3935
Improved visualization of optic nerve DWI using IRIS: comparison with conventional methods
Yutaka Hamatani1, Kayoko Abe2, Masami Yoneyama3, Jaladhar Neelavalli4, Yasuhiro Goto1, Isao Shiina1, Kazuo Kodaira1, Takumi Ogawa1, Mamoru Takeyama1, Isao Tanaka1, and Shuji Sakai2
1Department of Radioligical Services, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Diagnostic imaging & Nuclear Medicine, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Philips Healthcare, Bangalore, India
1Department of Radioligical Services, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Diagnostic imaging & Nuclear Medicine, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Philips Healthcare, Bangalore, India
Synopsis
IRIS (Image Reconstruction using Image-space Sampling Function) is a DWI sequence for Multi shot (Mhs) echo planar imaging (EPI) with phase correction. The purpose of this study is to investigate the usefulness of IRIS for optic nerve, in which SSh EPI-DWI tends to show poor image quality due to magnetic susceptibility artifacts. As a result of comparing image quality among Single shot (SSh) EPI-DWI, SSh turbo spin echo (TSE)-DWI, MSh TSE-DWI, and IRIS, IRIS was the best sequence to visualize the optic nerve. IRIS suppressed magnetic susceptibility artifacts most clearly, and can provide excellent contrast with high robustness.
Introduction
DWI provides image contrast that reflects the limiting water diffusion at the cellular level. Using DWI, various lesions, like ischemic disease and tumors in the body can be visualized as hyperintensity depending on the degree of diffusion limitation. Some studies reported that DWI of the optic nerve was useful for detecting optic neuritis and optic nerve tumors. 1,2,3,4 However, DWI of the optic nerve has some problems about artifacts due to differences in magnetic susceptibility between tissue and air. For this reason, single shot (SSh) echo planar imaging (EPI)-DWI, which is a commonly used sequence has high risks of image distortion, signal loss, and spatial blurring caused by susceptibility artifacts to demonstrate the optic nerve. SSh TSE-DWI is known to be useful for reducing susceptibility artifacts. 5,6 However, SSh TSE-DWI suffers from low signal noise ratio (SNR), and severe image blurring. On the other hand, multi shot (MSh) TSE-DWI combined with Multi Vane radial acquisition (MSh-MV-TSE DWI) has an advantage of reducing image blurring. However, MSh-MV-TSE DWI still suffers from low SNR. IRIS (Image Reconstruction using Image-space Sampling Function) is based on MSh EPI-DWI, which is combined with navigator-echo to correct the phase shift caused by the movement of each shot [Fig 1]. IRIS for the optic nerve is expected to create higher quality imaging with less ghost artifacts. In this study, we evaluated the usefulness of IRIS for depiction of the optic nerves by comparing image quality among SSh EPI-DWI, SSh TSE-DWI, MSh MV-TSE-DWI, and IRIS. 7,8Methods
Five healthy volunteers (4 males, 1 female, age 25-45 years old) were examined by 3.0T MRI (Ingenia, Philips Healthcare). The study was approved by the local IRB (Clinical Trial Review Board) and all subjects gave written informed consent. The image parameters were shown in Table 1. SPLICE (Split-echo acquisition of TSE signals) was used as SSh TSE-DWI because SPLICE improves SNR by collecting Stimulated echo (STE). MSh TSE-DWI is combined with Multi Vane acquisition. A visual evaluation of the optic nerve (artifact, image contrast, and overall image quality) was performed by three radiologists and radiological technologists using a 5-point scale: 0, non-evaluative; 4, excellent quality. The signal profile analysis of the optic nerve was performed on SSh EPI-DWI, SSh TSE-DWI, MSh TSE-DWI, IRIS, and T1WI that was used as a standard image.Results and Discussion
The susceptibility artifacts were significantly noted on SSh EPI-DWI, while IRIS showed the least artifacts. The image contrast of SSh TSE-DWI was the lowest, while SSh EPI-DWI and IRIS showed higher image contrast than both SSh and Msh TSE-DWI. IRIS was the best of overall image quality. The results of signal profile analysis were shown in Figure 3. The signal profiles of T1WI and IRIS were almost the same. The signal intensities of T1WI were almost the same as those of T1WI, while the image distortion was noted on SSh EPI-DWI. The signal intensities of SSh TSE-DWI and MSh TSE-DWI were lower, and SSh TSE-DWI and MSh TSE-DWI showed more prominent image distortion, compared to T1WI. SSh EPI-DWI is known to be sensitive to magnetic field inhomogeneity. In this study, SSh EPI-DWI was strongly affected by susceptibility artifacts which caused image distortion of the optic nerve even though SSh EPI-DWI had relatively high image contrast. Both SSh and MSh TSE-DWI succeeded to reduced blurring, however, lower SNR of TSE-DWI leaded to poorer image quality than SSh EPI-DWI and IRIS. IRIS is one of MSh EPI-DWI using phase correction to reduce ghost artifacts. In this study, IRIS was the best sequence to demonstrate the optic nerve. It was suggested that combination of high SNR on EPI-DWI and artifact suppression by Msh acquisition and phase correction of IRIS created good synergistic effects.Conclusion
IRIS can suppress the susceptibility artifacts while maintaining the higher nerve conspicuity with sufficient spatial resolution, image contrast and SNR compared to other DWI techniques in a clinically feasible acquisition time, and it has a potential to be a new commonly used DWI for the evaluation of the optic nerve.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Benjamin Bender et al. Diffusion restriction of the optic nerve in patients with acute visual deficit. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014 Aug;40(2):334-40. 2. Sevda Yılmaz et al. Changes of normal appearing optic nerve head on diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Clin Imaging. Mar-Apr 2017;42:60-63. 3. Ramsey Kilani et al. DWI findings of optic nerve ischemia in the setting of central retinal artery occlusion. J Neuroimaging. 2013 Jan;23(1):108-10. 4. Zareen Fatima et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in optic neuritis. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2013 Feb;64(1):51-5. 5. Zaw Aung Khant et al. Evaluation of pituitary structures and lesions with turbo spin-echo diffusion-weighted imaging. J Neurol Sci. 2019 Oct 15;405:116390. 6. Kenichiro Hirata et al. Comparison of the image quality of turbo spin echo- and echo-planar diffusion-weighted images of the oral cavity. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 May;97(19):e0447. 7. Gabrielle C Baxter et al. Improving the image quality of DWI in breast cancer: comparison of multi-shot DWI using multiplexed sensitivity encoding to conventional single-shot echo-planar imaging DWI. Br J Radiol. 2020 Sep 9;20200427. 8. Ximing Xu et al. Reliability and validity of multi-shot DWI in diagnosis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a study based on 3-T MRI. Eur Spine J. 2020 Jun;29(6):1219-1226.Figures
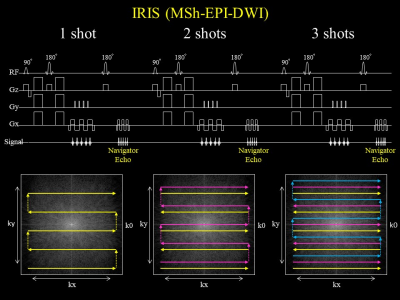
Figure 1.The IRIS
sequence chart. IRIS adopts multi shot acquisition which signal collection into
k-space is divided in the phase direction. Multi shot acquisition tends to
cause ghost artifacts, so IRIS applies navigator-echo for each shot to make phase
corrections.
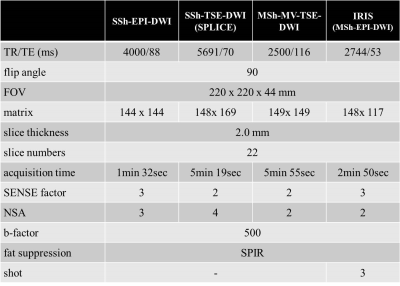
Table 1. The imaging parameters
of SSh-EPI-DWI、SSh-TSE-DWI (SPLICE)、MSh-MV-TSE、IRIS (MSh-EPI-DWI)
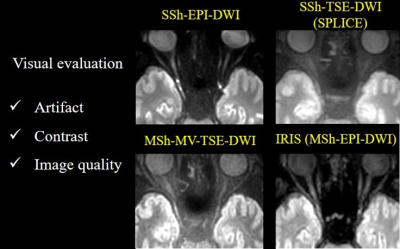
Figure 2. DWI of the optic
nerve on SSh EPI-DWI, SSh TSE-DWI, MSh. TSE-DWI, and IRIS. IRIS shows the least
artifacts and image distortion, and the optic nerve was demonstrated with the
highest image contrast on IRIS.
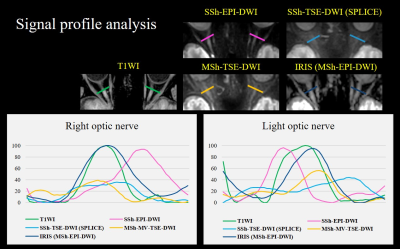
Figure 3. The Signal profile
analyses of the optic nerves on SSh EPI-DWI, SSh TSE-DWI, MSh. TSE-DWI, IRIS,
and T1WI were performed as shown in the Fig 3. The signal profiles show that
IRIS provides less image distortion and signal loss, and is most similar to
T1WI.