3154
KIBRA rs17070145 interacts with gender on brain gray matter volume and functional connectivity density in healthy young adults1Department of Radiology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2The Affiliated Brain Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4Institute for Brain Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
Synopsis
KIBRA rs17070145 and gender have been found to have associations with episodic memory. However, the underlying mechanisms and their combined effects on the brain gray matter volume (GMV) and functional connectivity density (FCD) remain unknown. This study found that KIBRA gene interacted with gender on the GMV and long-range FCD (lrFCD) using voxel-based morphometry (VBM) analysis. These findings underscored the importance of KIBRA and gender interactions as regards to brain structural and functional alterations, which is crucial for the neurobiological understanding of episodic memory.
Purpose
Kidney and brain expressed protein (KIBRA) rs17070145 has been found to have key roles in episodic memory and cognitive dysfunction. Several studies have reported gender differences in episodic memory performance. KIBRA and gender may jointly influence episodic memory; but, their interactions on brain gray matter volume (GMV) and functional connectivity density (FCD) remain unknown. The present study aimed to investigate interactions between KIBRA rs17070145 polymorphism and gender on brain GMV and FCD using a voxel-based analysis in 245 healthy young adults.Materials and Methods
The preprocessing of resting-state fMRI data and voxel-based morphology of structural MRI data were performed using SPM12. The FCD of each voxel was computed using a script written in Linux platform. Functional connections were calculated using Pearson’s linear correlation, and a functional connection existed if the correlation coefficient between any two voxels > 0.6. The GMV, short- and long-range FCD (lrFCD) of each voxel were calculated and compared using a two-way analysis of covariance with age and education as covariates.Results
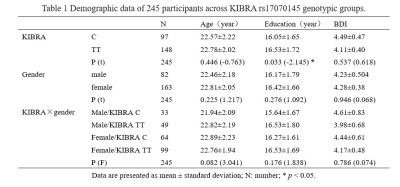
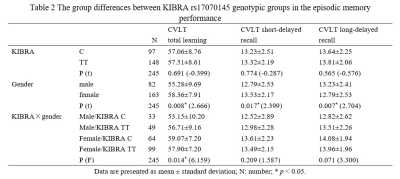
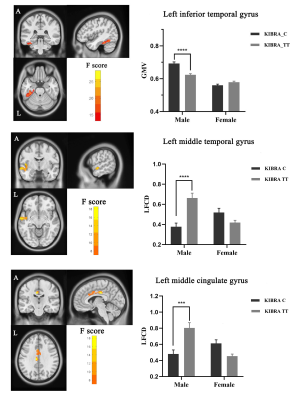
Among the four subgroups, male KIBRA C-allele carriers exhibited worse episodic memory performance. Meanwhile, this subgroup showed greater GMV in the inferior temporal gyrus, while decreased lrFCD in the left middle temporal gyrus and left middle cingulate gyrus than male TT homozygote. Seed-voxel correlation analyses also showed abnormal functional connectivity between these regions.Conclusion
Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) analysis revealed that KIBRA gene interacted with gender on the GMV and long-range FCD (lrFCD). The present study suggests that KIBRA gene influences the GMV in the left inferior temporal gyrus and lrFCD in the left middle temporal gyrus and left middle cingulate gyrus in a gender dependent manner. These findings underscored the importance of KIBRA and gender interactions as regards to brain structural and functional alterations, which is crucial for the neurobiological understanding of episodic memory.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(81720108022, 91649116, 81571040); the social development project of science andtechnology project in Jiangsu Province (BE2016605, BE2017707); key medical talentsof the Jiangsu province, the "13th Five-Year" health promotion project of the Jiangsuprovince (B.Z.2016-2020); Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Discipline (Laboratory)(ZDXKA2016020); the project of the sixth peak of talented people (WSN-138, BZ).Thefunders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision topublish, or preparation of the manuscript.References
1. Laukka EJ, Köhncke Y, Papenberg G, Fratiglioni L, Bäckman L. Combined genetic influences on episodic memory decline in older adults without dementia. Neuropsychology. 2020 Sep;34(6):654-666. doi: 10.1037/neu0000637. Epub 2020 Apr 30. PMID: 32352830.
2. Mazzeo S, Bessi V, Padiglioni S, Bagnoli S, Bracco L, Sorbi S, Nacmias B. KIBRA T allele influences memory performance and progression of cognitive decline: a 7-year follow-up study in subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment. Neurol Sci. 2019 Aug;40(8):1559-1566. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-03866-8. Epub 2019 Apr 5. PMID: 30953258.
Figures