2999
Deep Learning Reconstruction for DWI with b Values < 5000s/mm2: Improvement of Image Quality and Diagnostic Performance for Prostatic Cancer1Radiology, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan, 2Joint Research Laboratory of Advanced Medical Imaging, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan, 3Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan, 4Radiology, Fujita Health University Hospital, Toyoake, Japan
Synopsis
There have been no reports of major studies to the utility of DLR for DWI with high b values for improving image quality and detection performance for patients with prostatic cancers. We hypothesized that DLR could improve image quality and diagnostic performance of DWI with high values, and that an appropriate b value might be determined for this setting. The purpose of this study was thus to determine the utility of the DLR method for DWI and the appropriate b value for detecting prostatic cancer using a 3T MR system in routine clinical practice.
Introduction
Multiple studies have tested the diagnostic accuracy of high b value diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) for the detection of prostatic cancer, although there has been little agreement on the optimal b-value for DWI with a high b value (1-3). Typically, the highest b value used is between 1000 and 2000 s/mm2 and the most recent recommendation is 1400-2000 s/mm2 (4, 5). In addition, a few investigators have tested high b value DWI at more than 2000 s/mm2 and suggested a high b value of more than 2000 s/mm2 has the potential to improve prostatic cancer detection capability (6, 7). On the other hands, when the b value is increased, image quality of DWI usually deteriorates because of a reduction in signal intensities of normal anatomical structures and an increase in background image noise on DWI with a high b value. For this reason, deep learning reconstruction (DLR) has been introduced by a few vendors to improve imaging quality of not only central nervous system, but also body MR imaging (8-10). Moreover, Canon Medical Systems Corporation has introduced a newly developed DLR method known as Advanced intelligent Clear-IQ Engine (AiCE) for improving image quality and diagnostic performance for MR imaging with different imaging sequences. However, there have been no reports of major studies to the utility of DLR for DWI with high b values for improving image quality and detection performance for patients with prostatic cancers. We hypothesized that DLR could improve image quality and diagnostic performance of DWI with high values, and that an appropriate b value might be determined for this setting. The purpose of this study was thus to determine the utility of the DLR method for DWI and the appropriate b value for detecting prostatic cancer using a 3T MR system in routine clinical practice.Materials and Methods
Sixty patients (mean age: 67 years; range=49-79 years) with a mean serum prostate specific antigen (PSA) of 10.2±6.7 ng/mL (range=4.9-87.8 ng/mL) prospectively underwent DWI with b values of 0, 1000 (DWI1000), 3000 (DWI3000) or 5000 (DWI5000) s/mm2 as well as pathological examinations. All DWI data were reconstructed with and without DLR, and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) were then determined by measuring regions of interest (ROIs). Apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) in malignant and benign areas were also measured, while the PI-RADS v2.1 category of each zone at the apex, midportion and basal levels were determined by readers’ consensus. SNR and CNR of all DWIs with and without DLR were compared by paired t-test. ROC analyses were then compared for all DWIs with and without DLR for quantitative differentiation of malignant from benign areas. A p value less than 0.05 was considered as significant in this study.Results
Representative case is shown in Figure 1. For each b value, SNR and CNR of DWI with DLR were significantly higher than those without DLR (p<0.0001). Results of ROC analysis are shown in Figure 2. Whether applying DLR method or not, DWI3000 (with DLR: AUC=0.92, without DLR: AUC=0.91) and DWI5000 (with DLR: AUC=0.90, without DLR: AUC=0.90) were significantly larger than DWI1000 (with DLR: AUC=0.87, p<0.05; without DLR: AUC=0.86, p<0.05). When applied DLR method, AUC of DWI1000 and DWI3000 were significantly improved (p<0.05). Results of diagnostic performance among all methods are shown in Figure 3. Sensitivity and accuracy of DWI3000 with DLR were significantly higher than those of others (p<0.05).Conclusion
DLR is useful for improving image quality and diagnostic performance of DWI without any adverse effect on ADC assessment using a 3T MR system for patients with prostatic cancer.Acknowledgements
This study was financially and technically supported by Canon Medical Systems Corporation.References
- Thörmer G, Otto J, Reiss-Zimmermann M, et al. Diagnostic value of ADC in patients with prostate cancer: influence of the choice of b values. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22(8): 1820-1828.
- Tamada T, Kanomata N, Sone T, et al. High b value (2,000 s/mm2) diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in prostate cancer at 3 Tesla: comparison with 1,000 s/mm2 for tumor conspicuity and discrimination of aggressiveness. PLoS One. 2014; 9(5): e96619.
- de Perrot T, Scheffler M, Boto J, et al. Diffusion in prostate cancer detection on a 3T scanner: How many b-values are needed? J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016; 44(3): 601-609.
- Barentsz JO, Richenberg J, Clements R, et al.; European Society of Urogenital Radiology. ESUR prostate MR guidelines 2012. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22(4): 746-757.
- Turkbey B, Rosenkrantz AB, Haider MA, et al. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2.1: 2019 Update of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2. Eur Urol. 2019; 76(3): 340-351.
- Zhang K, Shen Y, Zhang X, et al. Predicting Prostate Biopsy Outcomes: A Preliminary Investigation on Screening with Ultrahigh B-Value Diffusion-Weighted Imaging as an Innovative Diagnostic Biomarker. PLoS One. 2016 ; 11(3): e0151176.
- Feng Z, Min X, Margolis DJ, et al. Evaluation of different mathematical models and different b-value ranges of diffusion-weighted imaging in peripheral zone prostate cancer detection using b-value up to 4500 s/mm2. PLoS One. 2017; 12(2): e0172127.
- Yokota Y, Takeda C, Kidoh M, et al. Effects of Deep Learning Reconstruction Technique in High-Resolution Non-contrast Magnetic Resonance Coronary Angiography at a 3-Tesla Machine Can Assoc Radiol J 2020:846537119900469.
- Akatsuka J, Yamamoto Y, Sekine T, et al. Illuminating Clues of Cancer Buried in Prostate MR Image: Deep Learning and Expert Approaches. Biomolecules 2019;9(11). doi: 10.3390/biom9110673.
- Qiu D, Zhang S, Liu Y, et al. Super-resolution reconstruction of knee magnetic resonance imaging based on deep learning Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2020;187:105059.
Figures
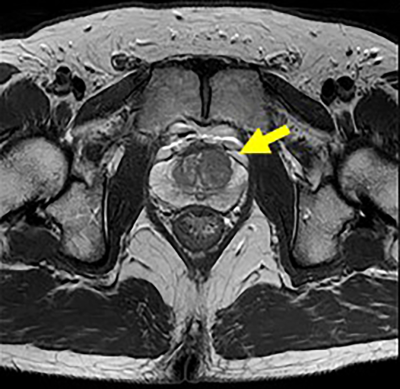
Figure 1. 51-year old patient with prostatic cancer in the left transitional zone
a: T2-weighted image shows a prostatic cancer as low signal intensity in the left transitional zone (arrow).
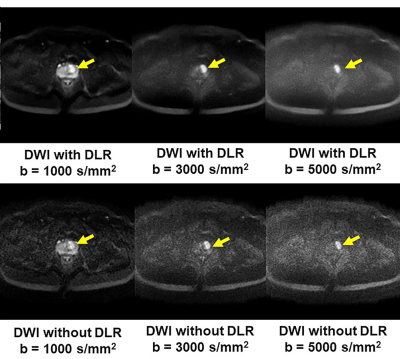
Figure 1. 51-year old patient with prostatic cancer in the left transitional zone
b: DLR improves image quality of DWIs for each b value. Each DWI shows the prostatic cancer as high signal intensity in the left transitional zone (arrow).
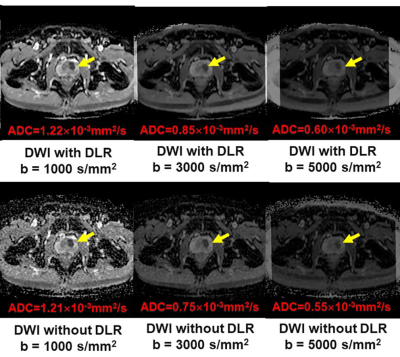
Figure 1. 51-year old patient with prostatic cancer in the left transitional zone
c: All ADC maps show the prostatic cancer as a hypointense signal in the left transitional zone (arrow).
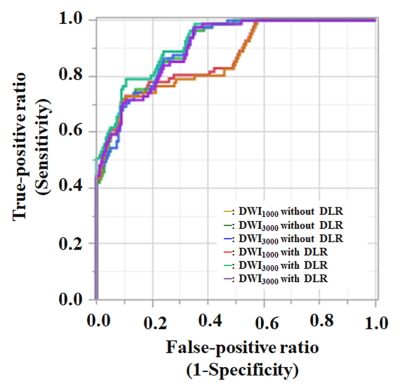
Figure 2. Results of ROC analysis for distinguishing malignant from benign areas.
Whether applying DLR method or not, DWI3000 (with DLR: AUC=0.92, without DLR: AUC=0.91) and DWI5000 (with DLR: AUC=0.90, without DLR: AUC=0.90) were significantly larger than DWI1000 (with DLR: AUC=0.87, p<0.05; without DLR: AUC=0.86, p<0.05). In addition, DWI1000 with DLR method and DWI3000 with DLR method were significantly higher than those without DLR method (p<0.05).
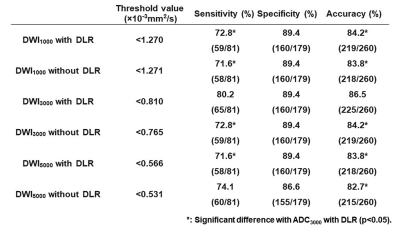
Figure 3. Results of compared diagnostic performance among all methods.
DLR could significantly improve specificity and accuracy of DWI3000 (p<0.05). In addition, specificity and accuracy of DWI3000 with DLR method were significantly higher than those of DWIs at other b values with and without DLR method (p<0.05).