2906
Free breathing respiratory triggered retrospectively cardiac gated (CARE-Sync) bSSFP cine imaging with radial acquisition
Isao Shiina1, Michinobu Nagao2, Masami Yoneyama3, Yasutomo Katsumata3, Yasuhiro Goto4, Kazuo Kodaira4, Takumi Ogawa4, Yutaka Hamatani1, Mamoru Takeyama4, Isao Tanaka4, and Shuji Sakai2
1Radiological Services, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Electronics Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Department of Radiological Services, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
1Radiological Services, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Electronics Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Department of Radiological Services, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
Synopsis
we investigate the clinical usefulness of respiratory-triggered cardiac cine radial MRI. Compared with the breath-hold scan, the left ventricular function values obtained from the breath-triggered scan showed a better correlation than the conventional free-breathing scan.
Synopsis
In this study, we investigate the clinical usefulness of respiratory-triggered cardiac cine radial MRI. Compared with the breath-hold scan, the left ventricular function values obtained from the breath-triggered scan showed a better correlation than the conventional free-breathing scan.Purpose
Cardiac cine MRI is commonly used as a standard method for left ventricular function analysis (1). Cine MRI requires multiple breath holds and often encounters difficult situations in pediatric and elderly patients. Free-breathing scans are performed on patients with poor breath-holding, but conventional free-breathing scans are imaged using artifact reduction technology (SMART), so it takes long time and is strongly affected by movement (2). Retrospective gating combined with respiratory triggering (CARE-Sync) (Fig. 1) was used to examine respiratory-synchronized cine MRI (3). In addition, it has been reported that radial collection is effective in reducing artifacts in cine MRI (4). This study we investigated to increasing the robustness of free-breathing CINE imaging using CARE-Sync with radial bSSFP sequence and its clinical usefulness by comparing breath-hold scans, free-breathing scans, free-breathing radial scans, CARE-Sync scans, and CARE-Sync radial scans.Metheod
Cardiac cine MRI images of eight healthy volunteers (age range: 30-42 years) show 3.0T MR system (Ingenia,Philips Healthcare). Five cine images were compared: breath-hold scan, free-breathing scan, radial scan, CARE-Sync scan, CARE-Sync radial scan. The reproducibility of left ventricular functional parameters was evaluated (left ventricular ejection fraction, LVEF%; terminal left ventricular dilatation) Volume, LVEDV ml; Left ventricular end systolic volume (LVESV ml) of the three methods. The functional analysis was performed by one radiologist and one radiologist. Technicians using available software (Ziostation 2, Ziosoft Co, Tokyo). Cardiac Cine-MRI Imaging Parameters: Cardiac Sync = Retrospective, Slice Thickness = 8mm, FOV 350mm, NSA = 1, Pixel size = 1.5X1.5mm, TR = 3.1msec, TE = 1.5msec, FA = 50 degrees, Number of heart phases = 20.Parameter correlation was analyzed by Brand Altman plot analysis.Results & Discussion
CINE image of breath-hold scan, free-breathing scan, free-breathing radial scan, CARE-Sync scan, and radial scan with CARE-Sync. (Fig. 2) In the Brand-Altman regression, free-breathing scans show the most non-uniformity among the five imaging methods, with radial scans and CARE-Sync scans having the highest uniformity, and CARE-Sync combined radial scans having the highest uniformity. (Fig. 3,4,5)Conclusion
The cardiac function values obtained from the CARE-Sync combined radial scan were in very good agreement with the measurements obtained from the breath-hold scan. The image quality is better than that of conventional free breath scans, and it can be expected to improve the quality of cardiac MRI examinations for patients who cannot hold their breath.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
(1) Germain P, et al: Inter-study variability in left ventricular mass measurement. Comparison between M-modeechography and MRI. Eur Heart J 13:1011-9, 1992. (2) Seitz J, et al: Reduction of motion artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging of the neck andcervical spine by long-term averaging. Invest Radiol 35: 380-4,2000. (3) Krishnamurthy R, et al. Clinical validation of free breathing respiratory triggered retrospectively cardiac gated cine balanced steady-state free precession cardiovascular magnetic resonance in sedated children. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2015;17:1. doi: 10.1186/s12968-014-0101-1 (4) Karen Holst,et,al:Left ventricular volume measurements with free breathing respiratory self gated 3-dimensional golden angle radial whole-heart cine imaging – Feasibility and reproducibility.Magnetic resonance imaging.2017Figures
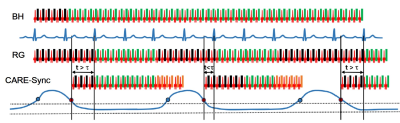
(Figure:1) Steady-state (SS) magnetization preparation methods for cardiac-gated balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) cine.
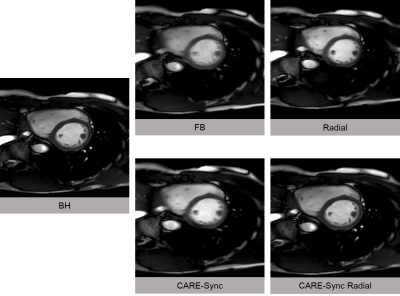
(Figure:2)Cine imaging of breath-holding,
free-breathing, free-breathing radial scan, CARE-Sync, and radial scan with
CARE-Sync.
Hold your breath for breath-holding, 2min32sec
for free breathing, 3min50sec for free-breathing radial scan, 2min10sec for
CARE-Sync, and radial scan with CARE-Sync. It's 6min40sec.
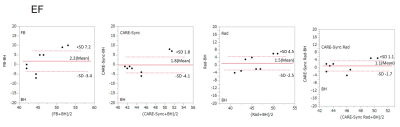
(Figure:3)Plot LVEF with Brand-Altman
between standard breath-holding and free-breathing, free-breathing radial
scans, CARE-Sync, and radial scans combining CARE-Sync.
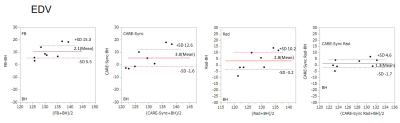
(Figure:4)Plot LVEDV with Brand-Altman between standard breath-holding and free-breathing, free-breathing radial scans, CARE-Sync, and radial scans combining CARE-Sync.
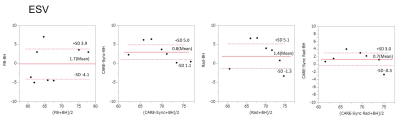
(Figure:5)Plot LVESV with Brand-Altman between standard breath-holding and free-breathing, free-breathing radial scans, CARE-Sync, and radial scans combining CARE-Sync.