campbell JSW, Park DJ, Pike GB, Polimeni JR, Tardif CL. Efficient whole-brain tract-specific T1 mapping at 3T with slice-shuffled inversion-recovery diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2021;86(2):738-753. PMID: 33749017.
5. Sanchez Panchuelo R, Turner R, Mougin O, Francis S. A 2D multi-shot inversion recovery EPI (MS-IR-EPI) sequence for high spatial resolution T1-mapping at 7T. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2018;27:0060.
6. Huber L (Renzo), Marrett S, Handwerker DA, Thomas A, Gutierrez B, Ivanov D, Poser BA, Bandettini PA. Fast dynamic measurement of functional T1 and grey matter thickness changes during brain activation at 7T. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2016;24:633.
7. de Smit F, Hoogduin H. Fast whole brain T1 mapping at 3 Tesla. In: Fortschritte Auf Dem Gebiet Der Röntgenstrahlen Und Der Bildgebenden Verfahren. ; 2005:177-A1.
8. Clare S, Jezzard P. Rapid T(1) mapping using multislice echo planar imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2001;45(4):630-634. PMID: 11283991.
9. Wu H, Dougherty R, Zhu K, Kerr A, Middione M. Fast T1 mapping using slice-shuffled Simultaneous Multi-Slice inversion recovery EPI. Annu Meet Organ Hum Brain Mapp. 2015:1592.
10. Grinstead JW, Wang D, Bhat H, Deshpande V, Cauley SF, Setsompop K, Benner T, Anderson VC, Rooney WD. Slice-accelerated Inversion Recovery T1 mapping. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2014;22:3215.
11. Renvall V, Witzel T, Wald LL, Polimeni JR. Fast variable inversion-recovery time EPI for anatomical reference and quantitative T1 mapping. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2014;22:4282.
12. Tisdall MD, Hess AT, Reuter M, Meintjes EM, Fischl B, van der Kouwe AJW. Volumetric navigators for prospective motion correction and selective reacquisition in neuroanatomical MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2012;68(2):389-399. PMID: 22213578.
13. Tisdall MD, Reuter M, Qureshi A, Buckner RL, Fischl B, van der Kouwe AJW. Prospective motion correction with volumetric navigators (vNavs) reduces the bias and variance in brain morphometry induced by subject motion. Neuroimage. 2016;127:11-22. PMID: 26654788.
14. Tisdall MD, Polimeni JR, van der Kouwe AJW. Motion-corrected 350 μm isotropic MPRAGE at 3 T using volumetric navigators (vNavs). Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2013;21:268.
15. Casey BJ, Cannonier T, Conley MI, Cohen AO, Barch DM, Heitzeg MM, Soules ME, Teslovich T, Dellarco DV, Garavan H, Orr CA, Wager TD, Banich MT, Speer NK, Sutherland MT, Riedel MC, Dick AS, Bjork JM, Thomas KM, Chaarani B, Mejia MH, Hagler DJ, Daniela Cornejo M, Sicat CS, Harms MP, Dosenbach NUF, Rosenberg M, Earl E, Bartsch H, Watts R, Polimeni JR, Kuperman JM, Fair DA, Dale AM. The Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study: Imaging acquisition across 21 sites. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2018.
16. Simegn GL, Van der Kouwe AJW, Robertson FC, Meintjes EM, Alhamud A. Real-time simultaneous shim and motion measurement and correction in glycoCEST MRI using double volumetric navigators (DvNavs). Magn Reson Med. 2019;81(4):2600-2613. PMID: 30506877.
17. Cohen O, Polimeni JR. Optimized inversion-time schedules for quantitative T1 measurements based on high-resolution multi-inversion EPI. Magn Reson Med. 2018;79(4):2101-2112. PMID: 28845547.
18. Marques JP, Kober T, Krueger G, van der Zwaag W, Van de Moortele P-F, Gruetter R. MP2RAGE, a self bias-field corrected sequence for improved segmentation and T1-mapping at high field. Neuroimage. 2010;49(2):1271-1281.
19. Marques JP, Zwiers MP. MP2RAGE Scripts - T1 map correction & Background noise removal. https://github.com/JosePMarques/MP2RAGE-related-scripts.
20. Chang Y, Splitthoff D, Lo W-C, Tisdall M, van der Kouwe AJW. Accelerated 3D EPI navigator for prospective motion correction. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2022. Submitted.
21. Bhat H, Tisdall M, Cauley S, Witzel T, Setsompop K, van der Kouwe A, Heberlein K. Simultaneous Multi-Slice (SMS) Accelerated EPI Navigators for Prospective Motion Correction in the Brain. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2015:0817.
22. Park DJ, Witzel T, Leppert I, Yen Y-F, Tardif C, Polimeni JR. Rapid multi-inversion SMS-EPI integrated with gradient-echo, spin-echo and diffusion-weighted EPI acquisitions. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2018;27:4229.
23. Grinstead JW, Anderson V, Sammi M, Rooney W. Optimization of high-resolution slice-accelerated inversion recovery T1 mapping at 7T. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2016;24:3260.
24. Renvall V, Witzel T, Bianciardi M, Polimeni JR. Multi-contrast inversion-recovery EPI (MI-EPI) functional MRI at 7 T. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2014;22:1488.
25. Ciris PA, Qiu M, Constable RT. Noninvasive MRI measurement of the absolute cerebral blood volume-cerebral blood flow relationship during visual stimulation in healthy humans. Magn Reson Med. 2014;72(3):864-875. PMID: 24151246.
26. Huber L, Ivanov D, Krieger SN, Streicher MN, Mildner T, Poser BA, Möller HE, Turner R. Slab-selective, BOLD-corrected VASO at 7 Tesla provides measures of cerebral blood volume reactivity with high signal-to-noise ratio. Magn Reson Med. 2014;72(1):137-148. PMID: 23963641.
27. Jin T, Kim S-G. Spatial dependence of CBV-fMRI: a comparison between VASO and contrast agent based methods. In: International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Vol 1. IEEE; 2006:25-28. PMID: 17946773.
28. Sanchez Panchuelo RM, Mougin O, Turner R, Francis ST. Quantitative T1 mapping using multi-slice multi-shot inversion recovery EPI. Neuroimage. 2021;234. PMID: 33781969.
29. Yen Y-F, Keenan KE, Stupic KF, van der Kouwe AJW, Polimeni JR. T1 mapping of NIST phantom at 7T. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2017;25:2889.
30. McDaniel P, Gagoski B, Tisdall MD, Kouwe AJW van der, Grant PE, Wald LL, Adalsteinsson E. Quantification of fetal motion tracked with Volumetric Navigator MRI acquisitions. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2015;23:2576.
Figures