4017
Investigation of A Fast-volumetric Four-dimensional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique for Abdominal Radiotherapy Tumor Motion Management1Department of Health Technology and Informatics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education/Beijing), Department of Radiation Oncology, Beijing Cancer Hospital & Institute, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Motion management plays an important role in abdominal cancer radiotherapy. Current motion measurement method using 2D Cine MRI is inefficient. However, there is no commercial four-dimensional MRI available for motion management. In this study, we aim to investigate a fast-volumetric four-dimensional MRI technique using commercial sequence for tumor motion management in liver cancer patient. Our preliminary results shown that the commercially available TWIST-VIBE 4D-MRI sequence is capable of measuring liver tumor motion accurately with an acceptable tumor contrast.
Introduction
Motion management is of great importance in radiation therapy especially for abdominal cancer.1 Currently, 2D Cine MRI is the predominate method for motion measurement in abdominal cancer.2 However, it has limited ability to measure motion in 3D and requires 3 individual scans in different directions for measurement. Therefore, it is preferred to use 4D-MRI for motion management in radiotherapy. Currently there is no commercial 4D-MRI sequence available for this application. These limitations could be potentially solved by commercially available fast dynamic 3D imaging. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the motion measurement accuracy and tumor contrast in liver tumor using a fast volumetric 4D Magnetic Resonance Imaging (4D-MRI) technique using commercial sequence.Methods
Thirty-four patients with liver tumor were included in this study with IRB approval and all patients underwent routine MRI scans with additional 4D-MRI scan on a 3.0 Tesla MRI scanner (Siemens, Skyra). A fast-volumetric sequence named TWIST-VIBE was used to acquire 4D-MRI images. The image parameters were TR = 3.44 ms, TE = 1.23/2.46 ms, flip-angle = 5o, receiver bandwidth = 1420 Hz/voxel, voxel size = 2.7x2.7x2.7 mm3, matrix size = 160x128, scanning time = 53 s. Dixon fat suppression was used to suppress the fat signal. The temporal resolution of 4D-MRI was ~0.69 s/volume. The scanning range covered the whole liver with 5 cm margin in both superior and inferior direction. The 4D-MRI sequence was performed before and immediately after the injection of Gadolinium contrast agent, termed as non-contrast 4D-MRI (4D-MRINC) and contrast-enhanced 4D-MRI (4D-MRICE) respectively. All images were analyzed in Matlab using in-house developed program. The tumor average motion amplitude (AMA) and maximum motion amplitude (MMA) in the superior-inferior (SI), anterior-posterior (AP), and medium-lateral (ML) directions were measured in two sets of 4D-MRI and three sets of 2D Cine MR images. The tumor signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and tumor-to-liver contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) were measured in 4D-MRI, 2D Cine, T1w, and T2w images.Results
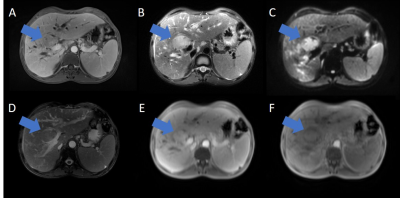
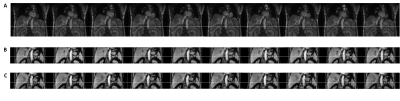
The 4D-MRI mages were successfully acquired using TWIST-VIBE sequence. An example of different MRI images were shown in Figure 1. The mean AMA measured from 4D-MRICE, 4D-MRINC, and 2D Cine MR images were 10.7±4.7, 2.7±1.1, 1.7±1.3 mm; 10.0±4.9, 3.0±0.7,1.7±1.3 mm; and 10.6±4.0, 2.3±2.0, 1.2±0.5 mm for SI, AP, and ML directions respectively. The mean MMA measured from 4D-MRICE, 4D-MRINC, and 2D Cine images were 13.0±4.8, 3.1±1.8, 1.9±1.2 mm; 13.2±5.2, 3.3±1.5,1.9±1.3 mm; and 12.5±3.9, 2.6±1.9, 1.4±0.8 mm for SI, AP, and ML directions respectively. No significant difference (p-values >0.05) was found among three sequences in three directions for both AMA and MMA measurement. An example of the coronal view of 4D-MRICE, 4D-MRINC, and 2D Cine MR images was shown in Figure 2. The mean tumor SNR measured from 4D-MRICE, 4D-MRINC, 2D Cine, T1w and T2w images are 19.5±12.4, 21.9±8.2, 31.4±26.3, 13.8±11.3, and 16.1±5.7 respectively. No significant difference (p-value > 0.05) was found between 4D-MRICE, 4D-MRINC and 2D Cine MR for tumor SNR. The mean tumor-to-liver CNR measured from 4D-MRICE, 4D-MRINC, 2D Cine MR, T1w and T2w images were 6.0±5.8, 5.2±4.3, 4.8±3.9, 9.0±5.5, and 11.7±11.6 respectively. No significant difference (p-value >0.05) was found between 4D-MRICE, 4D-MRINC, and 2D Cine MR for tumor-to-liver CNR.Conclusion
Our preliminary results demonstrated that the commercially available TWIST-VIBE 4D-MRI sequence is capable of measuring liver tumor motion accurately with an acceptable tumor contrast, holding great promises for tumor motion management in liver tumor radiation therapy.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Crane CH, Koay EJ. Solutions that enable ablative radiotherapy for large liver tumors: Fractionated dose painting, simultaneous integrated protection, motion management, and computed tomography image guidance. Cancer. 2016 Jul 1;122(13):1974-86. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29878. Epub 2016 Mar 7. PMID: 26950735; PMCID: PMC4911237.
2. Boldrini L, Cusumano D, Cellini F, Azario L, Mattiucci GC, Valentini V. Online adaptive magnetic resonance guided radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer: state of the art, pearls and pitfalls. Radiat Oncol. 2019 Apr 29;14(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1275-3. PMID: 31036034; PMCID: PMC6489212.