3189
Normal fetal development of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine: a post-mortem study based on magnetic resonance imaging1School of Medicine, Shandong First Medical University, School of Medicine, Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China, 2Department of Radiology, Shandong Provincial Hospital affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Diagnosis Imaging, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Before evaluating spinal pathology, it is essential to have knowledge of the normal spinal development at different gestational ages. Postmortem magnetic resonance imaging was performed on 55 fetuses (gestational ages, 17–42 weeks) by using three-dimensional T2-weighted sequences. The volumes of interest were manually outlined for the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and L1–L5 centrum ossification centers (COCs), and the COC volumes (COCVs) were calculated. The cervical, thoracic, and lumbar COCVs showed a positive relationship with gestational age.The cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and L1–L5 COCVs show good correlation with gestational age in the second and third trimesters.
Introduction:
Accurate measurement of spinal development is important for the prenatal diagnosis of spinal abnormalities. Before evaluating spinal pathology, it is essential to have knowledge of the normal spinal development at different gestational ages. This study aimed to measure the volumes of the normal fetal cervical, thoracic, and lumbar ossification centers and to study their volumetric changes with gestational age.Methods:
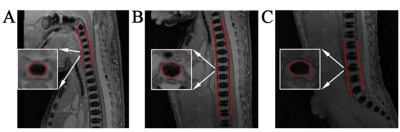
Postmortem magnetic resonance imaging was performed on 55 fetuses (gestational ages, 17–42 weeks) by using three-dimensional T2-weighted sequences. The volumes of interest were manually outlined for the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and L1–L5 centrum ossification centers (COCs), and the COC volumes (COCVs) were calculated. The correlation between COCV and gestational age was investigated.Results:
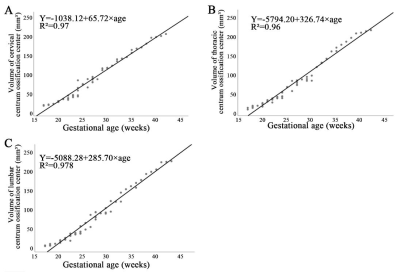
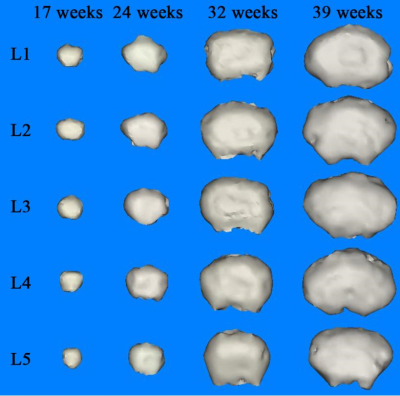
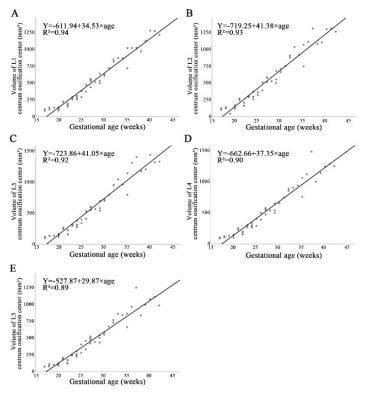
The cervical, thoracic, and lumbar COCVs showed a positive relationship with gestational age (P < .01). No gender differences were found in the volumetric development of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar COCs. The average volumetric growth rate per COC was larger in the lumbar spine than in the cervical and thoracic spine. The L1–L5 COCVs also showed a linear positive relationship with gestational age.Conclusion:
The cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and L1–L5 COCVs show good correlation with gestational age in the second and third trimesters. The L1 COCV is best suited as a marker for fetal cervical, thoracic, and lumbar development.Acknowledgements
no acknowledgementsReferences
[1]Wallny T,Schild RL,Fimmers R.Three-dimensional sonographic evaluation of the fetal lumbar spinal canal.J Anat 2002;200:439-443 PMID: 12090390.
[2]Öcal DF,Nas T.The place of four-dimensional ultrasound in evaluating fetal anomalies.Ir J Med Sci 2015;184:607-612.DOI:10.1007/s11845-014-1184-2 PMID:25142340
[3]Glenn OA.Magnetic resonance imaging of the fetal brain and spine: an increasingly important tool in prenatal diagnosis, part 1.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27:1604-1611.
[4]Prayer D,Brugger PC.Fetal MRI: techniques and protocols.Pediatr Radiol 2004;34:685-693.DOI:10.1007/s00247-004-1246-0
[5]Jian N,Tian MM,Xiao LX,et al.Normal development of sacrococcygeal centrum ossification centers in the fetal spine: a postmortem magnetic resonance imaging study.Neuroradiology 2018;60:821-833.DOI:10.1007/s00234-018-2050-0
[6]Russ PD,Pretorius DH,Manco-Johnson ML.The fetal spine.Neuroradiology 1986;28:398-407.
[7] Widjaja E,Whitby EH,Paley MN.Normal fetal lumbar spine on postmortem MR imaging.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27:553-559.
[8]De Biasio P,Ginocchio G,Aicardi G,et al.Ossification timing of sacral vertebrae by ultrasound in the mid-second trimester of pregnancy.Prenat Diagn 2003;23:1056-1059.DOI:10.1002/pd.722
[9]Schild RL,Wallny T,Fimmers R.The size of the fetal thoracolumbar spine: a three-dimensional ultrasound study.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16:468-472.DOI:10.1046/j.1469-0705.2000.00256.x
[10]Jalanko T,Rintala R,Puisto V.Hemivertebra resection for congenital scoliosis in young children: comparison of clinical, radiographic, and health-related quality of life outcomes between the anteroposterior and posterolateral approaches.Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011;36:41-49.DOI:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181ccafd4
[11]Chrzan R,Podsiadlo L,Herman-Sucharska I,et al.Persistent notochordal canal imitating compression fracture--plain film, CT and MR appearance.Med Sci Monit 2010;16:CS76-9
[12]Patinharayil G,Han CW,Marthya A,et al.Butterfly vertebra: an uncommon congenital spinal anomaly.Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33:E926-8.DOI:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31818ad3e1
[13]Growth of the human vertebral column. An osteological study.Acta Anat (Basel) 1971;79:570-580
[14]Bagnall KM,Harris PF.A radiographic study of the human fetal spine. 1. The development of the secondary cervical curvature.J Anat 1977;123:777-782
[15]Bagnall KM,Harris PF.A radiographic study of the longitudinal growth of primary ossification centers in limb long bones of the human fetus.Anat Rec 1982;203:293-299.DOI:10.1002/ar.1092030211
[16]Sepulveda W,Ximenes R,Wong AE,et al.Fetal magnetic resonance imaging and three-dimensional ultrasound in clinical practice: applications in prenatal diagnosis.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2012;26:593-624.DOI:10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2012.06.001
[17] Vignolo M,Ginocchio G,Parodi A,et al.Fetal spine ossification: the gender and individual differences illustrated by ultrasonography.Ultrasound Med Biol 2005;31:733-738.DOI:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2005.02.013
[18]Szpinda M,Baumgart M,Szpinda A,et al.Morphometric study of the T6 vertebra and its three ossification centers in the human fetus.Surg Radiol Anat 2013;35:901-916.DOI:10.1007/s00276-013-1107-3
[19]Baumgart M,Szpinda M.New anatomical data on the growing C4 vertebra and its three ossification centers in human fetuses.Surg Radiol Anat 2013;35:191-203.DOI:10.1007/s00276-012-1022-z
[20]MEYER DB.Roentgenographic investigation of the human skeleton during early fetal life.Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1956;76:455-468
Figures