Rushi Chen1, Yan Bai1, Qin Feng1, Menghuan Zhang1, Xianchang Zhang2, and Meiyun Wang1
1Henan provincial people's hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Conventional magnetic resonance imaging has limitations in differentiating Parkinson’s disease (PD) from essential tremors (ET). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) can non-invasively detect neurochemical alterations in biological tissues. In this study, we used MRS to obtain N-acetylaspartate (NAA)/creatine (Cr) and choline (Cho)/Cr ratios in the substantia nigra (SN) of patients with tremor-dominant PD and ET. The NAA/Cr ratio in the contralateral SN was significantly higher in patients with tremor-dominant PD than those with ET, whereas the Cho/Cr ratios showed no significant differences between groups. The findings suggest that MRS in the SN may be helpful in differentiating tremor-dominant PD from ET.
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD)
is a common movement disorder characterized by dopamine neuronal loss and neuroinflammation
in the substantia nigra (SN) on histopathology. However, tremor-dominant PD is
frequently misdiagnosed as essential tremors (ET). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) can non-invasively detect
neurochemical alterations such as N-acetylaspartate (NAA), creatine (Cr) and choline
(Cho) in biological
tissues. The purpose of this study was to assess NAA/Cr and
Cho/Cr ratios derived from MRS to differentiate tremor-dominant PD from ET.Methods
A total of 12 patients (mean age: 62 years; 5 males
and 7 females) with tremor-dominant PD and 12 age- and sex-matched
patients with ET were enrolled in this study. High-resolution 3D T2-weighed
image and signal voxel proton MRS data were collected on MAGNETOM Prisma
3T MR Scanner (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with a 64-channel
head-neck coil. A T2-SPACE sequence (field of view = 256 x 256 mm2; slice
thickness = 1 mm; repetition time = 3200 ms; echo time = 407 ms) was performed
on all patients. The 3D T2-weighted images were rebuilt in all three dimensions
for SN. Single-voxel MRS (repetition time = 2000 ms; echo time = 30 ms) was performed
on the SN of patients. The 1×1×1 cm3 voxel was placed on the left and right SN, respectively.
The Mann-Whitney U test was used to
evaluate the NAA/Cr and Cho/Cr ratios in the ipsilateral and contralateral SN between
the two groups. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results
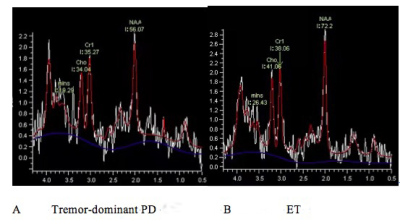
MRS
results from two representative subjects were shown in figure 1. The NAA/Cr ratio of the contralateral SN was significantly decreased
in patients with tremor-dominant PD
than in patients with ET (2.01±0.55 vs 2.45±0.89, P < 0.01). However, the NAA/Cr ratio of the ipsilateral
SN, as well as Cho/Cr ratio of the
bilateral SN had no significant differences
between the two groups (all P > 0.05).Discussion
Dopamine neuronal loss
and neuroinflammation were the pathological characteristics in SN of PD. The NAA/Cr
ratio in the contralateral SN was
significantly higher in patients with tremor-dominant PD than in those with ET,
whereas the NAA/Cr ratio of ipsilateral
SN could not separate tremor-dominant PD from ET. This finding indicated the neuronal
loss in the contralateral SN
was more obvious compared with the ipsilateral
SN in PD. In addition, the Cho/Cr ratio had no significant differences in the bilateral
SN between tremor-dominant PD and ET. Cho/Cr was decreased with neuronal loss while increased with inflammatory
cellular infiltration. Thus, the converse
influence on Cho/Cr ratio of the SN
may lead to no differences between tremor-dominant PD and ET.Conclusions
MRS
in the SN may be a useful tool in differentiating tremor-dominant PD from ET.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
Mazuel L, Chassain C, Jean
B, Pereira B, Cladière A, Speziale C, Durif F. Proton Mr spectroscopy for
Diagnosis and evaluation of Treatment efficacy in Parkinson
Disease. Radiology. 2016;278(2):505-13.