0952
Improved Neural Network-Based Coil Compression1Equal Contribution, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3The Harker School, San Jose, CA, United States, 4Rad/Pediatric Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
Synopsis
Coil compression is performed in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to enable smaller datasets and faster computation time. However, the traditional coil compression process is lengthy and lossy. In this work, we proposed a novel neural network-based coil compression method to achieve higher reconstruction accuracy and faster coil compression. Our method consistently achieved up to 1.5x lower NRMSE compared to SVD and GCC on the fastMRI knee dataset. The computational requirements of our method are practical, and inference runs 10 times faster than the traditional methods.
Introduction
MRI receiver arrays can include multiple coil elements 1, enabling parallel imaging (PI) 2,3,4 acceleration, resulting in higher signal to noise ratio (SNR). However, the large number of coils creates prohibitively large MRI datasets in space and infeasible computation time for reconstruction. Coil compression algorithms are effective in mitigating this problem by compressing data from many coils into fewer virtual coils.There are two main traditional methods for coil compression. One method is singular value decomposition 5 (SVD), but it is very slow. Another method is geometric coil compression 6 (GCC). Although GCC is faster than SVD, it is an iterative method, which is still computationally expensive. In addition, compression performance of both SVD and GCC is not very good when dimensionality of virtual coils is very low. Deep learning (DL) has been successful in a wide range of MRI applications, including reconstruction 7,8,9,10,11,12 and segmentation 13,14. DL has also been used for various types of data compression such as image compression 15,16 and genomic data compression 17,18. In this work, we propose and develop a neural network-based coil compression (NN-based CC) method to provide faster and more accurate compression.
Methods
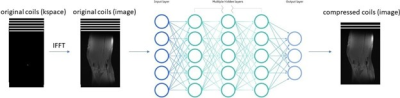
We propose a neural network-based framework to perform the coil compression task. Inputs to the network are the original 15 coil images, and network outputs are the virtual coil images. First, an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) is performed to convert the original 15 coils from k-space to the image domain. Then, we feed multi-coil images, slice-by-slice, into a fully connected neural network. In the output layer of the neural network, we generated a set of virtual coils with lower dimensionality than the original set of coils. We use square root of sum-of-square (SSOS) to combine individual coil images into one image. Then, we optimize the network parameters over the root mean square (RMS) loss between the SSOS image from the original coils and the SSOS image from the virtual coils. The framework of our model is shown in Figure 1.We train and test our model on the multi-coil knee data from fastMRI 19, which were acquired using a 15-channel knee coil array and a conventional Cartesian 2D TSE protocol on either 3T or 1.5 T scanners. Each subject volume contains slices of size 640x368 with 15 coils. There are 973 subjects (34742 slices) during training and 56 subjects (1959 slices) during testing. We compare our NN-based CC method with SVD and GCC, both implemented in BART 20, on the fastMRI test dataset. Experiments were performed on a Linux server with 2 GPUs (TITAN Xp and GeForce GTX 108) which had 64GB of RAM and 3TB of disk memory. We use normalized root-mean-square-error (NRMSE) between the original SSOS image and the compressed SSOS image to measure the compression accuracy.
Results
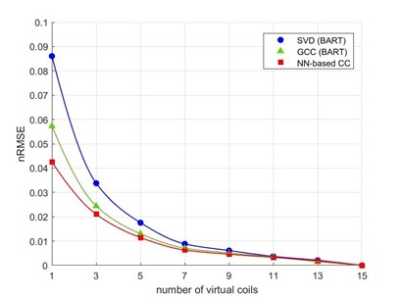
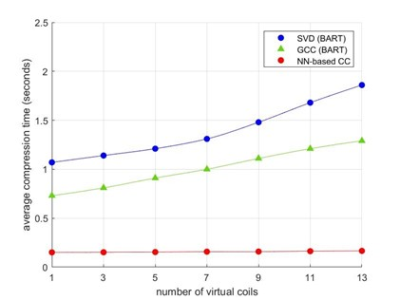
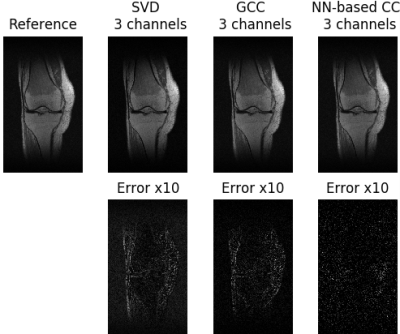
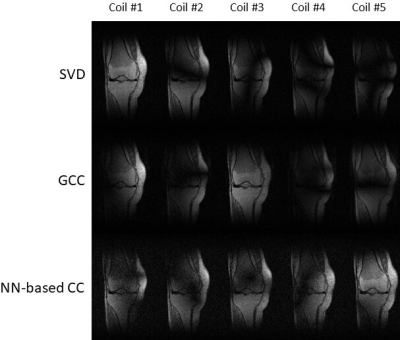
Compression accuracy, measured as the NRMSE between SSOS images from original coils and virtual coils, is shown in Figure 2 for different numbers of virtual coils and different coil compression methods. Our NN-based CC consistently achieved smaller NRMSE compared to SVD and GCC. Figure 3 shows the compression time for SVD, GCC and our NN-based CC. Our NN-based CC was much faster than the traditional methods across all numbers of virtual coils. In Figure 4, we also visualize the SSOS image from virtual coils and its difference from the original SSOS image for SVD, GCC and our NN-based CC. Information contained in each virtual coil compressed by SVD, GCC and our NN-based CC is shown in Figure 5.Discussion
As shown in Figure 2, NN-based CC out-performs the traditional methods SVD and GCC. Also, it performs much better than the traditional methods when the dimensionality of the virtual coils is very small. Specifically, it achieves more than 1.5x improvement in NRMSE over both SVD and GCC when the dimensionality of virtual coils is 1. As shown in Figure 3, another main advantage of the NN-based CC is that the compression time is much faster than the traditional methods. Although it took a long time to train our model (approximately 8 hours), training only needed to be done once, and inference time is significantly reduced compared to traditional iterative methods. One current limitation is that a different model needs to be trained for different dimensionality of virtual coils. For future work, we will explore generalizing one model to any dimensionality of virtual coils and different anatomies/geometries. We will also explore applying our method to non-Cartesian datasets.Conclusion
We proposed and developed a neural network-based model that achieved higher reconstruction accuracy than the traditional methods when it compressed original coils into smaller dimensionality of virtual coils. Our method also has applications in cases where the speed of coil compression is crucial. Once a neural network-based coil compression model is trained, it could be used to perform coil compression much faster than the traditional methods.Acknowledgements
Our group receives grant support from NIH R01EB009690, NIH U01EB029427, and GE Healthcare.
References
1. Roemer P, Edelstein W, Hayes C, Souza S, Mueller O. The NMR phased array. Magn Reson Med 1990; 16: 192–225.
2. Pruessmann K, Weiger M, Scheidegger M, Boesiger P. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med 1999; 42: 952–962.
3. Sodickson D, Manning W. Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn Reson Med 1997; 38: 591–603.
4. Griswold M, Jakob P, Heidemann R, Nittka M, Jellus V, Wang J, Kiefer B, Haase A. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med 2002; 47: 1202–1210.
5. Buehrer, M., Pruessmann, K.P., Boesiger, P. and Kozerke, S. (2007), Array compression for MRI with large coil arrays. Magn. Reson. Med. 57: 1131-1139. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.21237.
6. Zhang, T., Pauly, J.M., Vasanawala, S.S. and Lustig, M. (2013), Coil compression for accelerated
imaging with Cartesian sampling. Magn Reson Med, 69: 571-582. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24267
7. Hammernik, K., Klatzer, T., Kobler, E., Recht, M. P., Sodickson, D. K., Pock, T., & Knoll, F. (2018). Learning a variational network for reconstruction of accelerated MRI data. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 79(6), 3055-3071.
8. Mardani, M., Gong, E., Cheng, J. Y., Vasanawala, S., Zaharchuk, G., Alley, M., ... & Xing, L. (2017). Deep generative adversarial networks for compressed sensing automates MRI. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.00051.
9. Yang, G., Yu, S., Dong, H., Slabaugh, G., Dragotti, P. L., Ye, X., ... & Firmin, D. (2017). DAGAN: Deep de-aliasing generative adversarial networks for fast compressed sensing MRI reconstruction. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 37(6), 1310-1321.
10. Chen, F., Taviani, V., Malkiel, I., Cheng, J. Y., Tamir, J. I., Shaikh, J., ... & Vasanawala, S. S. (2018). Variable-density single-shot fast spin-echo MRI with deep learning reconstruction by using variational networks. Radiology, 289(2), 366-373.
11. Quan, T. M., Nguyen-Duc, T., & Jeong, W. K. (2018). Compressed sensing MRI reconstruction using a generative adversarial network with a cyclic loss. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 37(6), 1488-1497.
12. Lundervold, A. S., & Lundervold, A. (2019). An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Zeitschrift für Medizinische Physik, 29(2), 102-127.
13. Akkus, Z., Galimzianova, A., Hoogi, A., Rubin, D. L., & Erickson, B. J. (2017). Deep learning for brain MRI segmentation: state of the art and future directions. Journal of digital imaging, 30(4), 449-459.
14. Mardani, M., Gong, E., Cheng, J. Y., Vasanawala, S., Zaharchuk, G., Alley, M., ... & Xing, L. (2017). Deep generative adversarial networks for compressed sensing automates MRI. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.00051.
15. Dumas, T., Roumy, A., & Guillemot, C. (2018). Autoencoder based image compression: can the learning be quantization independent?. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 1188-1192). IEEE.
16. Akyazi, P., & Ebrahimi, T. (2019). Learning-based image compression using convolutional autoencoder and wavelet decomposition. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops.
17. Goyal, M., Tatwawadi, K., Chandak, S., & Ochoa, I. (2018). Deepzip: Lossless data compression using recurrent neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.08162.
18. Cui, W., Yu, Z., Liu, Z., Wang, G., & Liu, X. (2020, September). Compressing Genomic Sequences by Using Deep Learning. In International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks (pp. 92-104). Springer, Cham.
19. Zbonta, J., et al (2018), fastMRI: An Open Dataset and Benchmarks for Accelerated MRI, arXiv,
1811.08839
20. M. Uecker et al., "BART Toolbox for Computational Magnetic Resonance Imaging", Zenodo,
DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.592960
Figures