3879
The value of GRASP DCE-MRI for the differentiation between benign and malignant endometrium lesions1Zhongda Hospital,School of Medicine,Southeast University, NanJing, China, 2SIEMENS Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
This prospective study aimed to investigate the value of GRASP(Golden-angle RAdial Sparse Parallel)on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MRI (DCE-MRI) for the differentiation between benign and malignant lesions of endometrium on 88 patients. The results showed that the quantitative parameters include Kep and Ve of DCE-MRI have statistically significant difference between the benign and malignant endometrium lesions
Introduction
Endometrial cancer (EC) is the most common gynecological malignant tumor. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a routinely used imaging modality for preoperative evaluation of EC, and DCE has been proven to be an important diagnostic tool for differentiation between benign and malignant endometrium lesions (1.2). However, even using parallel imaging methods, such as SENSE, GRAPPA or CAIPI, can not ensure a high spatial and temporal resolution simultaneously, which leads to the failure to detect lesions smaller than 5mm using DCE. Recent study reported that Golden-angle RAdial Sparse Parallel (GRASP) DCE-MRI extremely improved DCE spatial and temporal resolution by applying radial trajectory in k-space acquisition and compressed sensing algorithm for image reconstruction. Previous studies demonstrated that GRASP DCE was successfully conducted for body, breast, and head/neck imaging (3). The purpose of this study was to prospectively evaluate the value of the quantitative DCE parameters, including Ktrans, Kep and Ve, using GRASP sequence for patients with endometrial tumor, especially for lesions smaller than 5 mm. Furthermore, a possible cutoff of the useful parameters were also discussed.Methods
From August 2020 to November 2020, 88 patients (women, mean age, 54.5years; range, 27–81 years) with clinical suspicion of female pelvic malignant lesions were enrolled in this study. All MR examinations were performed on a 3 T MRI scanner (MAGNETOM Vida, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). The axial T1W, T2W, DWI, ADC and Sagittal T2W images were acquired before contrast injection. Then followed with the GRASP VIBE sequence for DCE acquisition, the detailed parameters were: TR/TE =4.1/1.86/ms, thickness = 3mm, slices = 40, FOV = 240 × 240mm2, matrix = 224 × 224, radial views = 1982, voxel size = 1.1 × 1.1 × 3.0 mm3, total acquisition time = 5min38sec, contrast injection was conducted when the GRASP sequence started for 20 seconds ( 2.5 mL/s, 0.2 ml per kilogram of body weight), and DCE images were reconstructed with a temporal resolution of 9.4s (35periods). Axial delayed contrast-enhanced T1W images were obtained after the GRASP sequence. The quantitative DCE parameters, i.e. Ktrans, Kep and Ve, were derived using the standard Tofts model on workstation (SIEMENS Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). For data analysis, the sensitivity and specificity of all the calculated parameters mentioned above were assessed. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was utilized to examine the accuracy of values with statistic important.Results
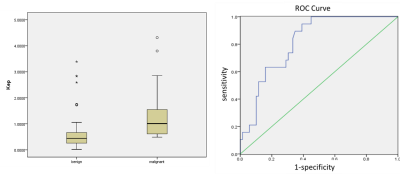
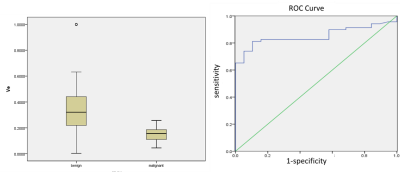
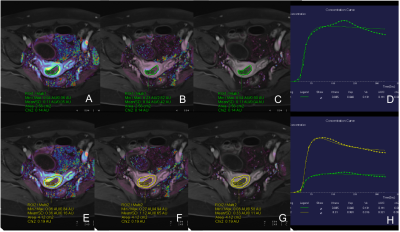
There were 69 and 19 patients for benign and malignant endometrium lesions enrolled in this study, respectively. The Kep value were significantly lower in the benign group compared with that in the malignant group (0.627 ± 0.673min−1 v.s. 1.412 ± 1.143 min−1; p<0.05). The area under the ROC curve of the Kep values is 0.82, and the optimal cutoff point is 0.527 min−1(sensitivety:0.95, specificity:0.61),(figure1). Further, the Ve value was slightly higher in the benign group compared with that in the malignant group (0.340± 0.198 v.s. 0.147 ± 0.057; p<0.05). The area under the ROC curve of the Ve values is 0.85, and the optimal cutoff point is 0.206, (sensitivety:0.81, specificity:0.90) (figure2). The Ktrans value did not show statistically significant difference between the 2 groups (0.157 ± 0.134 min−1 v.s. 0.231 ± 0.233 min−1; p>0.05). The Ktrans, Kep and and Ve values of the superficial myometrial layer did not show statistically significant difference between the two groups. DCE parameters of a representative patient were shown in Figure 3.Discussion & Conclusions
In this study, DCE MRI with high temporal and spatial resolution was successfully conducted for all the patients using GRASP VIBE sequence. The results indicated that the Kep values in the benign group were lower than that in the malignant group, while the Ve values were higher in the benign group than that in the malignant group; but the Ktrans value were no statistically significant difference between the 2 groups. The probability of missing small lesions is greatly reduced. In conclusion, GRASP VIBE sequence can be a useful tool for routine clinical precise to identifying benign and malignant endometrium lesions.Acknowledgements
Acknowledgements The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. This is prospective study and has been approved by Institutional Review Board (The certificate number:2020ZDSYLL220-P01).References
(1) Lin M , Zhang Q , Song Y , et al. Differentiation of endometrial adenocarcinoma from adenocarcinoma of cervix using kinetic parameters derived from DCE-MRI. European Journal of Radiology, 2020, 130:109190.
(2) Xu X , Li H , Wang S , et al. Multiplanar MRI-Based Predictive Model for Preoperative Assessment of Lymph Node Metastasis in Endometrial Cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 2019, 9.
(3) Heacock L , Gao Y , Heller S L , et al. Comparison of conventional DCE-MRI and a novel golden-angle radial multicoil compressed sensing method for the evaluation of breast lesion conspicuity. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2016.
Figures