0594
T2*-weighted dual-polarity skipped-CAIPI 3D-EPI: 400 microns isotropic whole-brain QSM at 7 Tesla in 6 minutes1German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE), Bonn, Germany, 2University Clinic and Outpatient Clinic for Radiology, University Hospital Halle (Saale), Halle, Germany, 3Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Bonn, Bonn, Germany
Synopsis
We propose a dual-polarity readout technique to eliminate residual segmentation artifacts in interleaved multi-shot EPI despite established echo time shifting. The method only requires retrospective averaging of two or more complex-valued images acquired with alternating EPI readout polarity across measurements. The approach has been integrated into a custom skipped-CAIPI 3D-EPI sequence, combining highly segmented EPI with CAIPIRINHA parallel imaging. We present dual-polarity skipped-CAIPI 3D-EPI for ultrahigh-resolution, rapid, motion-robust whole-brain T2*-weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping at 7 Tesla. We demonstrate its capability to acquire exquisite imaging contrast at 0.7mm and 0.4mm isotropic resolution in only 1:15 and 6:14 [min:s], respectively.
Introduction
At ultra-high fields (B0≥7T), gradient-echo (GRE) based T2*-/susceptibility-weighted imaging or quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) are fundamental MRI modalities. As these techniques rely on rather long TEs, whole-head coverage with high spatial resolution yields relatively long acquisition times (TA>10min) and, thus, higher sensitivity to motion-related artifacts. Echo planar imaging (EPI) is able to accelerate such acquisitions efficiently1. In particular, interleaved multi-shot 3D-EPI is well suited2,3 for high-resolution as the number of EPI readouts per shot can be adjusted freely to match the TE and TR, whilst minimizing geometric distortions along the primary phase encode direction (y-direction, w.l.o.g.).Recently, skipped-CAIPI sampling has been proposed for high spatiotemporal resolution EPI4. Skipped-CAIPI combines interleaved multi-shot segmentation with CAIPIRINHA parallel imaging5 and, thus, allows for higher and more flexible undersampling with EPI. We explore its application for fast ultra-high-resolution (400µm isotropic) whole-brain T2*-weighted imaging and QSM at 7T.
Methods
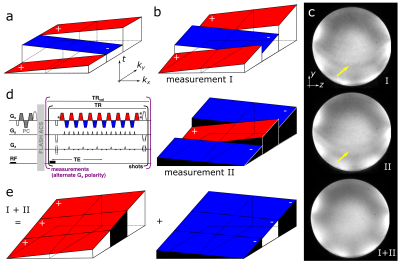
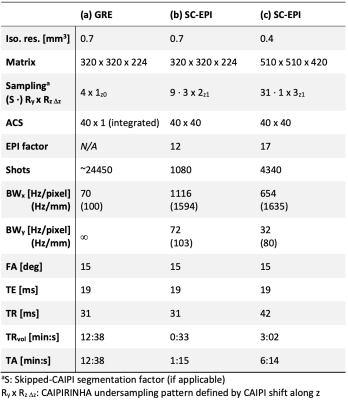
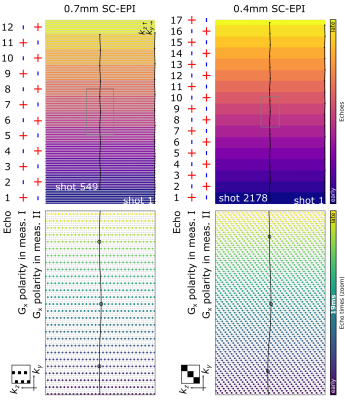
To provide excellent image quality at ultra-high resolutions throughout the brain, our custom skipped-CAIPI 3D-EPI sequence (SC-EPI)4 is extended by a dual-polarity averaging technique that eliminates residual segmentation artifacts. Despite the use of echo time shifting (ETS, Fig. 1a,b)6, such artifacts typically originate from particularly off-resonant regions (cf. Fig. 1c,I) due to remaining k-space discontinuities at off-center kx locations (frequency encode axis, w.l.o.g.). We propose to repeat such an affected SC-EPI measurement with inverted readout gradient polarity (d)7,4. As the sign of the artifact is inverted (Fig. 1c,II), averaging both measurements eliminates the artifact (c,I+II). This corresponds to averaging two completely continuous k-space signals composed of only the positive and only the negative readouts of measurements I and II (e). Further specific SC-EPI modifications include external acquisitions of only one initial phase correction scan (PC) and FLASH autocalibration scans (ACS) for time efficiency and PC-consistency across shots.A 700µm isotropic SC-EPI protocol (2 measurements within TA=1:15) was set up in accordance with a recent multi-vendor spoiled GRE-based QSM study at 7T8. The corresponding GRE protocol9 was reproduced as a reference (TA=12:38). Finally, a 400µm isotropic SC-EPI protocol was acquired (2 measurements within TA=6:14). All scans used sagittal slice orientation (y: posteroanterior), 1ms non-selective hard pulses10, FA=15° and TE=19ms. Further protocol parameters are listed in Tab. 1 and the respective skipped-CAIPI samplings are visualized in Fig. 2.
All data were acquired in one healthy female subject on a Siemens (Healthineers) MAGNETOM 7T Plus scanner using a 32-channel head receive coil and 1-channel circular polarized transmit coil. The latter is also used by the vendor-provided image reconstruction (“IcePAT”) as a reference receive coil for complex coil combination11. Complex-valued averaging was performed after parallel image reconstruction and coil combination. Susceptibility maps were then processed using NLM denoising12 of the real and imaginary images (only the 0.4mm EPI acquisition), phase unwrapping13, V-SHARP background field removal14 and homogeneity enabled incremental dipole inversion (HEIDI)15.
Results
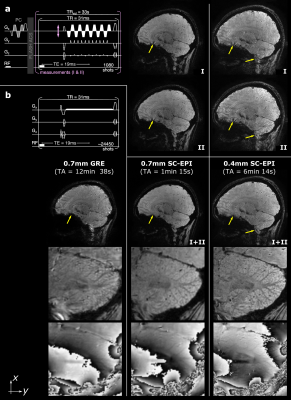
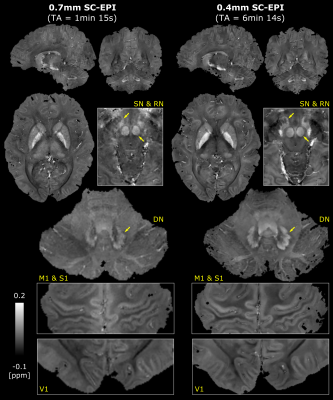
Fig. 3 shows sagittal example views including segmentation artifacts, in particular above the sphenoid sinus in SC-EPI measurements I and II. These are eliminated after averaging the two measurements (I+II). The remaining signal dropouts are reduced compared to the reference GRE measurement. The latter also shows pronounced motion artifacts even though the subject was asked to lay still. Zoomed T2*-weighted magnitude and phase images of the cerebellar cortex without NLM denoising demonstrate the gain in effective spatial resolution. Example views of the final susceptibility maps of both EPI scans are shown in Fig. 4.Discussion
The resulting T2*-weighted images (Fig. 3) and susceptibility maps (Fig. 4) demonstrate that rapid acquisitions of the whole-brain at ultra-high isotropic resolution using SC-EPI is feasible at 7T. The proposed dual-polarity technique eliminates residual segmentation artifacts at minimal implementation costs. Despite two measurements, TA was kept short by employing relatively strong parallel imaging. The g-factor noise penalty, that is not eliminated by averaging, was minimized through CAIPIRINHA sampling5. Compared to the long GRE acquisition, the shorter TAs of SC-EPI directly translated to less motion artifacts (Fig. 3).Overall, both SC-EPI scans yield comparable susceptibility values across various brain regions. The 0.7mm SC-EPI may benefit from lower noise, e.g. by two additional measurements (increasing the scan time by 66 seconds), by reduced undersampling or by applying a denoising algorithm.
The 0.4mm SC-EPI acquisition utilized its prolonged TR more SNR-efficiently by employing the largest EPI factor that fit TE=19ms. With additional denoising, the 0.4mm data shows exceptional susceptibility details across the whole brain allowing for studying smallest brain regions (e.g. laminar structure of the cortex, substructures in deep gray matter) in superb detail within TA of 6 min. Increasing FA according to the prolonged TR may even improve SNR.
Geometric distortions of SC-EPI data, as collected here, can be neglected, considering that the effective phase encode bandwidths of highly-segmented EPI are comparable to typical T2*-weighted GRE-based frequency encode bandwidths. Nonetheless, the short TA of SC-EPI would allow for additional reverse phase encode scans for retrospective distortion correction.
Conclusion
Dual-polarity skipped-CAIPI 3D-EPI allows for rapid, motion-robust whole-brain T2*-weighted imaging and QSM at unprecedented isotropic spatial resolution of 400µm. While traditional interleaved multi-shot EPI with echo time shifting remains feasible for most parts of the brain, the proposed dual-polarity technique ensures exquisite magnitude and phase contrast throughout the entire brain.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Langkammer, C., Bredies, K., Poser, B. a., Barth, M., Reishofer, G., Fan, A. P., Bilgic, B., Fazekas, F., Mainero, C., & Ropele, S. (2015). Fast quantitative susceptibility mapping using 3D EPI and total generalized variation. NeuroImage, 111, 622–630.
2. Zwanenburg, J. J. M., Versluis, M. J., Luijten, P. R., & Petridou, N. (2011). Fast high resolution whole brain T2* weighted imaging using echo planar imaging at 7T. NeuroImage, 56(4), 1902–1907.
3. Sati, P., Thomasson, D. M., Li, N., Pham, D. L., Biassou, N. M., Reich, D. S., & Butman, J. A. (2014). Rapid, high-resolution, whole-brain, susceptibility-based MRI of multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis Journal, 20(11), 1464–1470.
4. Stirnberg, R., & Stöcker, T. (2021). Segmented K‐space blipped‐controlled aliasing in parallel imaging for high spatiotemporal resolution EPI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 85(3), 1540–1551.
5. Breuer, F. A., Blaimer, M., Mueller, M. F., Seiberlich, N., Heidemann, R. M., Griswold, M. A., & Jakob, P. M. (2006). Controlled aliasing in volumetric parallel imaging (2D CAIPIRINHA). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 55(3), 549–556.
6. Feinberg, D. A., & Oshio, K. (1994). Phase errors in multi-shot echo planar imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 32(4), 535–539.
7. Hoge, W. S., & Polimeni, J. R. (2016). Dual-polarity GRAPPA for simultaneous reconstruction and ghost correction of echo planar imaging data. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 76(1), 32–44.
8. Rua, C., Clarke, W. T., Driver, I. D., Mougin, O., Morgan, A. T., Clare, S., Francis, S., Muir, K. W., Wise, R. G., Carpenter, T. A., Williams, G. B., Rowe, J. B., Bowtell, R., & Rodgers, C. T. (2020). Multi-centre, multi-vendor reproducibility of 7T QSM and R2* in the human brain: Results from the UK7T study. NeuroImage, 223(April), 117358.
9. Clarke, W.T., 2018. UK7T Network harmonized neuroimaging protocols. https://ora.ox.ac.uk/objects/uuid:55ca977f-62df-4cbf-b300-2dc893e36647
Protocols.zip > Siemens_Terra7T.pdf > T2star_0.7_single
10. Stirnberg, R., Brenner, D., Stöcker, T., & Shah, N. J. (2016). Rapid fat suppression for three-dimensional echo planar imaging with minimized specific absorption rate. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 76(5), 1517–1523.
11. Roemer, P. B., Edelstein, W. A., Hayes, C. E., Souza, S. P., & Mueller, O. M. (1990). The NMR phased array. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 16(2), 192–225.
12. Manjón, J. V., Coupé, P., Martí-Bonmatí, L., Collins, D. L., & Robles, M. (2010). Adaptive non-local means denoising of MR images with spatially varying noise levels. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 31(1), 192–203.
13. Abdul-Rahman, H. S., Gdeisat, M. a, Burton, D. R., Lalor, M. J., Lilley, F., & Moore, C. J. (2007). Fast and robust three-dimensional best path phase unwrapping algorithm. Applied Optics, 46(26), 6623–6635.
14. Wu, B., Li, W., Avram, A. V., Gho, S. M., & Liu, C. (2012). Fast and tissue-optimized mapping of magnetic susceptibility and T2* with multi-echo and multi-shot spirals. NeuroImage, 59(1), 297–305.
15. Schweser, F., Sommer, K., Deistung, A., & Reichenbach, J. R. (2012). Quantitative susceptibility mapping for investigating subtle susceptibility variations in the human brain. NeuroImage, 62(3), 2083–2100.
Figures