3480
the value of preoperative MRI measurements of Meckel cavity volume in percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal nerve1Department of Radiology, the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Wuhan, China
Synopsis
This retrospective study aimed to investigate the feasibility of preoperative MRI measurements of Meckel cavity volume using 3D SPACE sequence and its values in guiding percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal nerve. Our results showed that there was no statistically significant difference between the volume of Meckel cavity using the axis, coronal and sagittal directions of MRI images and intraoperative balloon filling volume. 3D SPACE is helpful to guide the operation in clinical application.
Background and Purpose
Percutaneous balloon compression is a clinically effective and economical method for the treatment of intractable idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia [1,2], which is usually performed under the monitoring of the C-arm X-ray machine, and introduces a balloon filled with nonionic contrast agent into the Meckel's cavity to compress the trigeminal nerve semi-lunar node. However, the X-ray radiation dose of an operation is unpredictable, which is associated with the level of the operator. if the balloon filling volume can be accurately judged before the procedure, the surgeons will be able to complete this procedure quickly and more accurately under X-ray intervention, which is bound to decrease the X-ray radiation dose accepted by operators and patients under fluoroscopy. In this retrospective study, we investigated the feasibility of preoperative MRI measurements of Meckel cavity volume and its value in guiding percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal nerve.Methods and Materials
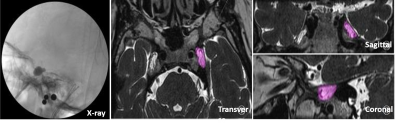
This study was approved by the ethics committee of our hospital. The preoperative MRI and surgical data of 31 patients with trigeminal nerve percutaneous balloon compression were retrospectively analyzed. These patients had an intraoperative lateral X-ray balloon that was pear-shaped. There were 17 males and 14 females, and the average age was 68.32±11.35 years (range, 48-92 years). All patients performed the MRI scanning on a 3T MRI scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) and a standard 20-channel head multi-channel coil. The Sampling Perfection with Application optimized Contrasts using different flip angle Evolution (SPACE) sequence was used for transverse axial scanning, and the coronal and sagittal positions were reconstructed by Multiplanar Reformation (MPR). The parameters of the 3D SPACE sequence were as follows: FOV 170 ×170 mm, layer thickness 0.5 mm, layer thickness 0.5 mm, TR 1400 ms, TE 155 ms, flip angle 120°, matrix 320×320, Averages 1.7, TA 9 min 23 sec. The outline of each layer of Meckel cavity was drawn step by step, and then the volume was calculated using the syngovia software. The volume data of Meckel cavities in three different directions were obtained (Figure 1). Paired sample t test was used for the statistical analysis. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results and Discussion
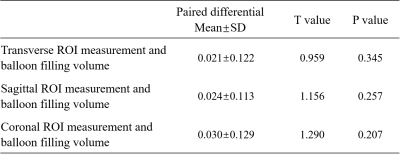
A total of 9 patients received surgery on the left side, and 22 patients on the right side. There was no statistically significant difference between the volume of Meckel cavity in the three directions of MRI images and intraoperative balloon filling volume (P=0.345,0.257, and 0.207), as shown in Table 1. The 3D thin-slice SPACE achieves submillimeter imaging, which can provide a more detailed anatomical image. In the present study, the azimuth of the SPACE sequence scanned is transverse, but clear coronal and sagittal images can be obtained through MPR 3D reconstruction. Through the comparative analysis of the measurement in three different directions, it was revealed that there is no significant difference in their volume in dealing with the Meckel cavity, which also verifies the feasibility of the volume measurement method from any direction. Our results also showed that the shape and size of the Meckel cavity had a good agreement between the plasticized section and the MRI images.Conclusions
It is feasible to measure the volume of Meckel cavity by preoperative MRI, and it has a guiding significance for the individualized selection of balloon filling volume in the percutaneous balloon compression of trigeminal nerve.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
Sivakanthan S , Gompel J J V , Alikhani P , et al. Response to Journal Club: Surgical Management of Trigeminal Neuralgia: Use and Cost-Effectiveness From an Analysis of the Medicare Claims Database[J]. Neurosurgery, 2014, 75(3):225-6.
Cheng, Jason S , Lim, et al. A Review of Percutaneous Treatments for Trigeminal Neuralgia[J]. Neurosurgery, 2014, 1:25-33.
Zhang Weiguo, Chen Jinhua, Zhang Shaoxiang, MRI and thin sectional anatomy of etal.Meckel cavity [J]. Journal of the third military Medical University, 2006 , 28 (1): 72-74.