1247
U-Net-based deep convolutional neural network for detection of superparamagnetic drug-eluting particles used for liver chemoembolization1Centre de recherche du Centre hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal (CRCHUM), Montreal, QC, Canada, 2Université de Montréal, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4Polytechnique Montréal, Montreal, QC, Canada
Synopsis
Magnetic steering of superparamagnetic drug-eluting particles (SMDEPs) loaded with anti-tumor drugs across hepatic arteries is a promising technique to perform segmental liver embolization for patients with hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs). These aggregates (20 ± 6 SMDEPs) are sequentially released with a specially designed injector through a catheter in the proper hepatic artery of a swine placed in an MRI. Manual segmentation was previously done to localize and count the particles (volume of the artifact) in each lobe. We propose to train a U-net over this pre-existing database. Dice similarity coefficient, accuracy, and precision were respectively 99.1%, 98.3%, and 84.6%.
Abstract
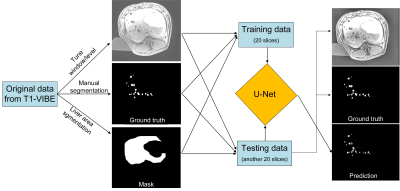
Introduction:Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide4. To improve patient survival after chemoembolization of HCCs, selective embolization at the segmental level is recommended. Magnetic navigation of superparamagnetic drug-eluting particles (SMDEPs) has been proposed as an alternative to the conventional transarterial chemoembolization performed with X-ray angiography1-3, 8, 9. Precisely localizing the delivered SMDEPs and knowing their exact number to assess treatment selectivity, i.e. tumor targeting, is key in improving patient outcomes and reducing unnecessary treatment (i.e. cost). Manual segmentation of the artifact is tedious, unreliable, and not applicable in clinical practice. Instead, we propose using a U-Net-based deep convolutional neural network10 to automatically artifacts to count the number of released particles (Fig. 1).
Methods:
Two thousands SMDEPs (262.6 ± 32.5 μm ) were consecutively injected into the liver of a living pig and scanned at 3T with T1 volumic sequence (T1-VIBE, out-of-phase) with : TR/TE = 5.2/1.4ms, FA = 9°, matrix size = 195 × 320 mm2, slice thickness = 3 mm, field of view = 282 × 347 mm2, bandwidth = 1040 Hz, slices = 72 (Fig. 2). Both training and testing data were composed of the following: 20 original slice images, 20 images to manually mark the artifact positions, and 20 images to mark the liver regions. These images were prepared using the 3D-SLICER software5. Then, the preprocessing included grayscale transformation, normalization, contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization, and gamma transformation before training. The deep learning network was trained with a processor Intel(R) Xeon(R) Silver 4114 CPU, 32GB RAM, and NVIDIA Quadro RTX5000 GPU. During the training, 9500 patches were randomly extracted from every image to upsample the training database. The ground truth was the manual segmentation of particle artifacts. The efficiency of U-Net prediction was compared to the manual segmentation in another 20 slices (Fig. 3). The DICE similarity coefficient7, precision, and accuracy were used to evaluate the segmentation at the voxel level.
Results:
The acquisition time of the T1-vibe sequence was 19 s. The proposed model provided excellent segmentation performance for the SMDEP-induced artifacts. The training process took about 62 min and the testing 5 min. DICE similarity coefficient was 99.1%, accuracy was 98.3%, and precision was 84.6% for the particle segmentation task.
Discussion:
The U-Net provided excellent segmentation performance compared to manual operation. The lack of precision (~15%) is related to the small data sample (20 slices of training, 20 slices of testing). More samples are expected to improve the prediction precision. Moreover, manual segmentation, based on the comparison of images with and without SMDEPs (baseline), is defined as the ground truth for the training set which may explain further the lack of precision. However, this U-net approach shows promising results for future clinical application using SMDEPs, such as automatically calculating the distribution of particles in each lobe, through the relationship between the artifact voxel count and the particle count6.
Conclusion:
The Comparison of U-Net prediction and manual segmentation showed a good similarity, which is promising for quickly, automatically, and accurately determining the locations of the SMDEPs through a U-Net-based deep convolutional neural network.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), Operating Grant - CHRP (CIHR Partnered) (CHRP 478474-15), Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), Operating Grant - CHRP (NSERC Partnered) (CPG-140179), Fonds de recherche du Québec en Santé (FRQS) and Fondation de l'association des radiologistes du Québec (FARQ) Clinical Research Scholarship (34939), Transmedtech and Siemens Healthineers. We also acknowledge support by the Lundbeck Foundation of Denmark (UBC-SUND Lundbeck Foundation Professorship to UOH (No. 2014-4176).
References
1. Dimov I. P., C. Tous, N. Li, U. O. Häfeli, S. Martel and G. Soulez. Future Advances in Diagnosis and Drug Delivery in Interventional Radiology Using MR Imaging-Steered Theranostic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Journal of vascular and interventional radiology: JVIR 32: 1292-1295. e1291, 2021.
2. Li N., Y. Jiang, R. Plantefève, F. Michaud, Z. Nosrati, C. Tremblay, K. Saatchi, U. O. Häfeli, S. Kadoury and G. Moran. Magnetic resonance navigation for targeted embolization in a two-level bifurcation phantom. Annals of biomedical engineering 47: 2402-2415, 2019.
3. Michaud F., N. Li, R. Plantefève, Z. Nosrati, C. Tremblay, K. Saatchi, G. Moran, A. Bigot, U. O. Häfeli and S. Kadoury. Selective embolization with magnetized microbeads using magnetic resonance navigation in a controlled‐flow liver model. Medical physics 46: 789-799, 2019.
4. Ozakyol A. Global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC epidemiology). Journal of gastrointestinal cancer 48: 238-240, 2017.
5. Pieper S., M. Halle and R. Kikinis. 3D Slicer. In: 2004 2nd IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging: nano to macro (IEEE Cat No. 04EX821)IEEE, 2004, p. 632-635.
6. Pouponneau P., G. Soulez, G. Beaudoin, J.-C. Leroux and S. Martel. MR imaging of therapeutic magnetic microcarriers guided by magnetic resonance navigation for targeted liver chemoembolization. Cardiovascular and interventional radiology 37: 784-790, 2014.
7. Sampat M. P., Z. Wang, S. Gupta, A. C. Bovik and M. K. Markey. Complex wavelet structural similarity: A new image similarity index. IEEE transactions on image processing 18: 2385-2401, 2009.
8. Shi Y., N. Li, C. C. Tremblay and S. Martel. A piezoelectric robotic system for MRI targeting assessments of therapeutics during dipole field navigation. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics 26: 214-225, 2020.
9. Tous C., N. Li, I. P. Dimov, S. Kadoury, A. Tang, U. O. Häfeli, Z. Nosrati, K. Saatchi, G. Moran and M. J. Couch. Navigation of Microrobots by MRI: Impact of Gravitational, Friction and Thrust Forces on Steering Success. Annals of biomedical engineering 1-13, 2021.
10. Xiancheng W., L. Wei, M. Bingyi, J. He, Z. Jiang, W. Xu, Z. Ji, G. Hong and S. Zhaomeng. Retina blood vessel segmentation using a U-net based Convolutional neural network. In: Procedia Computer Science: International Conference on Data Science (ICDS 2018), Beijing, China, 8-9 June 2018,2018.
Figures
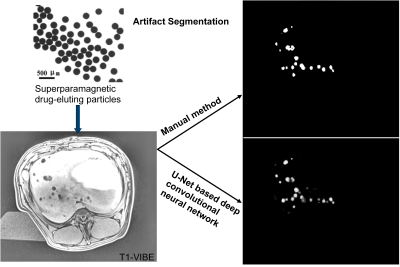
Figure 1. U-Net based deep convolutional neural network can localize the artifacts induced by the injected superparamagnetic drug-eluting particles in the liver of a living pig.
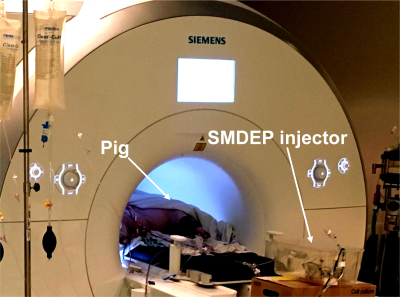
Figure 2. Setup of injecting SMDEPs into the liver of a living pig located in the MRI bore.