0560
Fast multi-compartment microstructure fingerprinting using deep neural networks1ICTEAM, Université Catholique de Louvain, Louvain La Neuve, Belgium
Synopsis
We estimate microstructural features of crossing fascicles in the white matter by using a fast multi-compartment fingerprinting, an extension of MR fingerprinting to diffusion MRI. The acceleration uses efficient sparse optimization and a dedicated feed-forward neural network to circumvent the inherent combinatorial complexity of the fingerprinting estimation. The accuracy of the results and the speedup factors obtained on in vivo brain data suggest the potential of our method for a fast quantitative estimation of microstructural features in complex white matter configurations.
Purpose
In previous work, we extended the MR Fingerprinting (MRF) framework1 to multi-compartment fingerprinting and applied it to multi-fascicle microstructure estimation of the white matter (WM) from diffusion MRI (dMRI)2. That approach allowed us to use a biophysically-realistic Monte Carlo simulator to represent the dMRI signal, similarly to the way a Bloch simulator models the MR signal in traditional “single-compartment” MRF. However, its multi-compartment nature negatively affects the inference runtime complexity as dictionary size increases. In this work, we leverage efficient sparse optimization and a dedicated feed-forward neural network, inspired in part by developments in MRF3,4,5 and in WM microstructure estimation6,7,8,9,10, and propose a 2-stage method for fast inference. We validate its efficiency and accuracy on data from the MGH Human Connectome Project (HCP).Methods
Signal model
We assume the dMRI signal in a WM voxel with intersecting populations of axons to result from the independent contribution of each population, weighted by its voxel occupancy fraction$$$\;\nu.\;$$$Each axon population is modeled by randomly-packed, straight, parallel cylinders with fixed intra-axonal diffusivity $$$D_{in}=2.0\mu{m}^2/ms$$$ and fixed diameter distribution. Alongside the volume fractions $$$\nu_k$$$, the free parameters to estimate in each population$$$\;k\;$$$are the fiber volume fraction $$$fvf_k$$$ and extra-axonal diffusivity$$$\;D_{ex,k}$$$. We restricted our analysis to 2-way population crossings.
Microstructure Fingerprinting
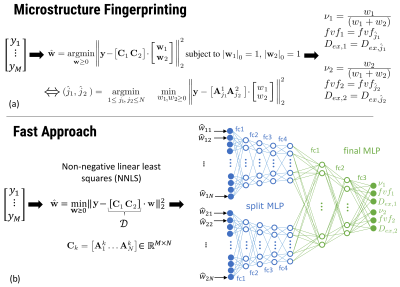
Figure 1 (a) summarizes the mathematical operations involved. In a precomputing phase, Monte Carlo simulations of the dMRI signal were performed in a single axon population for all combinations of 38 values of$$$\;fvf\;$$$and 10 values of$$$\;D_{ex},\;$$$leading to $$$N=380$$$ fingerprints $$$A_j\;(1\leq{j}\leq{N})$$$ stored in a canonical dictionary $$$C_0=\left[A_1 \dots A_N\right]\in\mathbb{R}^{M\times{N}}$$$. At runtime in each WM voxel, given measurements $$$ \mathbf{y}$$$, a matrix is formed by concatenating $$$C_1$$$ and $$$C_2$$$ obtained from rotating $$$C_0$$$ along the orientation of each population, detected using an external routine (here, constrained spherical deconvolution11). An exact solution is obtained by solving a large number $$$N^2$$$ of small non-negative linear least squares (NNLS) problems of 2 variables each, ensuring that only one fingerprint per compartment (i.e., axon population) contributes to the reconstructed signal. This $$$\mathcal{O}(N^2)$$$ complexity prevents the use of large dictionaries (large $$$N$$$) in practice.
Fast method
In the first stage (Fig. 1 (b)), the same matrix $$$[C_1 C_2]$$$ is assembled. However, one single NNLS problem of $$$2N$$$ variables is solved without any knowledge about that 2-compartment structure and without any sparsity constraint on the weight vector $$$\mathbf{w}$$$. This effectively projects the measurements $$$\mathbf{y}$$$ in the space of dictionary fingerprints. NNLS is known to naturally enforce sparsity12,13 and has an empirical runtime proportional to the number of matrix columns (here, $$$2N$$$), making it much more efficient than the exhaustive fingerprinting described above.
The second stage consists in passing the NNLS weight vector through a feed-forward neural network. The network initially has split arms independently processing the weights (unknowingly) attributed to each compartment by NNLS before merging into a common multi-layer-perceptron (MLP) for final parameter inference. The advantage of this architecture is to reduce the number of free parameters and facilitate training. The network was trained on synthetic dMRI data corrupted with Rician noise (SNR in 30-100).
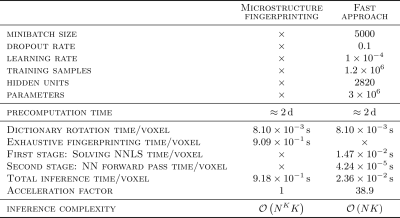
Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of both methods.
Experiments
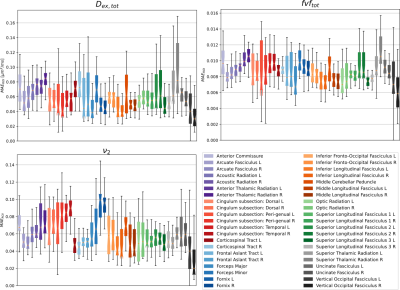
To assess efficiency and acuracy, the reference and the fast method were applied to the 34 healthy young adults of the MGH HCP dataset14. The parameter maps were projected into the XTRACT HCP probabilistic atlas15. The mean absolute error (MAE) for each WM property$$$\;(\nu,fvf,D_{ex})\;$$$ were averaged across WM regions and reported for each subject.
Results
Performance
As predicted by theory, the fast method was 1-2 orders of magnitude faster than the reference method (Table 1), with inference time dominated by the 1st stage NNLS problem.
Accuracy
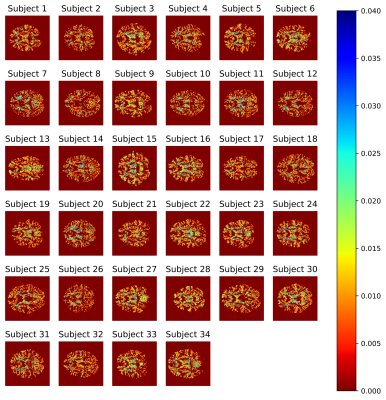
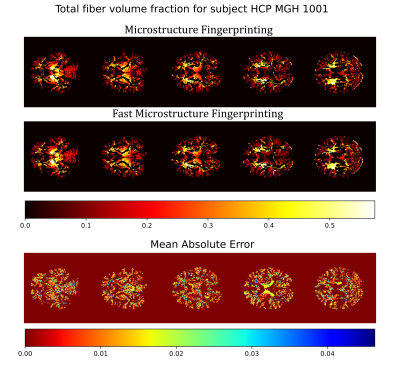
Overall, the estimates of WM properties obtained with the fast method were very close to those of the exhaustive microstructure fingerprinting across all 34 subjects and all brain regions (Figure 2). In the worst region of the worst subject, the error for$$$\;D_{ex}\;$$$represented 7% of the possible range in the dictionary (around 2.5% for most other regions); for fvf this was less than 2%. The errors were higher for the volume fractions$$$\;\nu\;$$$around 0.06. Figure 3 suggests that the error on fvf was kept under control even at the voxel level across the cohort. Figure 4 shows consistent fiber volume fraction maps for a representative subject.
Discussion and Conclusion
A neural network coupled with an optimization routine was used to estimate microstructural properties of crossing axon populations in an in vivo dataset. While the accelerated method was 1-2 orders of magnitude faster than the reference method, speedup factors are expected to be even larger with larger dictionaries as execution time of the fast method grows linearly rather than quadratically with dictionary size. In vivo results suggested the ability of our framework to extract accurate microstructural properties when dealing with crossing fascicles. This suggests the potential to deal with larger dictionaries and consequently use more complex models to represent populations of axons in the WM, all the while leveraging the superior modeling capabilities of Monte Carlo simulations.Acknowledgements
Quentin Dessain is a research fellow of the Fonds de la Recherche Scientifique - FNRS of Belgium.References
1. Ma, D., Gulani, V., Seiberlich, N., Liu, K., Sunshine, J.L., Duerk, J.L. and Griswold, M.A., 2013. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting. Nature, 495(7440), pp.187-192.
2. Rensonnet, G., Scherrer, B., Girard, G., Jankovski, A., Warfield, S.K., Macq, B., Thiran, J.P. and Taquet, M., 2019. Towards microstructure fingerprinting: estimation of tissue properties from a dictionary of Monte Carlo diffusion MRI simulations. NeuroImage, 184, pp.964-980.
3. Cohen, O., Zhu, B. and Rosen, M.S., 2018. MR fingerprinting deep reconstruction network (DRONE). Magnetic resonance in medicine, 80(3), pp.885-894.
4. Fang, Z., Chen, Y., Liu, M., Xiang, L., Zhang, Q., Wang, Q., Lin, W. and Shen, D., 2019. Deep learning for fast and spatially constrained tissue quantification from highly accelerated data in magnetic resonance fingerprinting. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 38(10), pp.2364-2374.
5. Lundervold, A.S. and Lundervold, A., 2019. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Zeitschrift für Medizinische Physik, 29(2), pp.102-127.
6. Ye, C., 2017. Tissue microstructure estimation using a deep network inspired by a dictionary-based framework. Medical image analysis, 42, pp.288-299.
7. Gibbons, E.K., Hodgson, K.K., Chaudhari, A.S., Richards, L.G., Majersik, J.J., Adluru, G. and DiBella, E.V., 2019. Simultaneous NODDI and GFA parameter map generation from subsampled q‐space imaging using deep learning. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 81(4), pp.2399-2411.
8. Ye, C., Li, X. and Chen, J., 2019. A deep network for tissue microstructure estimation using modified LSTM units. Medical image analysis, 55, pp.49-64.
9. Ye, C., Li, Y. and Zeng, X., 2020. An improved deep network for tissue microstructure estimation with uncertainty quantification. Medical image analysis, 61, p.101650.
10. de Almeida Martins, J.P., Nilsson, M., Lampinen, B., Palombo, M., While, P.T., Westin, C.F. and Szczepankiewicz, F., 2021. Neural Networks for parameter estimation in microstructural MRI: a study with a high-dimensional diffusion-relaxation model of white matter microstructure. bioRxiv.
11. Tournier, J.D., Calamante, F. and Connelly, A., 2007. Robust determination of the fibre orientation distribution in diffusion MRI: non-negativity constrained super-resolved spherical deconvolution. Neuroimage, 35(4), pp.1459-1472.
12. Lawson, C.L. and Hanson, R.J., 1995. Solving least squares problems. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.
13. Canales-Rodríguez, E.J., Legarreta, J.H., Pizzolato, M., Rensonnet, G., Girard, G., Rafael-Patino, J., Barakovic, M., Romascano, D., Alemán-Gómez, Y., Radua, J. and Pomarol-Clotet, E., 2019. Sparse wars: A survey and comparative study of spherical deconvolution algorithms for diffusion MRI. NeuroImage, 184, pp.140-160.
14. Setsompop, K., Kimmlingen, R., Eberlein, E., Witzel, T., Cohen-Adad, J., McNab, J.A., Keil, B., Tisdall, M.D., Hoecht, P., Dietz, P. and Cauley, S.F., 2013. Pushing the limits of in vivo diffusion MRI for the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage, 80, pp.220-233.
15. Warrington, S., Bryant, K.L., Khrapitchev, A.A., Sallet, J., Charquero-Ballester, M., Douaud, G., Jbabdi, S., Mars, R.B. and Sotiropoulos, S.N., 2020. XTRACT-Standardised protocols for automated tractography in the human and macaque brain. Neuroimage, 217, p.116923.
Figures