0227
Application of Super-Paramagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle to improve tumor visualization for MR-guided liver SBRT using Elekta Unity MR-Linac
Danny Lee1, Seungjong Oh1, Min-sig Hwang1, Mary McCauley1, Daniel Pavord1, Kyung Lim Yun1, Jason Sohn1,2, and Alexander V. Kirichenko1,2
1Radiation Oncology, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 2Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, United States
1Radiation Oncology, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 2Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, United States
Synopsis
Ablative SBRT to liver malignancies on MRI-Linac is a novel and rapidly evolving technology allowing visualization of tumor and nearby organs at risk (OAR). Reliable identification of liver tumors has direct impact on radiotherapy planning and outcome. SPION agent Ferumoxytol® (Feraheme, AMAG Pharmaceuticals, Waltham, MA) was applied as MRI contrast during adaptive planning on Elekta Unity MR-Linac. Compared to the non-contrast images, liver tumors after Ferumoxytol® injection, were superiorly visible for accurate delineation during the entire treatment course. This study is the first to report the impact of SPION contrast agent on liver tumor visualization in a 1.5T Elekta MR-Linac.
INTRODUCTION:
The off-label use of SPION agent Ferumoxytol® (Feraheme, AMAG Pharmaceuticals, Waltham, MA) has rapidly grown as an alternative MRI contrast agent1 and it is known to be safe in patients with impaired kidney function. SPIONs are trapped by the hepatic Kupffer cells (KCs) and produce strong T1, T2, and T2* relaxation effects in the liver parenchyma. Malignant tumors with lack of KCs exhibit no signal change, resulting in increased tumor-to-liver contrast difference for MR detection. Once IV injected, SPIONs stay within hepatic KCs for several weeks allowing precise targeting of hepatic tumors with conformal avoidance of residual hepatic parenchyma and nearby OAR. SPION was recently used for MR-guided liver radiotherapy on a 0.35T MR-Linac2 but not in a high-field 1.5T MR-Linac. The purpose of this study is to assess visualization of liver tumors utilizing SPION-enhanced 1.5T MRI during per-fraction adaptive SBRT planning on Elekta Unity MR-Linac (Elekta; Stockholm, Sweden).METHODS:
We investigated two liver cancer patients with primary and metastatic liver malignancies completed MRI simulations and treatments on Elekta Unity MR-Linac and underwent 5-fraction MR-guided liver SBRT delivered every other day. For liver imaging (Figure 1), a T2 3D TFE (Turbo Field Echo) MR pulse sequence in a 1.5T Unity Philips MR scanner built in the Unity with two MR receiver coils (a 4 channel anterior coil and a 4 channel posterior coil) was used and typical imaging setup parameters were TR/TE = 1800/205 ms, FOV = 400×400 mm2, pixel size = 1.56×1.56 mm2 and image matrix = 256×256, thickness = 2.2 mm and flip angle = 8o. A navigator window was set at the liver dome scout (1/3 in lung side and 2/3 in liver side) and 233 images were taken in each image set acquired for 250 to 410 seconds. In the first MRI simulation (pre-SPION), an MR image set with navigation was acquired as a baseline followed by injection of SPION contrast agent Ferumoxytol®. The second MRI simulation (post-SPION) was repeated at 72 hours after Ferumoxytol® injection. Next, a daily MR image set during per-fraction MR-guided liver SBRT was acquired for online treatment plan adaptation. Liver tumors were visually identified to evaluate: (1) the improvement of tumor visualization between pre- and post-SPION image sets, and (2) the consistency of tumor imaging during per-fraction MR image sets.RESULTS:
Compared to pre-SPION image sets, SPION improved tumor visualization on post-SPION images across two liver tumors. Tumor boundary is clearly shown on post-SPION images (Figure 2(e), (f) and (g)) on the background of negatively enhancing liver parenchyma. During MR-guided liver SBRT, SPION also maintained the consistency of tumor visualization across five per-fraction MR images (Figure 3).DISCUSSION:
Online treatment plan adaptation requires superior tumor contrast for fast and accurate delineation of target tumors and OAR. We utilized SPION contrast agent to negatively enhance liver parenchyma due to a shortened T2 relaxation time and thus relatively enhance tumor visualization (Figure 2(e), (f) and (g)), which can (1) minimize delineation uncertainty and shorten treatment planning time, (2) reduce treatment planning target volume and (3) spare OAR(s) during MR-guided liver SBRT (Figure 3).CONCLUSION:
This was the first study to directly determine the impact of SPION contrast agent Ferumoxytol® on visualization of liver tumors during per-fraction adaptive planning on the 1.5T Elekta Unity MR-Linac. Liver tumor boundaries were clearly visible for delineation of targets and OAR(s). Our results demonstrate that once IV injected SPION can facilitate consistent visualization of liver tumors on the day of treatment planning and throughout the entire treatment course, which could be a preferable imaging technique for achieving fast online treatment plan adaptation and more accurate MR-guided liver SBRT.Acknowledgements
Our study is supported by a grant from Elekta.References
- Gerda T, et al. Current and potential imaging applications of Ferumoxytol for MRI. Kidney international. 2017:92(1):47-66.
- Yukihiro H, and Etsuko T. Superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced MRI-guided stereotactic ablative radiation therapy for liver metastasis. Reports of Practical Oncology and Radiotherapy. 2021:26(3):470-474.
Figures
Figure 1. An example of
patient setup in Elekta Unity MR-Linac. A 1.5T Unity Philips MR scanner with MR
receiver coils (A 4 channel anterior coil and a 4 channel posterior coil).
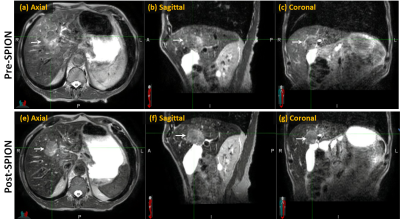
Figure 2. An example of pre-
and post-SPION image sets. Pre- and post-SPION images in first and second rows,
respectively. The white arrow indicates liver tumors.
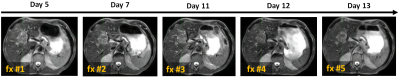
Figure 3. An example of five
daily-MR image sets used for online treatment plan adaptation. Day 5, 7, 11, 12
and 13 indicate how many days after Ferumoxytol® injection, and fx
#1, #2, #3, #4 and #5 indicate the sequential number of fractionations.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2022/0227