1720
Multi-parameter Magnetic Resonance Quantitative Evaluation of Pancreatic Cancer with Vascular Invasion1Department of Radiology, Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, SIEMENS Healthineers, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
In this study, the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of quantitative parameters derived from T2WI+DKI+DCE combined model for pancreatic cancer vascular invasion were evaluated based on the pathological results as the gold standard. Combined T2WI+DKI+DCE quantitative analysis can improve the specificity and accuracy of diagnostic efficiency of pancreatic cancer vascular invasion. There were significant differences in MD, MK, Ktrans, Kep and Ve between vascular invasion group and non-vascular invasion group. The diffusion parameters and perfusion information are highly consistent, which can provide reliable evidence for preoperative non-invasive diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Introduction
To analyze the value of multi-parameter magnetic resonance (mpMRI) in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer with vascular invasion from two aspects: morphology and function, so as to provide a reliable diagnostic basis for preparing the clinical treatment plans.Methods
Totally 31 case data of pancreatic cancer patients diagnosed in our hospital from January 2020 to March 2021 were enrolled in this study. All patients underwent multi-parameter magnetic resonance imaging (T1WI, T2WI, DKI, DCE-MRI) before surgery, then all patients underwent pancreatic cancer surgery. Two experienced radiologists analyzed these obtained images according to the image reports and combined them with the pathological results. Taking pathological results as the gold standard, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of quantitative parameters derived from T2WI, DKI, DCE, T2WI+DKI, T2WI+DCE, and T2WI+DKI+DCE for the diagnostic capabilities of pancreatic cancer vascular invasion were calculated using diagnostic laboratory methods. Kappa consistency test was used to evaluate the consistency of the two radiologists' analysis of image data. The images obtained by DKI scanning were input into the post-processing software MITK, Importing the images obtained from DCE into the Tissue 4D software on the Siemens Syngo.via workstation to calculate and analyze each cancer ROI’s MD, MK from DKI and Ktrans, Kep, Ve values from DCE. Then use Independent-Sample T-Test to compare pancreatic cancer with vascular invasion group (16 cases) and the non-vascular invasion group (15 cases). Draw ROC curve to analyze the efficacy of each parameter in diagnosing pancreatic cancer vascular invasion, Spearman’s correlation was used to analyze the correlation between DKI and DCE parameters.Results
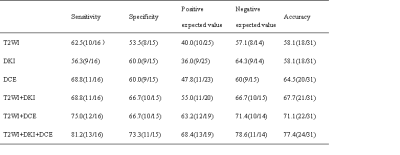
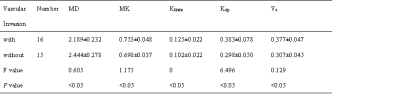
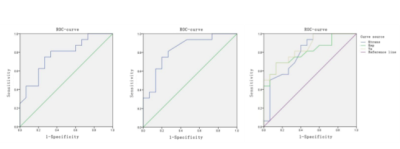
The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of T2WI were 62.5%, 53.5%, 58.1%; those of DKI were 56.3%, 60.0%, 58.1%; those of DCE were 68.8%, 60.0%, 64.5%; those of T2WI+DKI were 68.8%, 66.7%, 67.7%; those of T2WI+DCE were 75.0%, 66.7%, 71.1%; those of T2WI+DKI+DCE were 81.2%, 73.3%, 77.4%, respectively (Table 1). These two diagnostic radiologists analyzed image datas with good consistency, Kappa=0.834. MD, MK, Ktrans, Kep, Ve were significantly different between the vascular invasion group and the non-vascular invasion group (p<0.05) (Table 2). Each parameter’s AUC of ROC curve was 0.773, 0.829, 0.794, 0.802, 0.846 (p<0.05). Take MD = 2.285×10-3mm/s2, MK = 0.72, Ktrans = 0.103, Kep = 0.337, and Ve = 0.353 as thresholds, the sensitivity of these parameters to diagnose vascular invasion of pancreatic cancer was 73.33%, 75%, 87.5%, 68.8%, 68.8%. The specificity of them was 75%, 80%, 60%, 86.7%, 86.7%, respectively (Figure 1). MD was negatively correlated with Ve (r=-0.533, p<0.05). MK was positively correlated with Ktrans (r=0.481, p<0.05), also positively correlated with Ve (r=0.869, p<0.05).Conclusion
The combined analysis of T2WI+DKI+DCE can improve the specificity and accuracy of diagnostic efficiency of vascular invasion of pancreatic cancer, and provide an important diagnostic basis for pancreatic cancer’s preoperative treatment. The quantitative diffusion parameters and perfusion information of pancreatic cancer with vascular invasion are highly consistent. The quantitative values from DKI and DCE have the potential to evaluate pancreatic cancer with vascular invasion, providing an accurate reference for non-invasive diagnosis and treatment.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] DABABOU S, MARROCCHIO C, ROSENBERG J, et al.A meta analysis of palliative treatment of pancreatic cancer with high intensity focused ultrasound[J]. J Ther Ultrasound,2017,5(1):9.
[2] HALBROOK C J, LYSSIOTIS C A.Employing metabolism to improve the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer[J].Cancer Cell,2017,31(1):5-19.
[3] Katz MH, H wang R, Fleming JB, et al.Tumor-node metastasis staging of pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2008;58(2):111-125.
[4] Sheng RF, Wang HQ, Yang L, et al.Diffusion Kurtosis imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging in assessment of liver fibrosis stage and necroinflammatory activity.Abdom Radiol(NY),2017,42(4):1176-1182.
[5] Fusari M, Maurea S, Imbriaco M, Mollica C, Avitabile G, Soscia F, Camera L, Salvatore M.Comparison between multislice CT and MR imaging in the diagnostic evaluation of patients with pancreatic masses.Radiol Med,2010,115:453-66.
[6] García-Figueiras R, Baleato-González S, Padhani AR, et al. How clinical imaging can assess cancer biology. Insights Imaging 2019;10:28.
[7] El Beltagi AH, Elsotouhy AH, Own AM, Abdelfattah W, Nair K, Vattoth S. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of head and neck cancer: performance and potential.Neuroradiol J 2019;32:36–52.
[8] Connolly M, Srinivasan A. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Head and Neck Cancer: Technique, Limitations, and Applications. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am2018;26:121–33.
[9] Kabadi SJ, Fatterpekar GM, Anzai Y, Mogen J, Hagiwara M, Patel SH. DynamicContrast-Enhanced MR Imaging in Head and Neck Cancer. Magn Reson ImagingClin N Am 2018;26:135–49.
[10] Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani a, et al.Diffusion kurtosis imaging: The quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging.Magn Reson Med,2005,53(6):1432-1440.
Figures