1845
3D Multiscale Weighted Total Variation Registration for MR Image-Guided Catheter Interventions1Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2Schulich Heart Centre, Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, Canada
Synopsis
During MR-guided cardiac catheter intervention, the catheter may be misaligned due to the respiratory motion of the heart. To improve the myocardial border alignment, GPU-based edge-preserving image registration is developed to accurately align highly undersampled 3D cone-trajectory image-based navigators for motion characterization. The edge-preserving registration technique improved myocardial border alignment across differing spatial resolutions and acceleration factors in-silico.
Introduction
Real-time image-based navigators (iNAVs) acquired every heartbeat for cardiac motion estimation show promise to improve catheter alignment with the heart wall in prior volumes during MR-guided cardiac interventions1-3. Myocardial tissue is displaced by cardiac and respiratory motion. To compensate for respiratory motion, image-based rigid motion correction uses 2D iNAVs that align myocardial borders and correct respiratory motion estimation by 2D/3D registration with a prior anatomical reference1-3. However, the through-plane motion is poorly characterized by 2DiNAVs, leading to large catheter misalignment in this direction1-3. During the cardiac intervention, an accuracy of less than 2.5 mm between the catheter tip and the target tissue is desired4. To this end, we aim to use non-Cartesian cone-trajectory 3D iNAVs to rapidly acquire 3D volumes, track 3D non-rigid heart motion, and correct the catheter position on a heartbeat-by-heartbeat basis. However, 3DiNAVs require aggressively undersampled scans, which affects motion estimation. In this study, we develop an in-silico simulated framework with MRXCAT to explore multiscale-weighted total variation (wTV) denoising and edge-preserving image registration to align myocardial borders of 3D iNAVs acquired at various spatial resolutions5.Methods
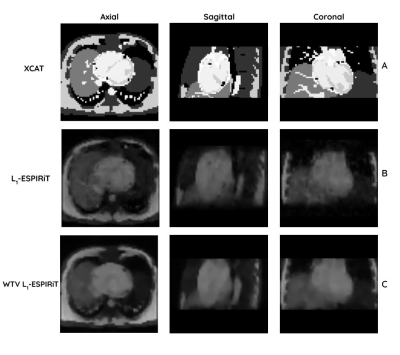
In-silico Simulation:3D iNAVs at different respiratory phases were simulated with an in-silico Cardiac-Torso (XCAT) anatomical phantom with gradient-recalled echo (GRE) image contrast shown in Fig. 15. We applied an NUFFT operator to transform phantom data into k-space, where we performed non-Cartesian cone sampling6. The 3DiNAV GRE signal model was simulated at TE = 0.5ms; TR = 6ms; flip angle = 6° and FOV = 28$$$\times$$$28$$$\times$$$14cm. Simulated 3D iNAV isotropic resolutions ranged from 4.4 to 7.4 mm, and temporal window of typical diastole 200ms, so higher spatial resolution is associated with an increased acceleration factor (AF) (Fig. 1). $$$L_1$$$-ESPIRiT iterative reconstruction was performed with the Berkeley Advanced Reconstruction Toolbox (BART)7-10. We simulated motion across 20 respiratory phases, with the end-expiratory phase being used as a reference iNAV for registration.
Registration Framework:
wTV denoising was used to enhance the edges in the 3D iNAVs while reducing statistical noise11. wTV is an ideal candidate for edge-preserving registration as it regularizes the high-frequency noise while preserving the physiological features that correlate with large edges. This allows for improved myocardial alignment in the edge-preserving registration. After images were denoised, non-rigid motion estimation was performed with Airlab GPU-based registration12. In particular, the normalized gradient field (NGF) loss function was used to emphasize edge alignment13:$$NGF(A, B) = \int_\Omega\left( 1-{\left\langle\nabla A(x),\nabla B(x)\right\rangle^2_\eta\over\|\nabla A(x)\|_\eta^2 \|\nabla B(x) \|_\eta^2}\right)dx$$
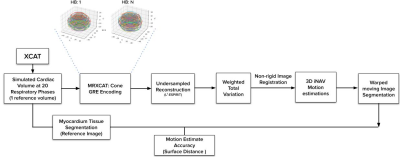
Here, the inner product $$$\left\langle u,v \right\rangle_\eta = u\cdot v +\eta^2$$$ is used to control which edges correspond to signal or noise. Multiscale images were denoised with different $$$\eta$$$ and iteratively registered to obtain a final deformation field (Fig. 2); this method was compared against the commonly used Diffeomorphic Demons (DD) registration method implemented in SimpleITK14,15. The registration accuracy of the myocardial alignment was evaluated across resolutions and respiratory phases with mean surface distance (MSD) serving as a proxy for catheter alignment accuracy. The overall pipeline is shown in Fig. 3.
Results
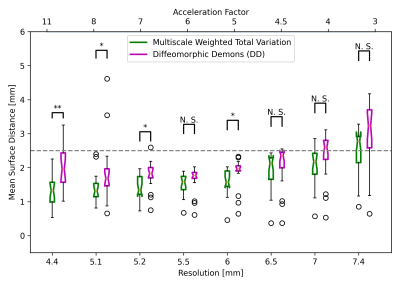
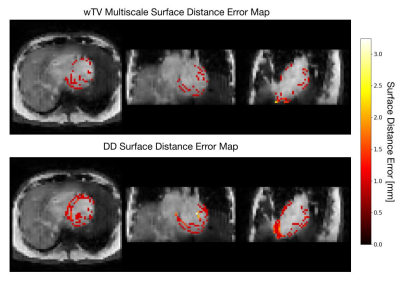
Comparisons between the GPU-based edge-preserving wTV multiscale registration and DD MSD accuracy over the spatial resolution and AF is shown in Fig. 4. The surface distance error distribution across the left ventricle is shown in 3D for both registration methods, where the wTV multiscale deformation tends to reduce the error at the edges compared to DD (Fig. 5).wTV multiscale registration returns lower median error than standard non-rigid DD registration over all spatial resolutions and AF, with many resolutions having statistically significant differences. We find the optimal resolution to be 6mm, striking a balance between minimizing AF and reducing aliasing artifacts with registration error below the 2.5mm target.
Discussion
At higher resolutions, wTV multiscale registration is robust to the artifacts associated with the high-resolution residual aliasing since the voxel-by-voxel registration focuses on aligning edges and structural accuracy, as opposed to the global image in DD (Fig. 4 & 5). wTV multiscale registration at coarser scales emphasizes aligning large edges that correspond to gross anatomy whereas finer scales align smaller edges that correspond to details in tissue structure resulting in small errors due to artifacts. At low resolutions, both registration methods perform similarly due to the poor image quality and blurred edges from the large voxel size, leading to poor alignment between myocardial borders which is consistent with literature16.GPU-based implementation computation time is promising for real-time interventions: 3D iNAV reconstruction is performed within 5 s, wTV denoising in 28 ms, and 3D image registration takes 5-8 seconds. This motivates deep learning reconstruction and registration to accelerate calculations further17,18.
Our study is limited by the simulation framework and the image contrast; in vivo high-resolution images suffer from increased motion artifacts, and GRE images do not delineate tissue boundaries as clearly as SSFP images. These factors may contribute to our optimal resolution being lower than other groups observe16, so will be explored in future implementations.
Conclusion
The proposed GPU-based edge-preserving image registration is robust to undersampling artifacts and improves the motion accuracy and the computation time, thereby allowing for accurate motion characterization catheter intervention.Acknowledgements
We acknowledge research funding from Ted Rogers Centre for Heart Research, Ontario Research Fund, CIHR grant MOP-93531 and our research agreement with HeartVista.References
1. Xu, R., Athavale, P., Nachman, A., & Wright, G. A. (2014). Multiscale registration of real-time and prior MRI data for image-guided cardiac interventions. IEEE transactions on bio-medical engineering, 61(10), 2621–2632. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2014.2324998
2. Xu, R., Athavale, P., Krahn, P., Anderson, K., Barry, J., Biswas, L., Ramanan, V., Yak, N., Pop, M., & Wright, G. A. (2015). Feasibility Study of Respiratory Motion Modeling Based Correction for MRI-Guided Intracardiac Interventional Procedures. IEEE transactions on bio-medical engineering, 62(12), 2899–2910.
3. Xu, R., & Wright, G. A. (2016). GPU accelerated dynamic respiratory motion model correction for MRI-guided cardiac interventions. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine, 136, 31–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.08.003
4. Ciaccio, E. J., Ashikaga, H., Kaba, R. A., Cervantes, D., Hopenfeld, B., Wit, A. L., Peters, N. S., McVeigh, E. R., Garan, H., & Coromilas, J. (2007). Model of reentrant ventricular tachycardia based on infarct border zone geometry predicts reentrant circuit features as determined by activation mapping. Heart rhythm, 4(8), 1034–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2007.04.015
5. Wissmann, L., Santelli, C., Segars, W. P., & Kozerke, S. (2014). MRXCAT: Realistic numerical phantoms for cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Journal of cardiovascular magnetic resonance: official journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 16(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-014-0063-3
6. Gurney, P. T., Hargreaves, B. A., & Nishimura, D. G. (2006). Design and analysis of a practical 3D cones trajectory. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 55(3), 575–582. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20796
7. Uecker, M., Lai, P., Murphy, M. J., Virtue, P., Elad, M., Pauly, J. M., Vasanawala, S. S., & Lustig, M. (2014). ESPIRiT--an eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel MRI: where SENSE meets GRAPPA. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 71(3), 990–1001. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24751
8. Tamir JI, Ong F, Cheng JY, Uecker M, Lustig M. (2016) Generalized Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction using The Berkeley Advanced Reconstruction Toolbox, ISMRM Workshop on Data Sampling and Image Reconstruction, Sedona
9. Uecker M, Ong F, Tamir JI, Bahri D, Virtue P, Cheng JY, Zhang T, Lustig M. (2015) Berkeley advanced reconstruction toolbox. ISMRM 23rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Toronto. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med.23, 2486.
10. Uecker M, Virtue P, Ong F, Murphy MJ, Alley MT, Vasanawala SS, Lustig M. (2013) Software Toolbox and Programming Library for Compressed Sensing and Parallel Imaging, ISMRM Workshop on Data Sampling and Image Reconstruction, Sedona
11. Athavale, P., Xu, R., Radau, P., Nachman, A., & Wright, G. A. (2015). Multiscale properties of weighted total variation flow with applications to denoising and registration. Medical image analysis, 23(1), 28–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2015.04.013
12. Sandkühler, R., Jud, C., Andermatt, S., & Cattin, P.C. (2018). AirLab: Autograd Image Registration Laboratory. ArXiv, abs/1806.09907.
13. Haber, E., & Modersitzki, J. (2007). Intensity gradient-based registration and fusion of multi-modal images. Methods of information in medicine, 46(3), 292–299. https://doi.org/10.1160/ME9046
14. Vercauteren, T., Pennec, X., Perchant, A., & Ayache, N. (2009). Diffeomorphic demons: efficient non-parametric image registration. NeuroImage, 45(1 Suppl), S61–S72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.040
15. Lowekamp, B. C., Chen, D. T., Ibáñez, L., & Blezek, D. (2013). The Design of SimpleITK. Frontiers in neuroinformatics, 7, 45. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2013.00045
16. Koundinyan, S.P., Cheng, J., Malavé, M.O., Yang, P.C., Hu, B.S., Nishimura, D.G., & Baron, C.A. (2019). Unravelling the Effect of Spatial Resolution and Scan Acceleration on 3D Image-Based Navigators for Respiratory Motion Tracking in Coronary MR Angiography. arXiv: Medical Physics.
17. Malavé, M. O., Baron, C. A., Koundinyan, S. P., Sandino, C. M., Ong, F., Cheng, J. Y., & Nishimura, D. G. (2020). Reconstruction of undersampled 3D non-Cartesian image-based navigators for coronary MRA using an unrolled deep learning model. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 84(2), 800–812. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.28177
18. Munoz, C., Qi, H., Cruz, G., Küstner, T., Botnar, R. M., & Prieto, C. (2021). Self-supervised learning-based diffeomorphic non-rigid motion estimation for fast motion-compensated coronary MR angiography. Magnetic resonance imaging, 85, 10–18. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2021.10.004
Figures