1597
2D iDQC-MRS suggests that bone marrow fatty acids are more saturated for postmenopausal osteoporosis
Jianfeng Bao1, Xiao Wang1, Yong Zhang1, and Jingliang Cheng1
1Department of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
1Department of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Synopsis
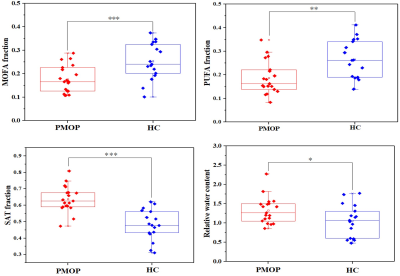
Postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMOP) in the female elderly population has become one of serious health problems of the rapidly aging society in China. The aim of this work was to preliminary investigate the changes of bone marrow fatty acid composition in the presence of trabecular bone of PMOP and age-matched healthy controls (HC) using 2D intermolecular double-quantum coherence based magnetic resonance spectroscopy (iDQC-MRS). We found monounsaturated fatty acids (P < 0.001) and polyunsaturated fatty acids(p < 0.01) were significant higher lower in the PMOP group. The lower unsaturated fatty acids levels may play an important role in the pathogenesis of PMOP.
INTRODUCTION
The aim of this work was to preliminarily investigate the changes of bone marrow fatty acid composition in the presence of trabecular bone of postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMOP) and age-matched healthy controls (HC) using 2D intermolecular double-quantum coherence based magnetic resonance spectroscopy (iDQC-MRS).METHODS
Thirty-six PMOP women and healthy postmenopausal women were recruited to participate in this study, and women with osteoporosis (n = 19, mean age = 60.9, SD = 2.6) and healthy postmenopausal women (n = 17, mean age = 58.8, SD = 3.5). All MR data were acquired using 3.0 T Siemens Trio Whole Body MR imaging units (Siemens Medical, Erlangan, Germany). Beyond the traditional main fat peak (1.3 ppm) and water peak (4.7 ppm), additional four crossing peaks of the fatty acids (FAs) were well resolved: allylic methylene (2.0 ppm), terminal methylene (2.2 ppm), diallylic methylene (2.7 ppm) and olefinic (5.3 ppm) and obtained in the L4 lumbar spine using using 2D acquisition iDQC-PRESS sequence 1,2. The unsaturated fatty acids including the monounsaturated fatty acids (MOFAs) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) were then calculated, and the terminal methylene peaks was used as the as an internal standard. All the measurements and calculated index were compared between the two groups, and the relationships were evaluated using Spearman correlation coefficients.RESULTS
As shown in Fig.1, MOFAs (P < 0.001) and PUFAs (p < 0.01) were statistically significant higher lower in the PMOP group compared with HC. Accordingly, the saturated fatty acids (SATs) significant (P < 0.001) higher fractions than in PMOP than that of HC. What’s more, limited by the micrometer-scaled detection distance, the relative water content shows higher values in PMOP as well.DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
The lower unsaturated fatty acids levels in the L4 of the PMOP patients suggest that unsaturated fatty acids may play an important role in the pathogenesis of PMOP. The reduced unsaturated fatty acids levels (equivalent to the increased saturated levels) in the PMOP patients may be associated with dysfunction of the balance between osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81601470).References
1. Bao JF, Zhuang YC, Chen Z, et al. Detection of fatty acid composition of trabecular bone marrow by localized iDQC MRS at 3 T: A pilot study in healthy volunteers. Magn Reson Imaging. 2021;77:28-35. 2. 2. Chen Z, Chen ZW, Zhong JH. High-resolution NMR spectra in inhomogeneous fields via IDEAL (intermolecular dipolar-interactionenhanced all lines) method. J Am Chem Soc 2004;126:446–447.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2022/1597