4229
Improvement of distortion-free diffusion tensor imaging of lumbar nerve roots using direct coronal MultiVane-SPLICE diffusion-weighted MRI.1Radiology, Eastern Chiba Medical Center, Tonage, Japan, 2Division of Health Sciences, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4General Medical Services, Chiba University Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba, Japan, 5Orthopaedic Surgery, Eastern Chiba Medical Center, Chiba, Japan, 6Faculty of Health Sciences, Institute of Medical, Pharmaceutical and Health Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan
Synopsis
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has a severe problem such as high geometric distortion and body motion. To solve these problems, we attempted to apply a split acquisition of fast spin-echo signals for diffusion imaging (SPLICE) instead of conventional Mx-eliminated TSE-DTI. In addition, so as to improve the incoherent signal phase due to motion, SPLICE was combined with MultiVane (known as PROPELLER) which is to sample k-space in a rotating fashion using a set of radially directed blades. In this study, we evaluated the effect of accuracy and reproducibility of the quantitative values in lumbar nerve roots using MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI.
PURPOSE
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) based on single-shot echo planar imaging sequence (EPI-DTI) is established method to evaluate lumbar nerve roots compression, because several studies have shown that DTI and tractography of human lumbar nerves can visualize and quantitatively evaluate lumbar nerves by fractional anisotropy (FA)1,2. However, EPI-DTI has a severe problem such as high geometric distortion. To solve these problems, we attempted to apply DTI based on single-shot Turbo Spin Echo sequence (TSE-DTI)3. Additionally, we tried to apply a split acquisition of fast spin-echo signals for diffusion imaging (SPLICE) instead of conventional Mx-eliminated TSE-DTI3 for reducing partial volume effect4. SPLICE is insensitive to the phase of magnetization and is expected to improve SNR5. In abdominal region of the lumbar spine, artifacts such as respiration, body motion and intestinal gas can adversely affect quantitative values. In previous study so as to improve the incoherent signal phase due to motion, SPLICE was combined with MultiVane (known as PROPELLER) which is to sample k-space in a rotating fashion using a set of radially directed blades6. In this study, we aimed at improving the quantitative performance. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of accuracy and reproducibility of the quantitative values in lumbar nerve roots using MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI [Fig.1].METHODS
All subjects were examined with 3.0T whole-body clinical system (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare). The study was approved by the local IRB, and written informed consent was obtained from all subjects. We compared SNR (lumbar nerve root and vertebral body) and FA values between SPLICE-DTI and MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI in lumbar nerve roots of three healthy volunteers. Additionally, lumbar nerve roots of five patients (24-71y, 2 females, 3 males) who have unilateral neurological symptom were examined using MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI. We evaluated the relationship of average FA values between bilateral nerve roots at normal levels and at symptomatic levels. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were calculated based on the results of two measurements made by two radiological technologists for all quantitative values.Imaging parameters for SPLICE-DTI were; Coronal, voxel size=3.0mm3, FOV=350×350mm2, b-value=400s/mm2, MPG=32 directions, TR=4000ms, TE=52ms, and total acquisition time=6m50s. Imaging parameters for MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI were; Coronal, voxel size=3.0mm3, FOV=350×350mm2, b-value=400s/mm2, MPG=15 directions, TR=3500ms, TE=61ms, radial percentage=190% and total acquisition time=7m40s.RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
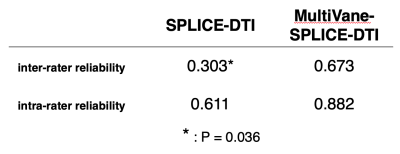
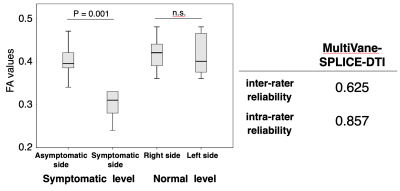
SNR and FA values in MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI were higher than those of SPLICE-DTI [Fig.2]. In addition, isotropic diffusion images of MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI depicted well lumbar nerve roots more distally compared to SPLICE-DTI because lumbar nerve roots maintained high signal sufficiently [Fig.2A, B]. ICC (inter-rater reliability and intra-rater reliability) in MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI were higher than those of SPLICE-DTI [Fig.3]. ICC in patient study using MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI showed a high correlation as well as the volunteer study [Fig.4]. At the symptomatic level, FA values in MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI of symptomatic side were significantly lower than those of asymptomatic side [Fig.4]. Intraneural edema and demyelination caused by compression injury indicated decreasing the FA values because of decreased diffusion anisotropy of the nerves. Therefore, measurement accuracy of the FA values is very important for evaluation of nerve injury. MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI might achieve higher measurement accuracy and reproducibility of FA values due to its lower distortion, high SNR and averaging procedure of body motion by radial acquisition.CONCLUSION
MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI might improve measurement accuracy and reproducibility of FA values for evaluation of lumbar nerve roots.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. BalbiV, et al. Tractography of lumbar nerve roots: initial results. Eur Radiol 2011;21(6):1153–9.
2. Eguchi Y, et al. Quantitative evaluation and visualization of lumbar foraminal nerve root entrapment by using diffusion tensor imaging: preliminary results. Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32(10):1824–9.
3. Sakai T, et al. Distortion-free diffusion tensor imaging for evaluation of lumbar nerve roots: Utility of direct coronal single-shot turbo spin-echo diffusion sequence. Magnetic Resonance Imaging 49 (2018) 78–85
4. Sakai T, et al. Improvement of distortion-free diffusion tensor imaging for evaluation of lumbar nerve roots: Utility of direct coronal single-shot turbo spin-echo diffusion sequence with a split acquisition. ISMRM2019 #2887
5. Schick F. SPLICE: sub-second diffusion-sensitive MR imaging using a modified fast spin-echo acquisition mode. Magn Reson Med. 1997 Oct;38(4):638-44.
6. Jie Deng, et al. Multishot Diffusion-Weighted SPLICE PROPELLER MRI of the Abdomen. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine59:947–953 (2008)
Figures
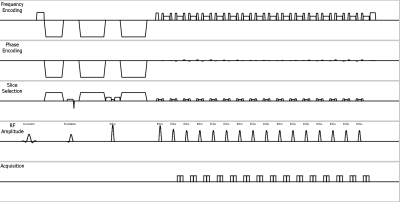
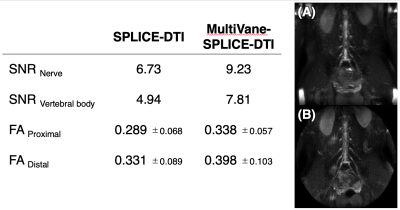
Fig.2 Comparison of SNR and FA values between SPLICE-DTI with MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI.
Partial Maximum Intensity Projection image (20mm thickness) shows on A (SPLICE-DTI) and B (MultiVane-SPLICE-DTI).