3667
Evaluation of bone marrow infiltration in the newly diagnostic Multiple Myeloma with Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-weighted MRI1Radiology, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Diagnosis Imaging, Siemens Healthineers China, Beijing, China, 3Scientific Marketing, Diagnosis Imaging, Siemens Healthineers China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging (IVIM-DWI) can simultaneously acquire diffusion parameters and perfusion parameters without intravenous administration, compared with conventional diffusion imaging. This study investigated the application of IVIM in the newly diagnostic multiple myeloma (NDMM) patients.
Introduction
More than 80% of the new diagnostic MM patients have osteolytic lesions[1]. The impact of bone marrow infiltration which causes morbidity and mortality remains a major problem in clinical treatment and affects patients’ life quality. Therefore, the early diagnosis of bone lesions of MM and appropriated therapeutic strategy is very important. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive method to evaluate bone marrow involvement. Compared with routine MRI, intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging (IVIM-DWI) can provide simultaneously diffusion parameters and perfusion parameters without intravenous administration, then these parameters can be quantitatively analyzed[2]. This study used IVIM-DWI in the newly diagnostic multiple myeloma (NDMM) patients to evaluate the difference and characteristics of the imaging microcirculation vertebral MM bone marrow and normal bone marrow, and the correlation between IVIM parameters and clinical parameters were explored. In addition, IVIM parameters in the diagnosis of MM patients were compared.Methods
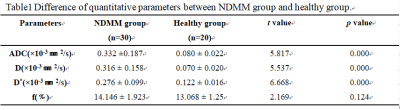
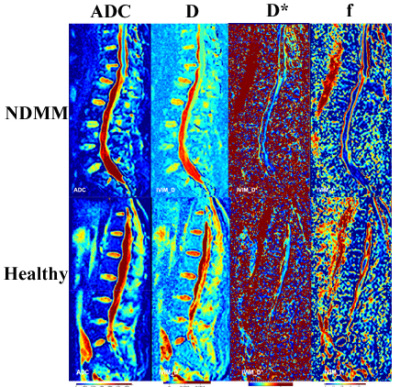
Thirty newly diagnostic multiple myeloma (NDMM) patients(average age 63.02 ± 10.04 years,16 males,14 females)previously histopathologically confirmed and twenty healthy volunteers (average age 61.42 ± 3.60 years, 8 males, 12females) were enrolled and underwent IVIM-DWI imaging. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), diffusion coefficient (D), pseudo diffusion (D*), and perfusion fraction (f) parameters from IVIM-DWI were acquired and compared between two groups. The Spearman correlation between IVIM-DWI parameters and clinical parameters were analyzed in NDMM group. Moreover, Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis of discrimination between normal and MM group was performed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of ADC, D and D*.Results
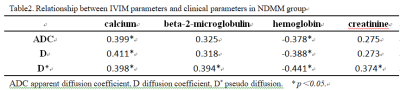
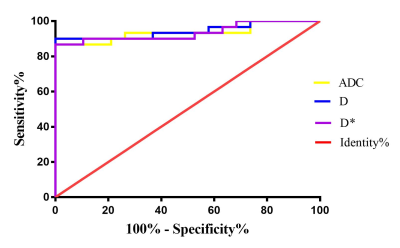
Table 1 showed that the NDMM group had significantly higher values for ADC, D and D* than those for healthy group (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in pf between NDMM group and healthy group (p ﹥0.05, Table 1). As was shown in Table 2 and Fig2, the serum beta-2-microglobulin were positive correlated to D* (r = 0.394, p < 0.05).The serum calcium were positive correlated to ADC(r = 0.399, p < 0.05), D (r = 0.411, p < 0.05) and D*(r = 0.398, p < 0.05), respectively. However, the hemoglobin value were negatively correlated to ADC (r = - 0.378, p < 0.05), D (r = - 0.388, p < 0.05), and D* (r = 0.441, p < 0.05), respectively. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of ADC, D and D* were 0.935, 0.944, 0.935 and 0.931, respectively. Among these, D showed the highest sensitivity was 90.0%, and its Specificity was 94.7% (Table 3 and Fig3).Discussion and Conclusion
Renal insufficiency was one of CRAB common clinical manifestation in MM patients[1], which cannot meet the indications of intravenous contrast medium. Compared with routine MRI, IVIM-DWI can provide simultaneously diffusion parameters and perfusion parameters without intravenous administration[2].This study used IVIM parameters to quantitatively diagnose MM vertebral bone marrow and normal bone marrow and compare the diagnostic performance of ADC, D and D*. For diagnosing MM patients from healthy volunteers, the D showed the highest sensitivity was 90.0%, and its Specificity was 94.7%,with the cutoff value of 141.8×10-3㎜2/s.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] S.V. Rajkumar, Multiple myeloma: 2018 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management, American Journal of Hematology 93(8) (2018) 1091-1110.
[2] Y. Zhao, Q. Zhang, W. Li, Y. Feng, Y. Guo, Z. Xiang, S. Li, Assessment of Correlation between Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging of Sacroiliitis with Ankylosing Spondylitis, BioMed Research International 2017 (2017).
Figures