1248
Assessment of anal fistula using advanced diffusion-weighted imaging techniques: value of ZOOMit and RESOLVE1Xi'an Daxing Hospital, Xi'an, China, 2Siemens Healthineers, Ltd., Xi'an, China
Synopsis
This study investigated ZOOMit and RESOLVE DWI sequences to compare of the image quality of anal canal and the visibility of the fistula. The results showed that both ZOOMit DWI and RESOLVE DWI obtained high quality images, ZOOMit DWI sequence had higher fistula visibility and SNR of the fistula than those of RESOLVE DWI sequence. Our findings also suggest that ZOOMit DWI can be used as the preferred sequence for anal MR diffusion imaging.
Introduction/Purpose
Diffusion-weighted imaging(DWI) was helpful to assess anal fistula, because it can find smaller and more frequent fistulas at the same time, show the spread of the disease[1]. However, conventional DWI using single-shot echo planar imaging (EPI) sequence will cause image blur and geometric distortion, poor image spatial resolution, and poor display of anal anatomical details and small lesions[2]. Two technical advanced DWI techniques(ZOOMit and RESOLVE)[3,4] seem to have recently overcome the limitations of conventional DWI. The aim of this study was to evaluate the image quality of the anal canal and the visibility of the fistula using two advanced DWI techniques, to optimize the scanning scheme for obtainning high quality anal MR diffusion imaging.Method
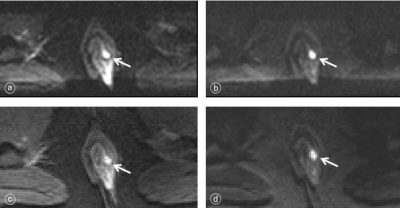
Twenty-two patients diagnosed as anal fistula in our hospital were enrolled in this study. All the patients underwent anal MRI examination at a 3T MR scanner (MAGNETOM Prisma, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany). Parameters about ZOOMit DWI sequencewere: TR 5200ms, TE 69ms, FOV = 150×73.3mm, scan matrix = 44×90, slice thickness = 3 mm, slice spacing = 0mm, voxel size = 1.67×1.67×3.00mm, b values=0, 50, 1000 s/mm2, acquisition time = 4 min 25 sec; Parameters about RESOLVE DWI sequencewere: TR 4180ms,TE 50ms, FOV = 150×73.3mm, scan matrix = 118×118, slice thickness = 3 mm, slice spacing = 0mm, voxel size = 1.69×1.69×3.00mm, b values=0, 50, 1000 s/mm2, acquisition time = 3 min 33 sec. Two senior radiologists subjectively scored fistula visibility, image deformation or artifacts, and overall image quality, and objectively evaluated the image signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the two DWI sequences. The normality of measured data was confirmed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Visual assessment was compared using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test for comparing matched samples. Quantitative ADC variables were tested for statistical significance using a paired t-test. A P value of <0.05 was used as the cutoff to infer statistical significance.Result
The fistula visibility, image deformation or artifacts and overall image quality of ZOOMit DWI sequence were better than those of RESOLVE DWI sequence (P < 0.001). The SNR-b50 of the ZOOMit DWI and RESOLVE DWI sequences were approximately 24.5±6.3, 17.3±5.9 (t=3.9, P<0.001), and the SNR-b1000 of the two sequences were about 13.9±4.3 and 11.1±3.5 (t=2.3, P=0.03). There was statistically significant difference in SNR-b50 and SNR-b1000 between ZOOMit DWI and RESOLVE DWI (P < 0.05).Discussion/Conclusion
In this study, two advanced DWI sequences of ZOOMit and RESOLVE were used to compare and analyze the image quality, fistula visibility and ADC value of anal fistula. ZOOMit DWI used both single-shot plane echo imaging and parallel radiofrequency pulse sequence, and only obtained high signals from the region of interest[2]. This new imaging technology can increase imaging speed, reduce curling artifacts, image distortion, and improve image space resolution, providing more anatomical details, thereby improving image quality[3]. The results suggest that both ZOOMit DWI and RESOLVE DWI obtained high quality images, and the image distortion, artifacts, the overall image quality, fistula visibility and SNR of the ZOOMit DWI sequence were better than those of the RESOLVE DWI sequence. ZOOMit DWI can be used as the preferred DWI sequence for anal canal imaging.Acknowledgements
We thanks Shaoyu Wang (Siemens Healthineers, Ltd., Xi’an, China) for technical support.References
1. Yoshizako T, Kitagaki H. A pictorial review of the impact of adding diffusion-weighted MR imaging to other MR sequences for assessment of anal fistulae. Jpn J Radiol. 2013,31(6):371-376.
2. Seeger A, Batra M, Süsskind D, et al. Assessment of uveal melanomas using advanced diffusion-weighted imaging techniques: value of reduced field of view DWI ("zoomed DWI") and readout-segmented DWI (RESOLVE). Acta Radiol. 2019,60(8):977-984.
3. Tamada T, Ream JM, Doshi AM, et al. Reduced Field-of-View Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Prostate at 3 Tesla: Comparison With Standard Echo-Planar Imaging Technique for Image Quality and Tumor Assessment. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2017,41(6):949-956.
4. Yıldırım İO, Sağlık S, Çelik H. Conventional and ZOOMit DWI for Evaluation of Testis in Patients With Ipsilateral Varicocele. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017,208(5):1045-1050.