0806
Feasibility of Flow-related Enhancement Brain Perfusion MRI1Institut für Diagnostische und Interventionelle Radiologie, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany, 2Institut für Diagnostische und Interventionelle Neuroradiologie, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
Synopsis
To test the feasibility of brain perfusion imaging exploiting flow-related enhancement during fast gradient echo sequences. Imaging was performed using Fast Low-Angle Shot (FLASH) and balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) sequences of a single axial slice with various imaging parameters at 1.5T and 3T. Perfusion-weighted maps were generated based on the Fourier decomposition method “Phase-REsolved FUnctional Lung” (PREFUL) MRI. The derived imaging protocol was evaluated in patients with metastases and a stroke showing high spatial overlap to post-contrast MRI and CT-perfusion. A cohort of 19 healthy individuals presented moderate, but significant regional correlation and high spatial Dice overlap to pCASL-MRI.
Introduction
The global burden of neurological diseases leads to enormous interest in imaging methods for numerous life-threatening conditions (1,2). Especially perfusion imaging plays a key role in the management of patients with ischemic strokes and brain tumors allowing to estimate tissue at risk prior to thrombectomy or surgery (3–6). The only contrast- and radiation-free technique to evaluate regional brain perfusion is arterial spin labeling (ASL)-MRI, which exploits magnetically labeled inflowing spins as an endogenous tracer (7). Unfortunately, low SNR, flow and motion artifacts may cause disturbances and long acquisition times. Flow-related enhancement is the basis of perfusion measurements in MRI techniques related to Fourier decomposition like Phase-REsolved FUnctional lung (PREFUL)-MRI, that has already been introduced to the field of lung imaging (8,9). The applied PREFUL technique is detecting the pulse wave and is very sensitive to both phase shifts and amplitude reductions by vascular occlusion or destruction (10–12). Applications focusing on central nervous system have not been examined so far. The aim of this study is to investigate the feasibility of brain perfusion imaging with the contrast- and radiation-free PREFUL-MRI technique in healthy volunteers and in patients with brain metastases and acute stroke with comparison to clinical reference standards.Methods
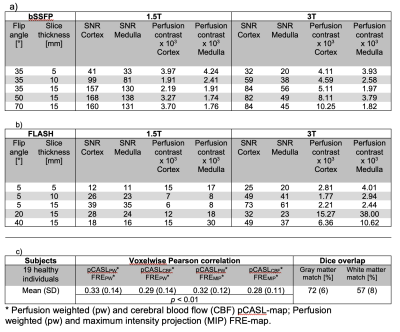
Data sets of one healthy individual were generated using Fast Low-Angle Shot (FLASH) and balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) sequences at 1.5T and 3T. Nineteen healthy individuals, three patients with cerebral metastases and one patient with an acute ischemic stroke underwent MRI using a bSSFP sequence (Magnetom Avanto and Vida, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany). The healthy cohort had pseudo-continuous ASL (pCASL), patients with metastases had post-contrast T1-weighted images and the stroke patient had CT perfusion imaging for comparison. MATLAB R2018a (The MathWorks, USA) was used for frequency analysis and postprocessing. The cardiac phase was estimated by piecewise fitting the averaged signal of a vessel ROI to a sine function. Perfusion-weighted maps presenting the maximum median amplitude of the full cardiac-cycle and temporal perfusion-weighted MIPs were calculated. Flow-related enhancement (FRE) perfusion maps were registered towards post-contrast images and the mean transit time map of the perfusion CT using advanced normalization tools (13). SNR was estimated from the ratio of the mean signal within the brain and its standard deviation (14,15). Perfusion contrast was calculated by the ratio of the perfusion signal amplitude and the mean signal of each voxel during the time series. Dice-similarity coefficients were calculated to quantify overlap of metastases in FRE and post-contrast images and the stroke area in the CT perfusion, respectively. Regional relationship between FRE-maps and pCASL-maps was evaluated by Pearson correlation analysis. Binary FRE- and pCASL-maps were calculated using the 40th percentile of the perfusion values as a threshold according to the average volume fraction of gray and white matter in healthy individuals (16). The spatial overlap was assessed by Sorensen-Dice coefficients.Results
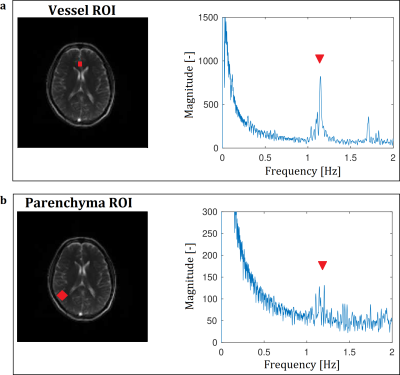
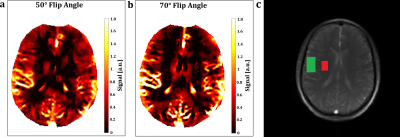
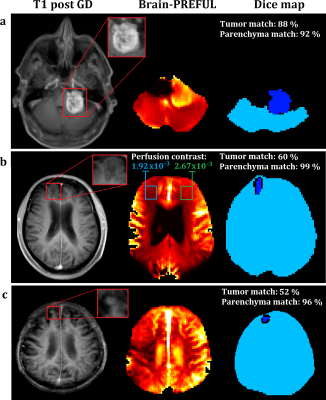
The frequency analyses of the bSSFP sequence presented a perfusion associated peak at the frequency of the heart within the vessel and parenchyma ROIs (Figure 1). It provided higher SNR and presented corticomedullary differentiation of the perfusion contrast at both field strengths (Table 1). An increase of the flip angle led to an increase of the perfusion contrast (Table 1 and Figure 2). The spatial overlap of the metastases ranged between 52% and 88% for the tumor and between 92% and 99% for the brain area (Figure 3). A patient with an acute stroke of his left hemisphere with high overlap of the healthy brain area of 94% and the left media-territory of 78% towards CT-perfusion is shown in Figure 4. The healthy cohort presented moderate significant regional correlation of around 0.3, but high spatial grey and white matter Dice overlap of 72% and 57% towards pCASL-MRI (Table 1).Discussion
In contrast to the bSSFP sequence, the FLASH presented no perfusion signal peak in the frequency analysis within the brain parenchyma. The flow-related signal enhancement in the bSSFP sequence increases with flip angle, because it affects spins depending on their velocity profile and their dephasing/TR (17). The differences of the perfusion contrast between the grey and white matter are within the range of previous reports using ASL, DSC, DCE and 15O inhalation PET (18–21). Various circumstances have to be taken in account: Fast imaging speed needs to be achieved to fulfill the Nyquist sampling theorem. This limits especially the spatial resolution and flip angle together with SAR-Limits. Our results indicated, that a flip angle of 35° is sufficient to generate corticomedullary differentiation within the physiological range. The maximum SNR of the bSSFP sequences was reached around 50° at 1.5T and around 70° at 3T. Future developments should focus on the optimization of the imaging parameters for certain clinical indications. Our results indicate potential benefits of determining phase-resolved perfusion and the phase shift of the pulse wave in clinical scenarios with vascular occlusion like ischemic strokes.Conclusion
In conclusion, we presented the feasibility of brain perfusion imaging using flow-related enhancement in healthy volunteers and patients with brain metastases and acute stroke. These results open up a new research field for a promising novel MRI technique for safe, fast and sensitive perfusion imaging in various pathologies within the brain.Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the German Center for Lung Research (DZL). The authors would like to express their gratitude to the radiographers Frank Schröder and Melanie Pfeifer from the Department of Radiology for their support with the MR measurements and patient care.References
1. Wang H, Naghavi M, Allen C, et al. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016;388:1459–1544 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1.
2. Johnson CO, Nguyen M, Roth GA, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:439–458 doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30034-1.
3. Ntaios G, Bornstein NM, Caso V, et al. The European Stroke Organisation Guidelines: A standard operating procedure. Int. J. Stroke 2015;10:128–135 doi: 10.1111/ijs.12583.
4. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke A.; 2019. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211.
5. Eilaghi A, Yeung T, d’Esterre C, et al. Quantitative Perfusion and Permeability Biomarkers in Brain Cancer from Tomographic CT and MR Images. Biomark. Cancer 2016;8s2:BIC.S31801 doi: 10.4137/bic.s31801.
6. Fussell D, Young RJ. Role of MRI perfusion in improving the treatment of brain tumors. Imaging Med. 2013;5:407–426 doi: 10.2217/iim.13.50.
7. Haller S, Zaharchuk G, Thomas DL, Lovblad K-OO, Barkhof F, Golay X. Arterial spin labeling perfusion of the brain: Emerging clinical applications. Radiology 2016;281:337–356 doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016150789.
8. Voskrebenzev A, Gutberlet M, Klimeš F, et al. Feasibility of quantitative regional ventilation and perfusion mapping with phase‐resolved functional lung (PREFUL) MRI in healthy volunteers and COPD, CTEPH, and CF patients. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018;79:2306–2314 doi: 10.1002/mrm.26893.
9. Bauman G, Puderbach M, Deimling M, et al. Non-contrast-enhanced perfusion and ventilation assessment of the human lung by means of Fourier decomposition in proton MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009;62:656–664 doi: 10.1002/mrm.22031.
10. Kaireit TF, Voskrebenzev A, Gutberlet M, et al. Comparison of quantitative regional perfusion-weighted phase resolved functional lung (PREFUL) MRI with dynamic gadolinium-enhanced regional pulmonary perfusion MRI in COPD patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019;49:1122–1132 doi: 10.1002/jmri.26342.
11. Behrendt L, Voskrebenzev A, Klimeš F, et al. Validation of Automated Perfusion-Weighted Phase-Resolved Functional Lung (PREFUL)-MRI in Patients With Pulmonary Diseases. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019:1–12 doi: 10.1002/jmri.27027.
12. Pöhler GH, Klimes F, Voskrebenzev A, et al. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension Perioperative Monitoring Using Phase‐Resolved Functional Lung (PREFUL)‐MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020;52:610–619 doi: 10.1002/jmri.27097.
13. Avants BB, Tustison NJ, Song G, Cook PA, Klein A, Gee JC. A reproducible evaluation of ANTs similarity metric performance in brain image registration. Neuroimage 2011;54:2033–2044 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.025.
14. Schroeder DJ, Inc EI. Astronomical Optics. Elsevier Science; 2000.
15. Bushberg JT, Seibert JA, Leidholdt EM, Boone JM, Goldschmidt EJ. The Essential Physics of Medical Imaging. Med. Phys. 2003;30:1936–1936 doi: 10.1118/1.1585033.
16. Lüders E, Steinmetz H, Jäncke L. Brain size and grey matter volume in the healthy human brain. Neuroreport 2002;13:2371–4 doi: 10.1097/01.wnr.0000049603.85580.da.
17. Markl M, Alley MT, Elkins CJ, Pelc NJ. Flow effects in balanced steady state free precession imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003;50:892–903 doi: 10.1002/mrm.10631.
18. Arakawa S, Wright PM, Koga M, et al. Ischemic Thresholds for Gray and White Matter. Stroke 2006;37:1211–1216 doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000217258.63925.6b.
19. LEENDERS KL, PERANI D, LAMMERTSMA AA, et al. CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW, BLOOD VOLUME AND OXYGEN UTILIZATION. Brain 1990;113:27–47 doi: 10.1093/brain/113.1.27.
20. Jakimovski D, Bergsland N, Dwyer MG, et al. Cortical and Deep Gray Matter Perfusion Associations With Physical and Cognitive Performance in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Front. Neurol. 2020;11:1–9 doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00700.
21. Parkes LM, Rashid W, Chard DT, Tofts PS. Normal cerebral perfusion measurements using arterial spin labeling: Reproducibility, stability, and age and gender effects. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004;51:736–743 doi: 10.1002/mrm.20023.
Figures