3215
The diagnostic value of MR dynamic enhancement quantitative parameter for usual interstitial pneumonia and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia1Radiology, Doctor, Zhan Jiang, China, 2doctor, Gui Lin, China, 3MR Research, Beijing, China
Synopsis
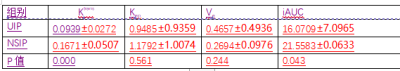
Different treatments were not given to patients [1]HRCT on diagnosis of atypical interstitial pneumonia appears to be powerless, so further examination of pathological biopsy is usually required. However, pathological biopsy often causes a series of complications and reduces the survival rate of patients[2]. This study aims to distinguish between UIP and NSIP using MRI dynamic enhancement quantitative parameters. The results showed that the blood flow in the lungs of UIP patients is significantly reduced. The quantitative parameters of MRI dynamic enhancement had potential in distinguishing UIP from NSIP.
Introduction
Pulmonary manifestations are different in patients with usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), and the main difference of manifestation is biological behavior. The lungs of UIP patients are mainly characterized by progressive fibrosis, while NSIP patients are mainly characterized by inflammation. Therefore, different MRI dynamic enhancement quantitative parameters might discriminate two types of patients, and the pseudo-color images might help differentiate one from the other.Methods
27 Patients with interstitial pneumonia who need to undergo frozen lung biopsy during treatment underwent dynamic enhanced MRI scan before the biopsy from March 2019 to January 2020.All patients were divided into UIP (N=10) and NSIP (N=17) groups based on imaging manifestations, combined pathology, and clinical diagnosis. Before the MRI examination, the patient was trained to steadily inhale, exhale, and hold breath to avoid breathing artifacts. Depending on breath frequency of the patient, the trigger window for scanning wass adjusted.After the routine scan,scan with reference to The DCE-MRI sequence was carried out on 3.5T MR scanner with following parameters: TE=1.66, TR=5.08, matrix=72×192, FOV=380×380mm, layer thickness 3.6mm, the first two scans with a flip angle = 5°and 15°,and the third one with a flip angle = 15. A total scan time was 5 minutes and 26 seconds. At the third scan, the contrast agent Gd-DOTA was injected with the total amount of 0.2mmol/kg at the injection rate was 2.0ml/s. After the injection, 20ml of normal saline was injected at the same rate. If the patient was diagnosed pathologically, the corresponding area was drawn on the slice of the largest lesion area on the dynamic enhancement map; if the patient was clinically confirmed patient, the largest lung lesion on the slice was drawn. When ROI was drawn, it should be avoided getting close to the pleural area.Results
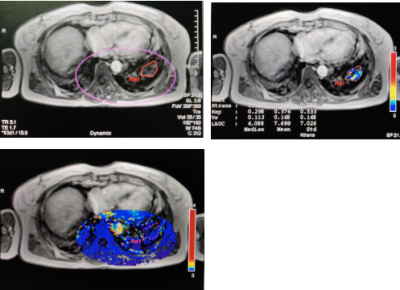
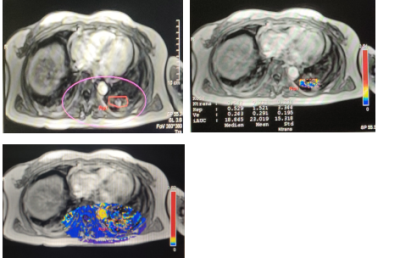
Statistically lower Ktrans, Kep,and iAUC values were found in patients with UIP than those with NSIP (P<0.05). The region of interest on the pseudo-colored dynamic enhancement images of UIP is mainly colored in blue while the lesion of the NSIP is mainly colored in yellow and blue.Discussion
This study verified the different biological expression between UIP- and NSIP- type interstitial pneumonia was indirectly manifested by the quantitative parameters of magnetic resonance dynamic enhancement images. In the pathological aspect, the lungs of UIP patients are dominated by progressive fibrosis, damaged blood vessels, which cause structural disorder of the lungs, and ultimately leading to the formation of irreversible honeycomb lungs. The lungs of NSIP patients are characterized by inflammation-related expressions, which normally lead to formation of new capillaries[3],so that the blood flow may be higher than UIP. This might explain Ktrans,Kep and iAUC were different as shown in dynamic pseudo-color pictures. The pathological type of interstitial pneumonia in the lungs can be detected based on magnetic resonance examination, which may assist to make a plan for anti-inflammatory or anti-fibrotic treatments more accurately.Conclusion
MRI dynamic enhancement examination has potentially diagnostic value for discrimination between UIP and NSIP and thus it may avoid complications caused by pathological examination.Acknowledgements
We thank GE MR for its intellectual support.References
[1]Fragoulis GE, Nikiphorou E, Larsen J, et al. Methotrexate-Associated Pneumonitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis-Interstitial Lung Disease: Current Concepts for the Diagnosis and Treatment. Front Med(Lausanne), 2019, 6:238.
[2]Hutchinson JP, Fogarty AW, McKeever TM, et al. In-Hospital Mortality after Surgical Lung Biopsy for Interstitial Lung Disease in the United States. 2000 to 2011. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016, 193(10):1161-1167.
[3]Tzouvelekis A, Anevlavis S, Bouros D. Angiogenesis in Interstitial Lung Diseases: a pathogenetic hallmark or a bystander?. Respir Res, 2006, 7(1):82-94.
Figures