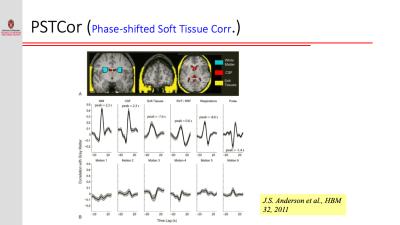
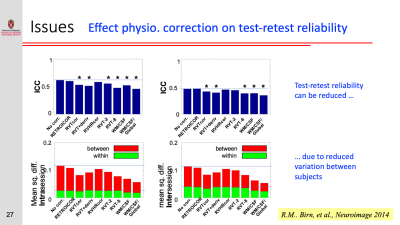
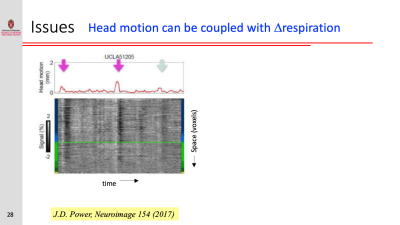
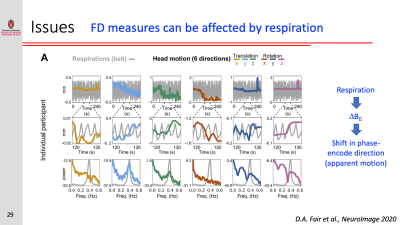
Physiological Contributions
Rasmus M. Birn1
1University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States
1University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States
Synopsis
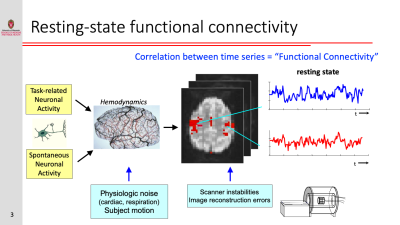
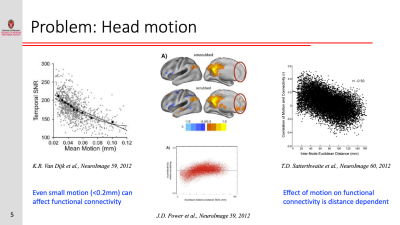
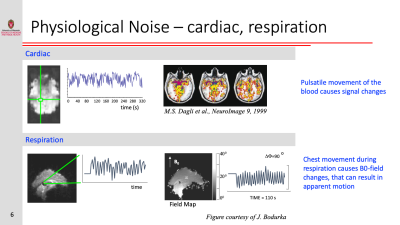
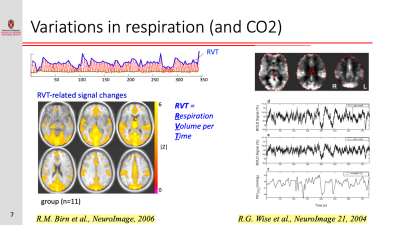
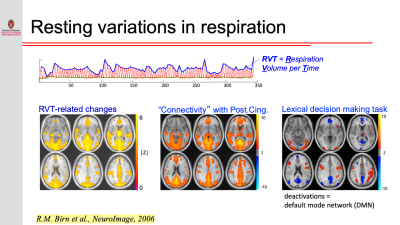
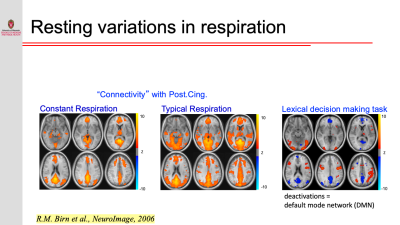
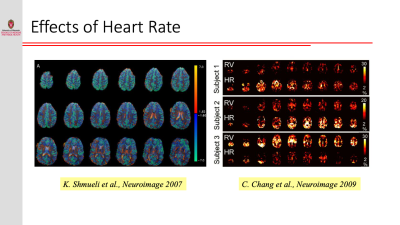
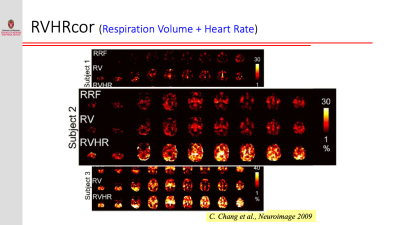
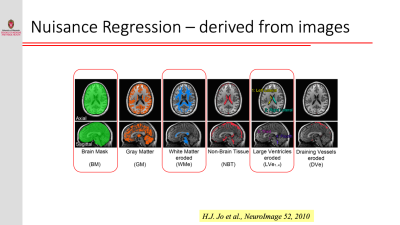
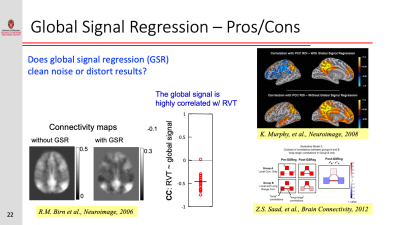
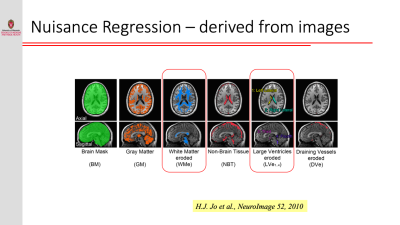
Resting-state functional connectivity is sensitive to various sources of noise, particularly head motion and physiological fluctuations resulting from the heart beat and respiration. This noise can cause both false positives and false negatives. A variety of tools have been developed to reduce the influence of this noise. These techniques include image registration, censoring high-motion time points, nuisance regression (where noise is modeled as additional regressors in a general linear model) and data-driven approaches such as independent component analysis (ICA).