3003
Radiomics Based on MR Imaging of Rectal Mucinous Adenocarcinoma: Assess Treatment Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy1Changhai Hospital, Shanghai, China, 2Huiying Medical Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China
Synopsis
The goal of this study was to investigate the value of high resolution T2-weighted–based radiomics in prediction of treatment response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) in patients with rectal mucinous adenocarcinoma (RMAC). The result demonstrated that the MRI based radiomics machine learning model could assess tumoral treatment response to nCRT in patients with RMAC.
Objective
Rectal mucinous adenocarcinoma (RMAC) is a subtype of rectal cancer comprising about 6.2–12.3% of cases. Compared with non-mucinous adenocarcinoma, RMAC is much less sensitive to nCRT. Recent studies have shown that magnetic resonance based radiomics analysis has important values in predicting the difference in curative effect in advance can provide a basis for the selection of neoadjuvant options. The purpose of this study was to investigate the treatment response to nCRT by using high resolution T2-weighted based radiomics in patients with RMAC.Methods
Sixty-four patients with RMAC underwent rectal MR imaging before nCRT in our hospital on a 3T scanner between March 2016 and July 2020. Surgical pathologic tumor regression grade (TRG) was used as the reference standard to evaluate the outcome of the treatment. TRG 0 and TRG 1 were classified as “good response” group, TRG 2 and TRG 3 was “poor response” group. One radiologist segmented the lesions on high resolution T2-weighted MRI. Radiomics features were extracted on a radiomics analysis platform (Radcloud, Huiying Medical Technology, Beijing, China), then the features were selected by least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) method to best predict the treatment performance. The Logistic Regression (LR) classifier was trained to predict which group the patient belong to. As leave-one-out cross validation (LOOCV) was used in the research, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was obtained.Results
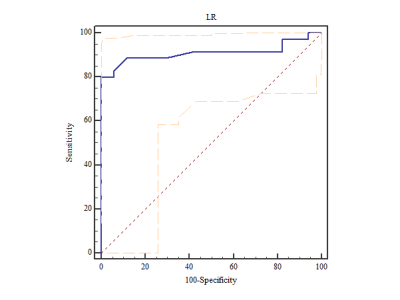
Of the 64 patients, 17 (26.6%) had good response. 1409 features were extracted, and 8 optimal features related to the TRG prediction were selected with LASSO algorithm. For the LR classifier, the area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.909 (95%CI: 0.797,0.971) (Figure 1).Conclusion
Our study demonstrated that the high resolution T2-weighted MRI-based radiomics before nCRT showed good classification performance related to TRG in patients with RMAC. The radiomics as imaging biomarkers have the potential to prediction of tumoral treatment response to nCRT.Acknowledgements
NAReferences
[1] Robert JG, Paul EK, Hedvig H, et al. Radiomics: image are more than pictures, they are data[J]. Radiology. 2016; 278(2):563-577.
[2] Wu J, Tha KK, Xing L, et al. Radiomics and radiogenomics for precision radiotherapy[J]. J Radiat Res. 2018; 59(suppl_1): i25-i31.
[3] Horvat N, Veeraraghavan H, Khan M, et al. MR Imaging of Rectal Cancer: Radiomics Analysis to Assess Treatment Response after Neoadjuvant Therapy[J]. Radiology. 2018; 287(3):833-843.
[4] Cao W, Wu L, Zhao Y, Zhou J, Li W, Wang X, Xu J, Zhou Z, Liang C. A New MRI-Defined Biomarker for Rectal Mucinous Adenocarcinoma: Mucin Pool Patterns in Determining the Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Therapy[J]. Front Oncol. 2020; 10:1425.