3683
Application of the quantitative parameter of diffusion tensor imaging in differential diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma and endometrial polyp1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), as a kind of MR functional imaging, can reflect the direction and free diffusion rate of the diffusion motion of water molecules in voxel. This study intends to investigate the value of endometrial polyp (EP) and endometrial carcinoma (EC) based on quantitative parameters of DTI, in order to improve the accuracy of diagnosis of the two diseases before treatment.
INTRODUCTION
Endometrial carcinoma (EC) and endometrial polyp (EP) are common endometrial diseases. EP can be treated by hysteroscopy, while EC is mainly treated by surgery, and postoperative chemoradiotherapy is often required [1,2]. Therefore, it is necessary to use effective preoperative examination to distinguish between the two diseases. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), which is a kind of MR functional imaging, is based on DWI and investigates the microstructure of tissues based on the anisotropy principle of the free thermal motion of molecules [3]. Multiple quantitative parameters can be obtained, average diffusion coefficient (DC avg), fractional anisotropy (FA), isotropy (Iso), volume ratio anisotropy (VRA), exponential attenuation (Exat) and T2-weighted trace(T2-WT).METHODS
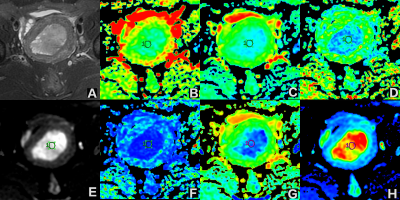
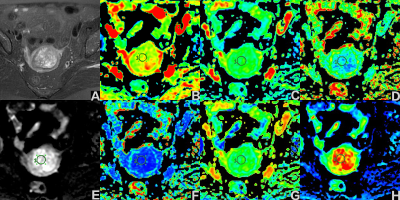
The data of 25 patients with EC and 20 patients with EP confirmed by surgery and pathology were retrospectively analyzed. All patients underwent 1.5T MR examination before surgery, and the scanning sequence included DWI and DTI. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of DWI and the parameters of DTI in the parenchyma were measured by two observers. The consistency of the measured results of the two observers and the difference of each parameter value between the two groups of patients were tested, the correlation between ADC and DC avg values of the two groups of patients was analyzed, and the differential efficacy of the parameters with statistical differences was evaluated.RESULTS
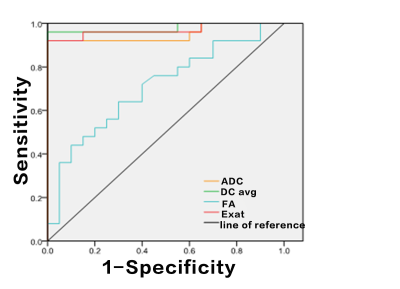
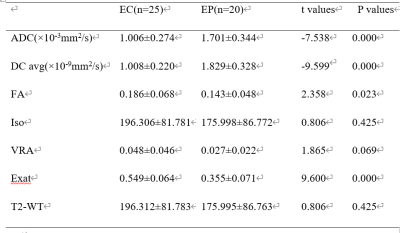
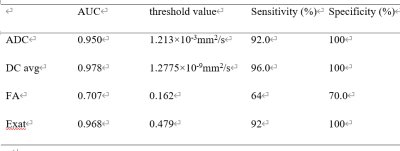
The two observers measured the consistency of the groups well (ICC>0.75). Values of ADC and DC avg in EC group were lower than those of EP group, FA and Exat values were higher than those of EP group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in Iso, VRA and T2-WT values between the two groups (P>0.05) (table 1, figure 1 and 2). The values of ADC and DC avg in EC and EP groups were correlated (r=0.749, 0.856, P<0.001). The AUC values of ADC, DC avg, FA and Exat were 0.950, 0.978, 0.707 and 0.968, respectively. The specific results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 3.DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS
Both DTI and DWI can reflect the dispersion of water molecules. DTI can represent the diffusion along multiple directions. Meanwhile, compared with DWI, DTI also has parameters such as FA and Exat can provide anisotropic diffusion information, thus making the diffusion path of water molecules more visible [4]. Therefore, DTI is more accurate in the diffusion of water-reflecting molecules, and can effectively differentiate endometrial cancer and endometrial polyp, among which the DC avg value was correlated with the ADC value of DWI sequence.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement.References
[1] Lee YC, Lheureux S, Oza AM. Treatment strategies for endometrial cancer: current practice and perspective. CurrOpinObstet Gynecol. 2017; 29:47‐58
[2] Zhang H, He X, Tian W, Song X, Zhang H. Hysteroscopic Resection of Endometrial Polyps and Assisted Reproductive Technology Pregnancy Outcomes Compared with No Treatment: A Systematic Review. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:618‐627
[3] UNG N, MATHUR M, CHUNG LK, et al. A Systematic Analysis of the Reliability of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Tractography for Facial Nerve Imaging in Patients with Vestibular Schwannoma [J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2016, 77(4):314-348.DOI:10.1016/j.clinimag.2016.10.016.
[4] GHOLIZADEH N, GREER PB, SIMPSON J, et al. Characterization of prostate cancer using diffusion tensor imaging: A new perspective [J]. Eur J Radiol,2019, 110:112-120. DOI:10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.11.026.
Figures