4151
Reproducibility of quantitative measures of intracranial arterial geometry: dependence on sequence and scanner platform differences1Radiology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States, 2Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Distal intracranial artery length measurement on TOF-MRA is a biomarker of age-related vascular changes but its measurement reproducibility in multi-center setting is unknown. We studied the dependence of measurement reproducibility on protocol and scanner platform variation. Reproducibility increased with increasing superior-inferior TOF-MRA coverage and consistency of imaging parameters. After correcting for these factors, high reproducibility was achieved between Philips 3T and Siemens 3T scanner platforms suggesting feasibility of quantitative intracranial vessel length measurements for multi-platform serial MRI studies.
Introduction
Artery length measurements on MRA have been suggested as biomarkers of age-related vascular changes over time (1). Intracranial artery feature extraction (iCafe) is one method to quantitatively measure proximal and distal artery lengths on TOF-MRA (2). A prior study of iCafe measurements performed on TOF-MRA on a Philips 3T scanner proved to have high inter-reader and inter-scan measurement reproducibility (3). However, reproducibility of iCafe artery length measurements may be scan protocol and scanner platform dependent. Therefore, the applicability of iCafe in multi-center, multi-platform situations where scan protocols may differ is unknown. Furthermore, distal intracranial artery length on iCafe was shown in prior studies to be the quantitative iCafe measure most associated with age-related vascular changes. However, distal artery length measurement is also more likely to be affected by variations in superior-inferior (S/I) FOV and variations in positioning of the S/I FOV between scan time-points. Visualization of distal arteries can also vary based on TOF-MRA protocol parameters. Such variations are more likely across scanner platforms in multi-center studies. Hence it is critical to study the reproducibility of distal artery length measurements across scan protocols in a multi-center, multi-platform setting.Aim
To investigate the factors determining inter-scan reproducibility of iCafe distal artery length namely, 1) scanner platform differences, 2) scan parameter differences, 3) S/I FOV differences.Methods
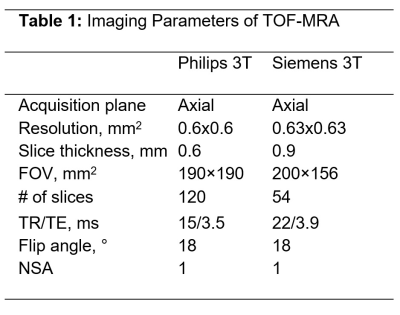
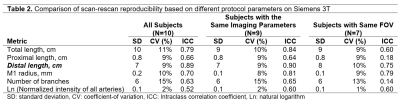
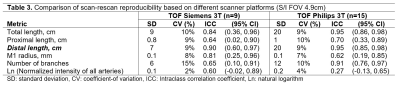
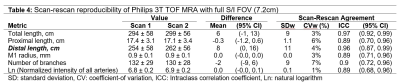
TTen subjects were scanned on a Siemens Trio 3T scanner. TOF-MRA was obtained with the parameters shown in Table 1. At a different institution, fifteen subjects were scanned on a Philips Ingenia CX 3T scanner and TOF MRA was obtained with parameters shown in Table 1. All subjects were rescanned within a two-week time interval with the same protocol as the first scan. Artery centerlines were drawn using the iCafe procedure and quantitative artery length and branching measurements were obtained as listed in tables 2 and 3. The coefficient of variation (CV) and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) were computed to determine the inter-scan reproducibility. All study procedures were reviewed and approved by local Institutional Review Boards, and all subjects provided written informed consent. Factors determining reproducibility: The improvement in reproducibility by reducing variation in protocol and FOV was investigated by comparing CV and ICC for subsets of the Siemens 3T scans. Three subsets: 1) complete set (N=10), 2) subset with consistent imaging parameters between the two scans (N=9); and 3) subset with consistent imaging parameters and matched FOV between the two scans (N=7) were compared (Table 2). The Philips 3T TOF S/I FOV (7.2cm) was reduced to match the Siemens 3T S/I FOV (4.9cm). CV and ICC were compared between the two 4.9cm FOV TOF-MRA iCafe measures to determine multi-platform reproducibility. Finally, the impact of reducing the S/I FOV on measurement reproducibility was determined by comparing the CV and ICC for full S/I FOV (7.2cm) and reduced S/I FOV (4.9cm) on the Philips 3T TOF-MRA.Results
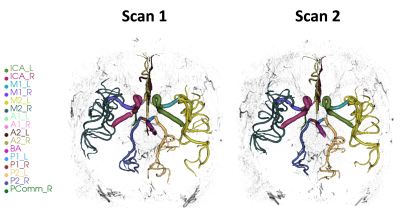
iCafe centerlines on the first and second time points (TP1 and TP2) were consistent both visually (figure 1) and quantitatively (tables 2 and 3). The primary measurement of distal vessel length had a consistently high ICC (0.9 or higher) across the subsets and CV of 9%. Other vessel length measurements (total length and proximal length) had similar CV (9-11%) but lower ICC. Other measures such as number of branches and normalized signal intensity had lower levels of reproducibility suggesting that these measures are not suitable as primary biomarkers in serial MRI studies. When S/I FOV was matched between Siemens 3T and Philips 3T, distal vessel length had comparable reproducibility on the two scanner platforms (table 3). Compared to the reduced S/I FOV of 4.9cm, measurements using the S/I FOV of 7.2cm proved more reproducible across all length and branching measurements (compare CV and ICC across tables 3 and 4).Conclusions
When the same FOV and TOF MRA protocol was used for reproducibility assessment, distal artery length measurements were highly reproducible (ICC = 0.9). Distal artery length measurement had a similar high reproducibility on both Philips and Siemens 3T (ICC > 0.9) when imaging parameters and S/I coverage were consistent between scans. This suggests that iCafe measured distal artery length measurements are reproducible in a multi-platform setting and therefore usable to monitor changes in multi-center studies using serial iCafe measurements. Mis-registration between time-points did not play a major role in determining reproducibility suggesting that scan positioning was consistent between the time-points. While the S/I FOV of 4.9cm centered on the circle of Willis and in the plane of the MCA was sufficient, lower S/I FOV is expected to increase distal artery measurement variability. Corroborating this, we found that measurement reproducibility was improved when S/I FOV was increased from 4.9cm to 7.2cm suggesting that full S/I FOV coverage of the brain is ideal for serial iCafe TOF-MRA measurements. Whole brain coverage will also negate variability due to mis-positioning of scans between two time-points. In summary, we identified the factors affecting iCafe distal artery length measurement inter-scan reproducibility. While both Siemens and Philips 3T TOF-MRA provided highly reproducible measurements, our results suggest that whole brain S/I FOV coverage of TOF-MRA can further improve inter-scan reproducibility in multi-center settings.Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by NIH grants R01HL103609 and R01NS092207References
1. Chen L, Sun J, Hippe DS, et al. Quantitative assessment of the intracranial vasculature in an older adult population using iCafe. Neurobiol Aging 2019;79:59-65.
2. Chen L, Mossa-Basha M, Balu N, et al. Development of a quantitative intracranial vascular features extraction tool on 3D MRA using semiautomated open-curve active contour vessel tracing. Magn Reson Med 2017.
3. Chen L, Mossa-Basha M, Sun J, et al. Quantification of morphometry and intensity features of intracranial arteries from 3D TOF MRA using the intracranial artery feature extraction (iCafe): A reproducibility study. Magn Reson Imaging 2019;57:293-302.
Figures