AI & NeuroOncology
Spyridon Bakas1
1University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States
1University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States
Synopsis
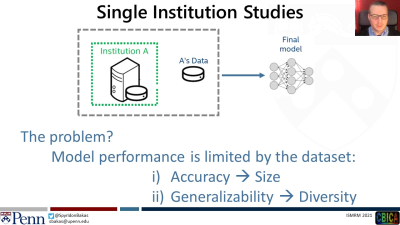
This talk introduces computational analytics towards speeding up scientific discovery and personalized diagnostics. It then focuses on two areas; a) radiogenomics, b) data-private collaborations. For radiogenomics, a hypothesis-driven study of the first imaging signature of EGFRvIII in glioblastoma, is presented, followed by data-driven studies on EGFRvIII and other EGFR mutations generating hypothesis for deeper investigations. Then, the first federated learning simulation in healthcare is discussed, followed by the first large-scale real-world federation in medicine, towards developing an AI model to detect glioblastoma boundaries based on 10,000 patients scans from >55 international collaborating sites, without sharing any patient data.