0377
Genetically Engineered “Multicolour” MRI Reporters for In Vivo Imaging of Transgenes Expression1Department of Molecular Chemistry and Materials Science, Weizmann institute of science, Rehovot, Israel, 2Department of Biomolecular Sciences, Weizmann institute of science, Rehovot, Israel, 3Department of Chemical Research Support, Weizmann institute of science, Rehovot, Israel, 4Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States, 5F.M. Kirby Research Center for Functional Brain Imaging, Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore, MD, United States
Synopsis
Genetically engineered multicolor fluorescent proteins have changed biomedical research by enabling multiplexed mapping of transgenes expression. However, although MRI reporter genes have been developed, the ability to monitor multiple reporters that are expressed simultaneously and present them in a multicolor fashion is still needed. Here, we present an MRI-based system, comprising computationally designed reporters (enzymes) combined with MRI-detectable synthetic probes (substrates) for non-invasive color-encoded MRI mapping of transgene expression. Systemically administered reporter probes exclusively accumulate in cells expressing the designed reporter genes allowing their spatial display as pseudo-colored CEST MRI maps as demonstrated in both tumor model and viral-delivery system.
Introduction
Genetically engineered fluorescent reporters has been indispensable for the decryption of biological complexity, and a broad palette of spectrally orthogonal, genetically encoded fluorescent proteins is in routine use. Nonetheless, light absorbance and scattering in live tissues have blocked their application to intact organs and animals. Reporter genes developed for MRI offer an attractive alternative for deep-tissue imaging in which non-invasive spatial maps of transgene expression can be overlaid on high-resolution anatomical views of the same subject1-6. However, MRI reporter genes do not possess the multiplex imaging capabilities needed for a simultaneous and colorful display of cellular processes. Moreover, the low-throughput capabilities of MRI-guided screening preclude the large-scale mutagenesis campaigns that have served so well in engineering fluorescent proteins7. Here, we capitalized on the frequency encodability CEST MRI8-9 to obtain MRI-based artificial colors, combined with an automated and computational evolution-based protein design method (PROSS10-11) to design fully orthogonal genetically engineered reporters (Figure 1a). The obtained dual-color imaging platform consists of two orthogonal deoxyribonucleoside kinase (dNK) (“reporter genes”) that were computationally designed to specifically phosphorylate two MRI-detectable synthetic deoxyribonucleosides (“reporter probes”). Systemically administered reporter probes (5-MDHT and pdC, i.e., CEST agents12-13) exclusively accumulate in cells expressing the designed reporter genes (HSV1-TK_7B and Dm-dNK_7C, respectively) and their spatial distribution can be displayed as spectrally-resolved pseudo-colored CEST MRI maps for non-invasive visualization of transgene expression.Methods
Reporter Probes: pdC was commercially available (Berry & Associates, Inc.). 5-MDHT was synthesized as previously described14.Computational model for dNK mutations: The PROSS algorithm was applied on Dm-DNK and HSV1-TK using the online webserver (http://pross.weizmann. ac.il), resulting in final variants, HSV1-TK_7B or Dm-dNK_7C, showing high expression and improved enzymatic activity.CEST MRI: In vitro and in vivo MRI experiments were carried out on a 15.2T scanner (Bruker, Germany), using a RARE sequence (TR/TE = 6000/20 ms, RARE factor = 8, 1 mm slice thickness, matrix size = 64x64), including a CEST module with a B1 saturation pulse applied for 4000 ms (3.6 μT saturation power, swept for±10 ppm) to acquire CEST-weighted images. Voxel-based B0 correction was performed using data obtained with the same parameters used for CEST except for TR = 1500 ms and B1/tsat = 0.5 μT /500 ms, swept from ±1ppm. CEST data processing was performed using custom-written scripts in MATLAB (MathWorks).
Inoculation of tumors and viruses: Stable CHOHSV1-TK_7B and CHODm-dNK_7C (CHO: Chineese hamster ovary) cell lines (2x105 cells/2mL PBS) or AAVHSV1-TK_7B and AAVDm-dNK_7C (AAV: Adeno-Associated Viruses of 2.1-5.9x1013 GC/ml) were intracranially injected (Figure 1b) into the striatum (coordinates: 1 mm posterior to Bregma, 2.0 mm lateral to the midline, 3.0 mm ventral to the surface of the skull) of 8-weeks-old female immunodeficient Hsd:Athymic (Envigo, Israel) or SJL/JCrHsd (Envigo, Israel) mice to generate intracranial tumors or viral infection respectively, in both hemispheres. Seven (CHO cells) or 14 (AAV solutions) days post inoculation mice were anesthetized and examined with MRI before and after an injection of a mixture of 5-MDHT and pdC (Figure 1c).
Results and discussion
First, we evaluated the CEST-MRI pseudo-color encoding of 5-MDHT and pdC (chemical structure shown in Figure 2a). The MTRasym plots (Figure 2b) showed negligible signal overlaps at Δωs of 5ppm (for 5-MDHT) and 6ppm (for pdC) enabling their mapping using pseudo-MRI-colors (Figure 2c) of magenta (Δω = 5ppm) and green (Δω = 6ppm). Then, we used the PROSS protein-stability design algorithm followed by a single point mutagenesis to obtain orthogonal dNK/substrate pairs, namely HSV1-TK_7B/5-MDHT and Dm-dNK_7C/pdC. To confirm the orthogonality of the automated designed reporters, CHO-cells expressing HSV1-TK_7B or Dm-dNK_7C transgenes were incubated with 5-MDHT and pdC mixture solution followed by examination of their CEST-MRI characteristics. A clear difference was obtained in the CEST maps obtained from CHOHSV1-TK_7B and CHODm-dNK_7C (Figure 3a) at the expected chemical-shift offsets which were assigned to magenta (Δω=5ppm) and green (Δω=6ppm) pseudo CEST-colors. Finally, we evaluated the in vivo performance of the developed multicolor reporter system by applying it in two different animal models. Seven days after intracranial injection of CHODm-dNK_7C and CHOHSV1-TK_7B cells, two CEST-MRI datasets were acquired, before and after intravenous administration of a solution containing a mixture of 5-MDHT and pdC. Subtracting the MTRasym maps (Δωs of 5ppm and 6ppm) obtained after the injection of the probes mixture from those obtained prior the injection resulted in a pseudo-colored CEST map (Figure 3b). Then, we extended approach to a non-tumor setting, where the engineered dNKs were delivered to the mouse brain using a viral vector (AAVDm-dNK_7C and AAVHSV1-TK_7B). Here again, a pseudo-colored CEST map was obtained (Figure 3c) reflecting the applicability of the designed reporter genes in an animal model that is used for wide range of applications. In both models the specific accumulation of the administrated probes due to their phosphorylation by the engineered dNKs is clearly showed by the detection of the CEST signal at Δω=5 (magenta) and 6 (green) ppm in HSV1-TK_7B or Dm-dNK_7C expressing regions, respectively.Conclusion
We demonstrated here the development and implementation of a genetically encoded reporter system, which enables MRI mapping transgene expression in a pseudo-multi-color fashion. Our approach extends the “multicolor” toolbox to thus far inaccessible deep tissues in live subjects.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Genove, G.; DeMarco, U.; Xu, H.; Goins, W. F.; Ahrens, E. T., A new transgene reporter for in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Med 2005, 11 (4), 450-4.
2. Cohen, B.; Ziv, K.; Plaks, V.; Israely, T.; Kalchenko, V.; Harmelin, A.; Benjamin, L. E.; Neeman, M., MRI detection of transcriptional regulation of gene expression in transgenic mice. Nat Med 2007, 13 (4), 498-503.
3. Gilad, A. A.; McMahon, M. T.; Walczak, P.; Winnard, P. T., Jr.; Raman, V.; van Laarhoven, H. W.; Skoglund, C. M.; Bulte, J. W.; van Zijl, P. C., Artificial reporter gene providing MRI contrast based on proton exchange. Nat Biotechnol 2007, 25 (2), 217-9.
4. Minn, I.; Bar-Shir, A.; Yarlagadda, K.; Bulte, J. W.; Fisher, P. B.; Wang, H.; Gilad, A. A.; Pomper, M. G., Tumor-specific expression and detection of a CEST reporter gene. Magn Reson Med 2015, 74 (2), 544-9.
5. Mukherjee, A.; Wu, D.; Davis, H. C.; Shapiro, M. G., Non-invasive imaging using reporter genes altering cellular water permeability. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 13891.
6. Schilling, F.; Ros, S.; Hu, D. E.; D'Santos, P.; McGuire, S.; Mair, R.; Wright, A. J.; Mannion, E.; Franklin, R. J.; Neves, A. A.; Brindle, K. M., MRI measurements of reporter-mediated increases in transmembrane water exchange enable detection of a gene reporter. Nat Biotechnol 2017, 35 (1), 75-80.
7. Shaner, N. C.; Campbell, R. E.; Steinbach, P. A.; Giepmans, B. N.; Palmer, A. E.; Tsien, R. Y., Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein. Nat Biotechnol 2004, 22 (12), 1567-72.
8. Liu, G.; Moake, M.; Har-el, Y. E.; Long, C. M.; Chan, K. W.; Cardona, A.; Jamil, M.; Walczak, P.; Gilad, A. A.; Sgouros, G.; van Zijl, P. C.; Bulte, J. W.; McMahon, M. T., In vivo multicolor molecular MR imaging using diamagnetic chemical exchange saturation transfer liposomes. Magn Reson Med 2012, 67 (4), 1106-13.
9. McMahon, M. T.; Gilad, A. A.; DeLiso, M. A.; Berman, S. M.; Bulte, J. W.; van Zijl, P. C., New "multicolor" polypeptide diamagnetic chemical exchange saturation transfer (DIACEST) contrast agents for MRI. Magn Reson Med 2008, 60 (4), 803-12.
10. Goldenzweig, A.; Goldsmith, M.; Hill, S. E.; Gertman, O.; Laurino, P.; Ashani, Y.; Dym, O.; Unger, T.; Albeck, S.; Prilusky, J.; Lieberman, R. L.; Aharoni, A.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J. L.; Tawfik, D. S.; Fleishman, S. J., Automated Structure- and Sequence-Based Design of Proteins for High Bacterial Expression and Stability. Mol Cell 2016, 63 (2), 337-346.
11. Khersonsky, O.; Lipsh, R.; Avizemer, Z.; Ashani, Y.; Goldsmith, M.; Leader, H.; Dym, O.; Rogotner, S.; Trudeau, D. L.; Prilusky, J.; Amengual-Rigo, P.; Guallar, V.; Tawfik, D. S.; Fleishman, S. J., Automated Design of Efficient and Functionally Diverse Enzyme Repertoires. Mol Cell 2018, 72 (1), 178-186 e5.
12. Bar-Shir, A.; Alon, L.; Korrer, M. J.; Lim, H. S.; Yadav, N. N.; Kato, Y.; Pathak, A. P.; Bulte, J. W. M.; Gilad, A. A., Quantification and tracking of genetically engineered dendritic cells for studying immunotherapy. Magn Reson Med 2018, 79 (2), 1010-1019.
13. Bar-Shir, A.; Liu, G.; Liang, Y.; Yadav, N. N.; McMahon, M. T.; Walczak, P.; Nimmagadda, S.; Pomper, M. G.; Tallman, K. A.; Greenberg, M. M.; van Zijl, P. C.; Bulte, J. W.; Gilad, A. A., Transforming thymidine into a magnetic resonance imaging probe for monitoring gene expression. J Am Chem Soc 2013, 135 (4), 1617-24.
14. Bar-Shir, A.; Liu, G.; Greenberg, M. M.; Bulte, J. W.; Gilad, A. A., Synthesis of a probe for monitoring HSV1-tk reporter gene expression using chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI. Nat Protoc 2013, 8 (12), 2380-91.
Figures
Figure 1. Principle of the design and application of multicolor MRI reporters for in vivo imaging.
(a) Schematic illustration of dNK1 (Dm-dNK) and dNK2 (HSV1-TK) design using computation and rational mutagenesis, (b) followed by intracranial delivery of the designed reporters (as CHO-tumors or AAV-constructs) into mouse brain, (c) generating the multicolor mapping of transgene expression using CEST-MRI following intravenous delivery of the reporter probes mixture (pdC and 5-MDHT).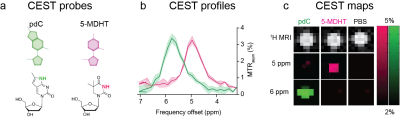
Figure 2. Multicolor imaging of MRI-detectable synthetic deoxyribonucleosides.
(a) Chemical structure of MRI-detectable synthetic deoxyribonucleosides, pdC and 5-MDHT. (b) MTRasym plots of pdC and 5-MDHT solutions emphasizing the spectral resolution of their obtained CEST profiles. (c) Multicolor CEST maps of PBS, pdC, and 5-MDHT solutions obtained at ∆w=5 and 6 ppm.
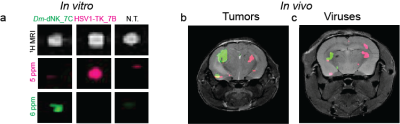
Figure 3. In vitro and in vivo multicolour imaging of genetically engineered reporters.
(a) 1H-MRI, and CEST maps (∆w= 5 and 6 ppm) of CHODm-dNK_7C and CHOHSV1-TK_7B cell lysates after incubation with a mixture of pdC and 5-MDHT. (b-c) In vivo MRI imaging of transgene expression represented as pseudo-colored CEST maps of inoculated tumors (b) and AAV-infected brain (c) obtained at ∆w=5 ppm (magenta) and ∆w=6 ppm (green) overlayed on anatomical MRI.