0815
Structural-functional interplay of the human placenta: in-vivo study using Pseudocontinuous Arterial Spin Labeling1Sagol Brain Institute, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2School of Computer Science and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel, 3Laboratory of FMRI Technology (LOFT), USC Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 4Sackler Faculty of Medicine and Sagol School of Neuroscience, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 5Division of Pediatric Radiology, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel, 6Division of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel, 7Ultrasound Unit, Lis Maternity Hospital, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel, 83Laboratory of FMRI Technology (LOFT), USC Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States
Synopsis
Adequate placental structure and function are crucial for fetal and maternal health. Here we assessed late-gestation placental perfusion (N=50, GA=31-38 weeks) using pseudocontinuous arterial-spin-labeling and radiomics feature-extraction, and their association with umbilical-cord insertion-site and the risk of fetal-growth-restriction (FGR). Increased blood-flow and arterial-transit-time were detected in our normal cases compared to earlier gestation as reported previously. Perfusion features differences were detected in placentas with marginal compared to central cord-insertion, indicating higher intensity heterogeneity. No differences were found between normal and FGR placentas. This study provides normal late-gestation placental perfusion values based on a large cohort, and implies on structural-functional associations.
Introduction
Adequate placental structure and function are vital for both fetal and maternal health. Placental-insufficiency, i.e. impairment of the placental function, is frequently associated with abnormal placental structure, and may often lead to fetal growth-restriction (FGR), which is associated with increased risk for morbidity in the neonatal, childhood and adulthood periods1. Several placental structural and functional parameters are known to characterize normal placental development and placental-insufficiency. Umbilical-cord insertion-site located closer to placental margins is one of the structural characteristics associated with FGR2. Reduced placental flow is a functional characteristic of FGR3, detected using uterine-artery Doppler ultrasound4. Several placental MRI studies using Arterial-Spin-Labeling (ASL) characterized changes in normal perfusion at different gestational-age (GA) ,and a few reported reduced flow in cases with FGR5. However, most studies on normal placentas were performed at early GA, reporting inconsistent results regarding changes with GA6-9. The aims of the current study were: (1) to assess normal placental perfusion using ASL at late GA on a large cohort of placentas of appropriately grown fetuses; (2) To investigate differences in placental perfusion parameters based on umbilical-cord insertion-site and on the presence or absence of FGR caused by placental-insufficiency.Methods
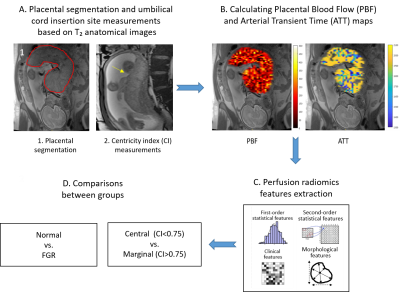
Subjects: Fifty placentas taken from women in the third trimester of pregnancy (31-38 weeks of gestation). MRI acquisition: Data were acquired on 3T Siemens MR magnets (PRISMA/Skyra). MRI protocol included high-resolution T2-weighted MRI (HASTE) with in-plane resolution of 0.93x0.93mm2 and slice thickness of 3mm to visualize the placental anatomy; and a multidelay 3D inner-volume GRASE free-breathing pCASL sequence, as reported by Shao et al 8 with three post-labeling delays (PLDs) of 1000, 1500 and 2000 msec. Labeling was placed at aortic bifurcation. Total pCASL acquisition time was ~7min. Image analysis: Data analysis pipeline is illustrated in Figure 1. A. Based on T2-weighted images (1) placental volume of interest (VOI) was drawn manually, and (2) umbilical cord-insertion site was measured as the relative distance from placental center (centricity index(CI)), based on10. Placentas with CI >0.75 were classified as marginal, and <0.75 as para-central. In 8 placentas, the umbilical cord-insertion site could not be detected. B. Placental-blood-flow (PBF) and arterial-transit-time (ATT) were calculated using a model-fitting according to8. C. Radiomics features including intensity-level and contrast were extracted using Pyradiomics11 from the PBF and ATT maps, within the VOI defined in A. D. Differences between normal placentas with para-central versus marginal cord-insertion, and between normal and FGR placentas were assessed for all features using t-test.Results and Discussion
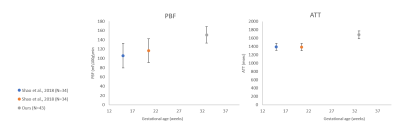
Fifty placentas were included in this study: 45 cases were normally developed (mean GA=32.9± 1.3, range 31-36) with no evidence of placental or fetal abnormalities, and 5 cases (mean GA=35.81± 1.43, range 34.5-37) were diagnosed as FGR, based on ultrasound and in three cases, histopathology validation. No significant differences in GA were detected between groups. Structural assessment: In 42/50 cases, 38 normal and 4 IUGR, the umbilical cord-insertion site was identified. 32 normal placentas had central cord-insertion (mean CI=0.27±0.19), and 6 had marginal (mean CI=0.82±0.06); 2 FGR placentas has para-central cord-insertion (mean CI=0.45±0.21), and 2 had marginal (mean CI=0.9±0). No significant differences in GA were detected between groups. Perfusion assessment: PBF and ATT maps were calculated for all placentas. Representative results for one placental slice are demonstrated in Figure 1B. Normal placental perfusion values were: PBF=150.8± 17 ml/100g/min; ATT=1679.4± 92 msec, at mean GA=32.9± 1.3 weeks. These perfusion results are similar to a previous study using the same method9 in normal fetuses with similar GA. Compared to previous studies at earlier GA8 using the same method, we detected higher PBF and ATT values12 (Figure 2 A and B, respectively). These results are in line with a previous ultrasound study that report increased placental perfusion with GA12. Within our normal cohort of 45 cases at small GA range (31-36 weeks), no significant perfusion changes were detected with GA. Differences between groups: No significant differences between normal placentas with para-central versus marginal cord-insertion were detected for mean PBF or ATT values. However significant lower values were detected on original first order Energy of PBF and ATT maps for marginal cases (p=0.02), and higher gray level non-uniformity of the PBF map (p=0.01), both indicating higher intensity heterogeneity in marginal placentas. No significant differences were detected between normal and FGR fetuses in PBF and ATT values, or any perfusion radiomics feature.Discussion and Conclusions
- This study provides normal perfusion values using pCASL on a large clinical cohort of fetuses at late GA.- Increased PBF and ATT values with GA were detected relative to previous studies, supporting increased placental perfusion with GA.
- This study demonstrates the association between placental perfusion and umbilical cord-insertion site.
- No differences were detected betweeen normal and FGR placentas, yet this may be due to the relatively small cohort of FGR cases, and the need to extract addditional perfusion parameters such as perfusion within specific placental regions.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Israel Innovation Authority.References
1. Leitner, Y., Fattal-Valevski, A., Geva, R., Eshel, R., Toledano-Alhadef, H., Rotstein, M., Bassan, H., Radianu, B., Bitchonsky, O., Jaffa, A.J., et al. (2007). Neurodevelopmental outcome of children with intrauterine growth retardation: a longitudinal, 10-year prospective study. J Child Neurol 22, 580-587.
2. Brouillet, S., Dufour, A., Prot, F., Feige, J.J., Equy, V., Alfaidy, N., Gillois, P., and Hoffmann, P. (2014). Influence of the umbilical cord insertion site on the optimal individual birth weight achievement. BioMed research international 2014, 341251.
3. Krishna, U., and Bhalerao, S. (2011). Placental insufficiency and fetal growth restriction. Journal of obstetrics and gynaecology of India 61, 505-511.
4. Pardi, G., Marconi, A.M., and Cetin, I. (2002). Placental-fetal interrelationship in IUGR fetuses--a review. Placenta 23 Suppl A, S136-141.
5. Lutz, A.B., Young-Lin, N., Leon-Martinez, D., Bianco, I.C., Seckel, E., Mrazek-Pugh, B., and Bianco, K. (2021). Measurement of Marginal Placental Cord Insertion by Prenatal Ultrasound Was Found Not to Be Predictive of Adverse Perinatal Outcomes. J Ultrasound Med 40, 2079-2086.
6. Harteveld, A.A., Hutter, J., Franklin, S.L., Jackson, L.H., Rutherford, M., Hajnal, J.V., van Osch, M.J.P., Bos, C., and De Vita, E. (2020). Systematic evaluation of velocity-selective arterial spin labeling settings for placental perfusion measurement. Magn Reson Med 84, 1828-1843.
7. Zun, Z., Zaharchuk, G., Andescavage, N.N., Donofrio, M.T., and Limperopoulos, C. (2017). Non-Invasive Placental Perfusion Imaging in Pregnancies Complicated by Fetal Heart Disease Using Velocity-Selective Arterial Spin Labeled MRI. Scientific reports 7, 16126.
8. Shao, X., Liu, D., Martin, T., Chanlaw, T., Devaskar, S.U., Janzen, C., Murphy, A.M., Margolis, D., Sung, K., and Wang, D.J.J. (2018). Measuring human placental blood flow with multidelay 3D GRASE pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling at 3T. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI 47, 1667-1676.
9. Daphna Link, N.A., Xingfeng Shao, Liat Ben-Sira, Leo Joskowicz, Ilan Gull, Danny J.J Wang, and Dafna Ben-Bashat. (2021). Multi-parametric functional and structural assessment of the placenta at late gestational ages using MRI Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med (2021).
10. Link, D., Many, A., Ben Sira, L., Tarrasch, R., Bak, S., Kidron, D., Gordon, Z., Yagel, S., Harel, S., and Ben Bashat, D. (2020). Placental vascular tree characterization based on ex-vivo MRI with a potential application for placental insufficiency assessment. Placenta 101, 252-260.
11. van Griethuysen, J.J.M., Fedorov, A., Parmar, C., Hosny, A., Aucoin, N., Narayan, V., Beets-Tan, R.G.H., Fillion-Robin, J.C., Pieper, S., and Aerts, H. (2017). Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer research 77, e104-e107.
12. Konje, J.C., Kaufmann, P., Bell, S.C., and Taylor, D.J. (2001). A longitudinal study of quantitative uterine blood flow with the use of color power angiography in appropriate for gestational age pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 185, 608-613.
Figures