3065
Neuromelanin-Related Proton Relaxation of Water: Influence from Iron and Copper1Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany, 2Department of Chemistry, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy, 3Institute of Biomedical Technologies, National Research Council of Italy, Segrate, Milan, Italy
Synopsis
Neuromelanin (NM) MRI has received increasing interest in applications to diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. A reduction of T1 associated with paramagnetic melanin-iron complexes is assumed to be the primary contrast mechanism. NM is able to chelate large quantities of iron but also, to a lesser extent, other transition metals, in particular copper. Here, we investigated the effect of different copper/iron concentrations bound to NM on water T1 and T2. Our results corroborate previous studies suggesting a concentration-dependent decrease of T1 for iron-loaded melanin. Additionally, we found a synergetic effect if both metals are simultaneously present leading to a pronounced T1-shortening.
Introduction
The decrease of neuromelanin (NM) concentrations in substantia nigra (SN) and locus coeruleus (LC) showed by MRI may provide an important biomarker in the evaluation of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease (PD) [1,2]. However, demonstration of a bijective correlation between signal intensities measured by “NM-MRI” (T1-weighted TSE) and local variations in NM concentrations is missing. Furthermore, potential reduction in T2∗ compared to almost unchanged T2 times associated with NM is of ongoing interest [3,4]. NM has a strong affinity for transition metals including iron and copper. Iron is the most abundant metal in both NM of SN and LC. However, the NM of SN has higher content of iron than NM of LC. Instead the NM of LC has higher content of copper than NM of SN [5,6].The primary contrast mechanism in NM-MRI appears to be a T1 reduction associated with melanin-iron complexes [7], whereas an influence of copper is currently not known. Therefore, we investigated the specific influence of different iron (Fe3+) and copper (Cu2+) loading in synthetic neuromelanin complexes at a clinical field strength of 3T. Both agar-based and polyacrylamide-based samples of two types of NM (pheomelanin and eumelanin) were examined to assess water relaxation in a group of synthetically produced models of NM .
Methods
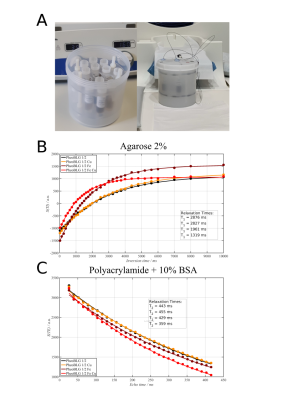
NM preparation: Melanin was synthesized by autoxidation of dopamine in presence of L-cysteine, iron and copper ions [8]. In addition, a certain amount of β-lactoglobulin (βLG) was added to mimic the protein moiety of NM pigment [8]. Molar ratios of iron and copper in relation to dopamine were 1/20 and 1/60, respectively. In case of the higher ions concentrations, a ratio of 1/5 to dopamine was utilized for both types (results not shown).Phantom preparation: Appropriate quantities (0.5 mg/ml) of the melanin preparations were suspended in the respective base gel (agarose or polyacrylamide with 10 % (w/w) of BSA). The different preparations (3 ml each) were placed in 7-ml plastic tubes. To avoid susceptibility effects from air boundaries, the melanin preparations were sandwiched in the tube between plugs of polyacrylamide. Finally, the tubes were placed in a 3d-printed sample holder inside a plastic cylinder filled with 1.5% low-melting agarose in PBS (phosphate buffered saline pH 7.4) with 0.1% Magnevist (Fig. 1). Before the MR exams, the phantom was allowed to reach room temperature.
MRI: Image data were acquired on a MAGNETOM Prismafit (Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) using a 32-channel head coil. Inversion-prepared-TSE with varying inversion times (TI = 25 … 10 000 ms, N = 33, TR = 12 s), and multi-echo (NEX = 32) spin-echo (ME-SE) were used for measuring T1 and T2, respectively (slice thickness 1 mm, in-plane nominal resolution: 0.6 × 0.6 mm2).
Results and Discussion
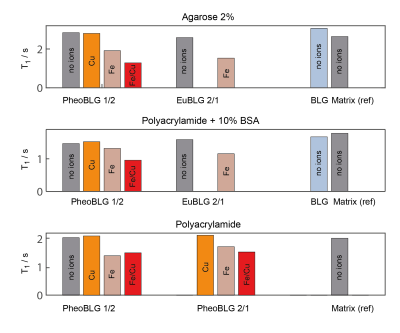
All relaxation data could be well fitted to mono-exponential recovery or decay curves within the experimental accuracy (Fig. 1).Spin-lattice relaxation: Despite potential volume restriction [4], metal-free NM had only a subtle effect on water relaxation. We observed (Fig. 2) that NM containing Fe3+ produces significant T1 shortening, as already observed earlier [4,7]. In contrast to previous assumption [4, 7], however, our results indicate distinct differences in water relaxation induced by NM-iron and NM-copper complexes if only a single ion species was present: Instead of similar relaxivities, we found an almost negligible effect due to the presence of Cu2+-containing NM as compared to a substantial T1 reduction induced by the presence of Fe3+-containing NM. Note that we can rule out that these effects are due to the presence of significant quantities of unbound Fe3+ or Cu2+ in the solvent under our experimental conditions [9].
Surprisingly, the simultaneous presence of copper and iron produced an enhanced shortening of the spin-lattice relaxation time (Fig. 2). This effect was independent of the underlying background matrix (agarose or polyacrylamide). Since the combined presence of iron and copper is a more realistic scenario in biological tissues, especially for NM of LC with an iron-copper ratio of approximately 3/1 [6], more attention should be given to this effect in future investigations and potential attempts to quantify NM contents.
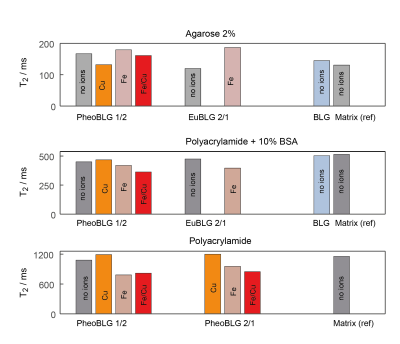
Spin-spin relaxation: The presence of metal-free NM or copper-containing NM had only little effect on the observed T2 relaxation time (Fig. 3). Minor changes in the spin-spin relaxation times were only obtained under conditions when NM containing either only iron or simultaneously iron and copper was present. However, marked effects were only for unrealistically high (with regards to a biological environment) concentration of added metal ions. Remarkably, the addition of metal ions resulted in comparable T2 effects independently of the type of ion or their concentrations.
Conclusion
With a growing interest of utilization NM as a biomarker in neurodegenerative diseases, there is a fundamental need for understanding the biophysical origins of contrast chances in brain tissue. Our results indicate different effects induced by the presence of the two main types of metal ions bound to NM in brain tissue. In particular, the effects on water proton spin-lattice relaxation may not show a simple linear behavior on the metal (or NM) content. More research is, hence, needed to understand the distinct effects from the presence of single or mixed ion species in different brain regions.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
(1) Sulzer D., Cassidy C., Horga G., Kang U.J., Fahn S., Casella L., Pezzoli G., Langley J., Hu XP, Zucca F.A., Isaias IU and Zecca L. Neuromelanin detection by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and its promise as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2018 Apr 10;4:11.
(2) Möller, H.E., Bossoni, L., Connor, J.R., Crichton, R.R., Does, M.D., Ward, R.J., Zecca, L., Zucca, F.A., and Ronen, I. (2019). Iron, myelin, and the brain: Neuroimaging meets neurobiology. Trends Neurosci 42, 384–401.
(3) Brammerloh, M., Morawski, M., Weigelt, I., Reinert, T., Lange, C., Pelicon, P., Vavpetič, P., Jankuhn, J., Jäger, C., Alkemade, A., Balesar, R., Pine, K., Gavriilidis, F., Trampel, R., Reimer, E., Arendt, T., Weiskopf, N., and Kirilina,E. (2020). Toward an early diagnostic marker of Parkinson’s: measuring iron in dopaminergic neurons with MR relaxometry. bioRxiv; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.01.170563
(4) Priovoulos, N., van Boxel, S. C. J., Jacobs, H. I. L., Poser, B. A., Uludag, K., Verhey, F. R. J., and Ivanov, D. (2020). Brain Struct Funct 225, 2757–2774.
(5) Zucca, F. A., Bellei, C., Giannelli, S., Terreni, M. R., Gallorini, M., Rizzio, E., Pezzoli, G., Albertini, A., and Zecca, L. (2006). J Neural Transm 113, 757–67.
(6) Zecca, L., Stroppolo, A., Gatti, A., Tampellini, D., Toscani, M., Gallorini, M., Giaveri, G., Arosio, P., Santambrogio, P., Fariello, R. G., Karatekin, E., Kleinman, M. H., Turro, N., Hornykiewicz, O., and Zucca,F. A. (2004). PNAS 101, 9843–9848.
(7) Trujillo P., Summers P.E., Ferrari E., Zucca F.A., Sturini M., Mainardi L.T., Cerutti S., Smith A.K., Smith S.A., Zecca L., Costa A. MRM 2017;78(5):1790-1800.
(8) Ferrari E. ,Capucciati A., Prada I., Zucca FA., D’Arrigo G., Pontiroli D., Bridelli MG., Sturini M., Bubacco L., Monzani E., Verderio C., Zecca .L, and Casella L. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8(3), 501-512
(9) Zucca, F. A., Basso, E., Cupaioli, F. A., Ferrari, E., Sulzer, D., Casella, L. and Zecca, L. (2014). Neuromelanin of the Human Substantia Nigra: An Update. Neurotoxicity Research 25, 13–23.
Figures