4104
Optimization of 3D prostate APTw MR imaging1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Bejing, China, 4Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Synopsis
Recently, prostate disease prevalence has been shown to increase gradually. Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) imaging, a molecular MRI technique at the protein level, has been applied in the diagnosis of prostate disease. This study aims to explore the optimal scan parameters for prostate APTw MR imaging. The preliminary results showed higher SNR of APTw images in central zones was acquired with the optimal scan parameters including the echo train length, the numbers and thickness of slices, FOV, the type of fold-over suppression and shimming, the size of voxel and phase encoding direction.
Introduction
Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) imaging can be used to assess the changes in the intracellular protein concentration and pH by detecting the proton exchange between the amide protons in endogenous mobile proteins and bulk-water protons1-2. APTw imaging had been applied in the diagnosis of brain tumor and the efficacy evaluation. To our knowledge, there are also few studies in prostate disease using 2D APTw imaging3. However, we found that the images obtained by prostate APTw imaging-based 3D-DIXON-TSE sequence is not clear enough to distinguish the lesion. The reasons may contribute to the APTw protocol designed for the brain scan not for the prostate. Therefore, in this study, we optimized the scan paraments of 3D APTw sequence, and evaluated the image quality of prostate APTw images with the default parameters and our optimal parameters in 24 patients with Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).Methods
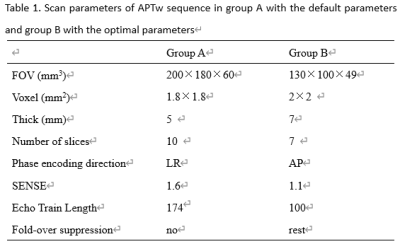
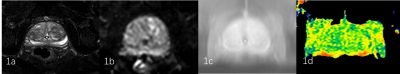
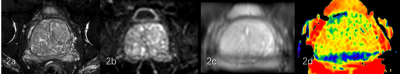
24 patients with BPH confirmed pathologically were included. Prostate APTw imaging were underwent a 3.0T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, the Netherlands). Other MR sequences included T2WI and , DWI. According to the APTw protocol with or without the optimal parameters, the patients were divided into two groups: group A (10 patients) with default parameters and group B (14 patients) with optimal parameters. Detailed scan parameters were listed in Table 1. After the MR scan is completed, the APTw images were transfer to the Intelli space Portal (ISP) workstation (Philips Healthcare). With the fusion images of APTw and DWI images, regions of interest (ROIs) were placed on central and peripheral zones of three slices (including the slice covering the largest dimension of prostate and its adjacent upper and lower slices) by two radiologists double-blindly. The signal intensity and standard deviation (SD) of ROIs in APTw images and M0 images were measured to calculate the SNR (SNR= signal intensity /SD) (Figure 1-2). Intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) was used to test the inter-observer consistency. T test was used to analyze the differences of APT signal intensity and SNR between the two groups.Results
The consistency of the data obtained by the two observers was good (ICC value > 0. 75). The significantly larger SNR value in central zones of group B (61.58 ±12.32) was observed than those of group A (39.40±21.56) (P <0.005). No significant difference of SNR in peripheral zones and APT values was observed between the two groups (p>0.05).Discussion and Conclusion
Better image quality in central zones of prostate was observed in APTw imaging with optimal parameters and had no effect on APT value. With the optimized parameters, the lesions occur in the central zone of the prostate may be able to be observed better.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.VAN ZIJL P C, ZHOU J, MORI N. Mechanism of magnetization transfer during on-resonance water saturation: A new approach to detect mobile proteins, peptides, and lipids. Magn Reson Med, 2003, 49(3):440-449.
2.JOKIVARSI K T, GROHN H I, GROHN O H. Proton transfer ratio, lactate, and intracellular pH in acute cerebral ischemia. Magn Reson Med, 2007, 57(4): 647-653.
3. Liu Na. Application progress of amide proton transfer imaging in tumor imaging. Journal of Practical Medical Imaging, 2020, 21(01): 50-52.
Figures