2932
Monaural auditory stimulation induces negative BOLD in the rat auditory pathway1Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown, Lisboa, Portugal
Synopsis
fMRI has been used to characterize the auditory pathway in rodents in the past, but unlike other modalities, these studies haven’t shown any prominent negative responses in any structure along the auditory pathway. Our findings reveal, for the first time, negative BOLD signals induced by monaural stimulation with broadband white noise in the ipsilateral inferior colliculus and contralateral striatum. These findings may shed light into the intercollicular dynamics in sound processing in the rat brain upon, e.g., sound localization or spatial navigation.
Introduction
Functional MRI (fMRI) has been used to characterize the auditory pathway in humans1, rats (tonotopy2,3, sound pressure level encoding4 or laterality5), and mice (tonotopy6), mainly evidencing positive BOLD responses (PBRs) along the different structures of the auditory pathway. However, although intercollicular ipsilateral suppression of responses to contralateral stimulation through excitatory/inhibitory effects has been previously suggested7,8, negative BOLD responses (NBRs) to auditory stimuli have not been yet reported in rodents. While the origin of NBR has yet to be clearly explained, three main mechanisms have been considered9: Vascular stealing; active neural suppression; and possible increased level of neuronal activity (e.g. an extended initial dip). Here, we investigated how monaural auditory stimulation can induce negative BOLD in prominent auditory pathway structures.Methods
Animal experiments were preapproved by the institutional and national authorities and carried out according to European Directive 2010/63. Adult Long Evans rats (n=7) were sedated with medetomidine10, temperature and respiration rate were monitored and kept stable.MRI experiments: A 9.4T BioSpec scanner (Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany) with an 86mm quadrature resonator for transmittance and a 4-element array cryoprobe (Bruker, Fallanden, Switzerland) for signal reception was used. Data was acquired under medical air (28%O2) with a GE-EPI sequence (TE/TR=14/1000ms, FOV=20x13mm2, in-plane resolution=250x250μm2, slice thickness=1mm, tacq=6min45s).
Auditory Stimulation: Broadband (5-45kHz) white noise at 80dB and presented monaurally into the animal’s left ear (Fig.1a). The rest of the ear was occluded with Vaseline-doused cotton to isolate external sounds. The stimulation paradigm consisted of eight repetitions of 15s stimulation and 45s rest (Fig.1b).
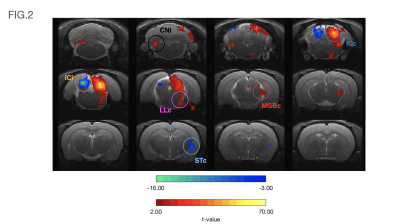
Data analysis: fMRI pre-processing steps included manual outlier correction; slice-timing (sinc-interpolation); smoothing (FWHM=0.250mm isotropic); mean-volume realignment and co-registration, followed by GLM (Fig.2) and ROI analysis(Fig.3).
Results
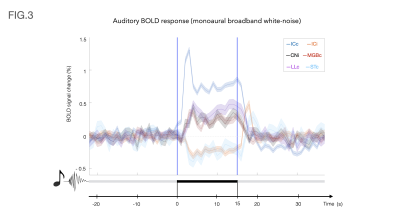
Auditory BOLD responses (Fig. 2), evidenced PBRs in the prominent auditory pathway regions including CNi, ICc, LLc and MGBc; NBRs were clearly observed in ICi and STc.The corresponding detrended time-courses (Fig. 3) show that ICc presents with the highest positive activation, while ICi and STc show a rather constant plateau of NBR during stimulation followed by a clear overshoot post-stimulation.
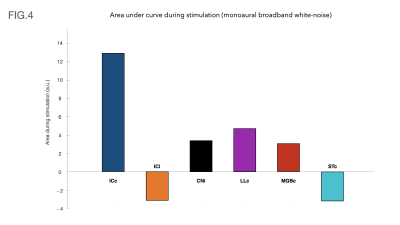
Fig.4 shows bar plots with the area under each ROI’s respective curves during the stimulation.
Discussion
Contralateral auditory structures and CNi responses are consistent with previous literature2,5, displaying clear positive BOLD activation throughout the main structures of the auditory pathway (except AC) (Fig. 3). In contrast, NBR responses were discovered in ICi and STc (Fig. 3).The former, although not previously reported, is not entirely surprising, as the ipsilateral suppression of responses to contralateral stimulation as a manner of gain control has been previously suggested7, possibly through MGB sending feedback inputs to the ipsilateral IC11,12, or intercollicular projections via the commissure of the inferior colliculi (CoIC)13-15, with stimulation of the CoIC producing both excitatory/inhibitory effects on IC neurons16-18. ICs do not operate in isolation; the largest afferent source to each IC has been suggested to be their contralateral IC19,20, through excitation, inhibition or a combination of both21.
Particularly, the role of the IC in binaural integration in rodents, specifically for sound localization, is of great interest. Yet, a lot of its underlying mechanisms remain mostly unclear. It has been suggested that ICc neurons exert contralateral dominance by a “push-pull”-like mechanism8, with contralaterally dominant excitation and more bilaterally balanced inhibition, from an ipsilaterally mediated scaling of contralateral response8. Moreover, intrinsic signals upon bilateral stimulation were shown to be weaker than those arising upon contralateral stimulation, suggesting an ipsilateral neural pathway suppressing neural responses evoked contralaterally7,22. Our findings thus pave the way to investigate these brain-wide responses upon ipsi/contra/bilateral stimulation.
Striatal neurons in the caudal region (TS) were suggested to play an essential role in auditory decisions23, with TS receiving cortical and thalamic auditory inputs, specifically from AC and MGB24. While these have been shown to provide a stable representation of sounds during auditory tasks23, more complex stimuli will be required to elucidate the NBRs observed in the striatum in this study.
To the best of our knowledge, previous auditory fMRI studies in rodents have not shown these negative activations, whether upon monaural or binaural stimulations2,5. Our main hypothesis on the discrepancy is that the anesthetic regimes (Medetomidine VS Isofluorane) affect brain states, thereby affecting the BOLD signals25.
Conclusion
We provide a first characterization of NBRs upon monaural auditory stimulation, displaying clear ipsilateral negative activation on the IC and contralateral Striatum. This bodes well for investigating brain-wide sound processing mechanisms in rodents, in particular, sound localization, but also the underlying significance of NBRs in general.Acknowledgements
This study was funded in part by the European Research Council (ERC) (agreement No. 679058). The authors acknowledge the vivarium of the Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown, a facility of CONGENTO which is a research infrastructure co-financed by Lisboa Regional Operational Programme (Lisboa 2020), under the PORTUGAL 2020 Partnership Agreement through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (Portugal), project LISBOA-01-0145-FEDER-022170.
The authors would like to thank Francisca F. Fernandes for the assistance in the fMRI data analysis.
References
1. Wessinger CM, Buonocore MH, Kussmaul CL, Mangun GR. Tonotopy in human auditory cortex examined with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1997 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0193(1997)5:1<18::AID-HBM3>3.0.CO;2-Q.
2. Cheung MM, Lau C, Zhou IY, et al. BOLD fMRI investigation of the rat auditory pathway and tonotopic organization. Neuroimage 2012 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.01.087.
3. Cheung MM, Lau C, Zhou IY, et al. High fidelity tonotopic mapping using swept source functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 2012 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.031.
4. Zhang JW, Lau C, Cheng JS, et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of sound pressure level encoding in the rat central auditory system. Neuroimage 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.09.069.
5. Lau C, Zhang JW, Cheng JS, Zhou IY, Cheung MM, Wu EX. Noninvasive fMRI Investigation of Interaural Level Difference Processing in the Rat Auditory Subcortex. PLoS One 2013 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070706.
6. Blazquez Freches G, Chavarrias C, Shemesh N. BOLD-fMRI in the mouse auditory pathway. Neuroimage 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.10.027.
7. Tsytsarev V, Tanaka S. Intrinsic optical signals from rat primary auditory cortex in response to sound stimuli presented to contralateral, ipsilateral and bilateral ears. Neuroreport 2002 doi: 10.1097/00001756-200209160-00019.
8. Xiong XR, Liang F, Li H, et al. Interaural level difference-dependent gain control and synaptic scaling underlying binaural computation. Neuron 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.06.012.
9. Wade AR. The negative BOLD signal unmasked. Neuron 2002 doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(02)01138-8.
10. Weber R, Ramos-Cabrer P, Wiedermann D, Van Camp N, Hoehn M. A fully noninvasive and robust experimental protocol for longitudinal fMRI studies in the rat. Neuroimage 2006 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.08.028.
11. Kuwabara N, Zook JM. Geniculo-collicular descending projections in the gerbil. Brain Res. 2000 doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02695-0.
12. Caicedo A, Herbert H. Topography of descending projections from the inferior colliculus to auditory brainstem nuclei in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1993 doi: 10.1002/cne.903280305.
13. Adams JC. Crossed and descending projections to the inferior colliculus. Neurosci. Lett. 1980 doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90246-3.
14. Saldaña E, Merchań MA. Intrinsic and commissural connections of the rat inferior colliculus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992 doi: 10.1002/cne.903190308.
15. Ayala YA, Malmierca Dr. MS. Stimulus-specific adaptation and deviance detection in the inferior colliculus. Front. Neural Circuits 2012 doi: 10.3389/fncir.2012.00089.
16. Ito T, Bishop DC, Oliver DL. Two classes of GABAergic neurons in the inferior colliculus. J. Neurosci. 2009 doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3454-09.2009.
17. Moore DR, Kotak VC, Sanes DH. Commissural and lemniscal synaptic input to the gerbil inferior colliculus. J. Neurophysiol. 1998 doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.80.5.2229.
18. Reetz G, Ehret G. Inputs from three brainstem sources to identified neurons of the mouse inferior colliculus slice. Brain Res. 1999 doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(98)01230-X.
19. Games KD, Winer JA. Layer V in rat auditory cortex: Projections to the inferior colliculus and contralateral cortex. Hear. Res. 1988 doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(88)90047-0.
20. Moore DR. Auditory brainstem of the ferret: Sources of projections to the inferior colliculus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1988 doi: 10.1002/cne.902690303.
21. Keine C, Rübsamen R, Englitz B. Inhibition in the auditory brainstem enhances signal representation and regulates gain in complex acoustic environments. Elife 2016 doi: 10.7554/eLife.19295.
22. Nelken I, Bizley JK, Nodal FR, Ahmed B, King AJ, Schnupp JWH. Responses of auditory cortex to complex stimuli: Functional organization revealed using intrinsic optical signals. J. Neurophysiol. 2008 doi: 10.1152/jn.00469.2007.
23. Guo L, Walker WI, Ponvert ND, Penix PL, Jaramillo S. Stable representation of sounds in the posterior striatum during flexible auditory decisions. Nat. Commun. 2018 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03994-3.
24. Jiang H, Kim HF. Anatomical inputs from the sensory and value structures to the tail of the rat striatum. Front. Neuroanat. 2018 doi: 10.3389/fnana.2018.00030.
25. Paasonen J, Stenroos P, Salo RA, Kiviniemi V, Gröhn O. Functional connectivity under six anesthesia protocols and the awake condition in rat brain. Neuroimage 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.01.014.
26. Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. London Acad. Press 2009.
Figures
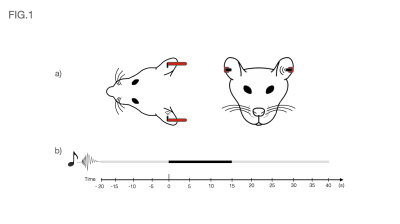
Fig1 a) Schematic of the auditory setup used. Headphones were positioned on both sides of the animal for consistency, but sound was only delivered on the left side throughout the stimulation paradigm. The rest of the ear was occluded with Vaseline-doused cotton to isolate external sounds.
Fig1 b) Auditory paradigm used in this study consisted of eight repetitions of 15s stimulation (Broadband 5-45kHz white noise at 80dB and presented monaurally into the animal’s left ear) and 45s rest.