2900
Rapid Personalisation of Left Ventricular Meshes using Differentiable Rendering1University and ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Synopsis
We present a novel method for volumetric left ventricle mesh personalisation from cardiac MR images. The proposed method does not require any ground-truth mesh training data. Additionally, it corrects for slice misalignment and can propagate these correction back to the original image data. The method is expressive enough to capture diverse morphology, and is also differentiable, allowing for direct inclusion in deep-learning pipelines. We demonstrate that our mesh personalisation approach works robustly on both healthy and pathological anatomy.
Introduction
This work is concerned with robust and accurate prediction of volumetric shape meshes of the left ventricle (LV) from cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) images. Predicting such meshes is a key step for both accurate personalised simulation (e.g. constructing a ‘digital twin’ [1]), and the generation of diverse realistic synthetic data with known ground truth anatomy through conditional synthesis [2,3] or physics-based simulation [4]. Moreover, accurate mesh prediction is valuable in itself, facilitating the inference of various clinically relevant indices and enabling inter/intra-study comparison and statistical analysis at larger scales than currently possible.Our proposed method overcomes a number of particular obstacles associated with CMR mesh prediction: Firstly, it does not require any ground-truth paired mask and mesh training data. Secondly, it corrects for slice misalignment (as occurs in practice between breath-holds) and can propagate these correction back to the original image data. Additionally, the method is expressive enough to capture diverse (i.e. including pathological) morphology.
Background
There has been considerable work on pixel/voxel based segmentation of the heart from MR images. Convolutional neural networks (CNN) have been shown to produce state-of-the-art results, yielding precise pixel-based segmentation masks, recently achieving human-level accuracy on LV segmentation through the use of large labelled training sets [5].Our method builds on these automatic segmentation methods, combining the pixel information from each individual slice to predict a coherent volumetric mesh. Producing a mesh from voxelized data is a classic problem in computer science [6], however, the specific requirements of cardiac mesh prediction (e.g. handling slice misalignment) differentiate it from general mesh fitting. A number of approaches have been recently proposed [7-10]. However, to the best of our knowledge our approach is the first to produce volumetric meshes, explicitly correct for slice misalignment, and avoid the need for training data. We also demonstrate the method works robustly on real (and pathological) MR data.
In the proposed approach we differentiably render and slice a volumetric LV mesh (see below). We are unaware of any previous use of differentiable rendering approaches in medical imaging, and have drawn from computer graphics and machine learning literature [11-15].
Methods
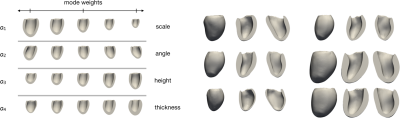
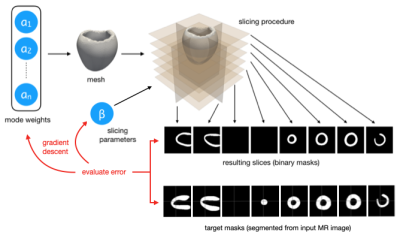
We propose to directly fit a LV shape model to the segmentation masks produced from multi-slice MR images. Using an LV shape model restricts the predictions to lie on a learned manifold of feasible LV morphologies, and additionally reduces the dimensionality of the required prediction by two orders of magnitude (specifically, we predict 2-25 (scalar) modes rather than the positions of 3000 nodes in 3D space). We employ an existing linear LV shape model [16] which captures the morphological variation seen in a cohort of 40 3D cardiac images. Such variations are described by orthonormal modes obtained by applying Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) to the set of anatomically consistent meshes derived from the dataset [16,17]. The expressiveness of the shape model is shown in Figure 1.From an input MR exam we first extract all slices from all series, re-sample them to 1mm×1mm in-plane resolution, and position them relative to one another in 3D space. Next, the LV myocardium in each slice is segmented using a U-Net [18] based CNN. This results in a number of 2D myocardium masks positioned in 3D space. These mask images represent our “target” segmentation.
As our mesh rendering and slicing steps are differentiable, we can perform gradient descent to find the parameters that yield the LV masks most similar to those obtained from the input MR images. Specifically, we optimise the modes of the shape model, as well as its position and orientation in space. We also learn in-plane offsets for each slice independently to correct for slice misalignment. See Figure 2 for details.
Experiments and Results
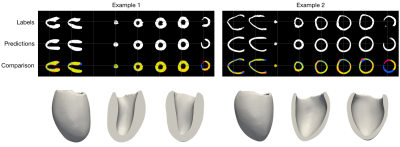
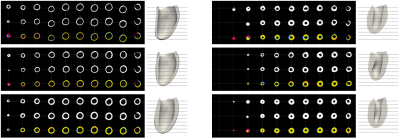
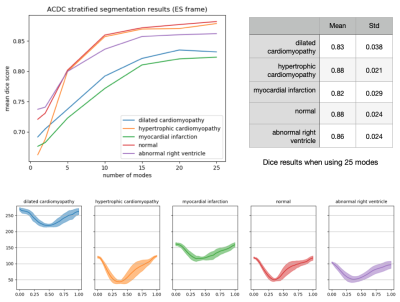
To evaluate our method we use the “Multi-Modal Whole Heart Segmentation” (MMWHS [19-22]) and “Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge” (ACDC [23]) datasets. All experiments are performed on one TitanX GPU. Fitting a mesh to all 30 time frames of an exam containing 12 slices takes approximately 3-5 minutes.Example results of our approach on MMWHS are shown in Figure 3. Additional results on pathological anatomy from ACDC are shown in Figure 4. Lastly, quantitive results for dice accuracy of the fitted mesh (relative to the predicted segmentations) are shown in Figure 5, along with predictions of LV cavity volume over the cardiac cycle, for ACDC data stratified by pathology.
Discussion and Conclusion
We have demonstrated a method for LV mesh personalisation that corrects for slice misalignments and works robustly across real pathological data. The method is fast and fully differentiable, allowing inclusion in end-to-end deep learning methods.The approach relies on the expressivity of the underlying shape model. One result of this is that meshes produced by our method cannot be straightforwardly used to further improve the shape model itself. There is potential to address this limitation by applying a final “shape correction step” that allows all vertices to move independently.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge support form the Swiss National Science Foundation Grant PZ00P2_174144.References
[1] Corral-Acero, J., Margara, F., Marciniak, M., Rodero, C., Loncaric, F., Feng, Y., Gilbert, A., Fernandes, J.F.,Bukhari, H.A., Wajdan, A., et al.: The ‘digital twin’ to enable the vision of precision cardiology. European Heart Journal. (2020)
[2] Joyce, T., Kozerke, S.: 3D medical image synthesis by factorised representation and deformable model learning.In: International Workshop on Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging. pp. 110–119. Springer (2019)
[3] Abbasi-Sureshjani, S., Amirrajab, S., Lorenz, C., Weese, J., Pluim, J., Breeuwer, M.: 4d semantic cardiacmagnetic resonance image synthesis on xcat anatomical model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.07089 (2020)
[4] Duchateau, N., Sermesant, M., Delingette, H., & Ayache, N. (2017). Model-based generation of large databases of cardiac images: synthesis of pathological cine MR sequences from real healthy cases. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 37(3), 755-766. (2017)
[5] Bai, W., Sinclair, M., Tarroni, G., Oktay, O., Rajchl, M., Vaillant, G., Lee, A.M., Aung, N., Lukaschuk, E.,Sanghvi, M.M., et al.: Human-level CMR image analysis with deep fully convolutional networks (2017)
[6] Lorensen, W.E., Cline, H.E.: Marching cubes: A high resolution 3d surface construction algorithm. ACMsiggraph computer graphics21(4), 163–169 (1987)
[7] Villard, B., Grau, V., Zacur, E.: Surface mesh reconstruction from cardiac mri contours. Journal of Imaging4(1), 16 (2018)
[8] Villard, B., Zacur, E., Grau, V.: Isachi: Integrated segmentation and alignment correction for heart images.In: International Workshop on Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart. pp. 171–180. Springer (2018)
[9] Xu, H., Zacur, E., Schneider, J.E., Grau, V.: Ventricle surface reconstruction from cardiac mr slices using deep learning. In: International Conference on Functional Imaging and Modeling of the Heart. pp. 342–351. Springer (2019)
[10] Joyce, T., Buoso, S., Xu, Y., Kozerke, S.: A Machine Learning Approach to Left Ventricle Mesh Prediction from Multi-Slice MR Images. In: Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 28. p. 2230 (2020)
[11] Lunz, S., Li, Y., Fitzgibbon, A., Kushman, N.: Inverse graphics gan: Learning to generate 3d shapes fromunstructured 2d data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.12674 (2020)
[12] Niemeyer, M., Mescheder, L., Oechsle, M., Geiger, A.: Differentiable volumetric rendering: Learning implicit3d representations without 3d supervision. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.07372 (2019)
[13] Peng, S., Niemeyer, M., Mescheder, L., Pollefeys, M., Geiger, A.: Convolutional occupancy networks. arXivpreprint arXiv:2003.04618 (2020)
[14] Sawhney, R., Crane, K.: Monte carlo geometry processing: A grid-free approach to pde-based methods onvolumetric domains. ACM Trans. Graph.39(4) (2020)
[15] Yariv, L., Atzmon, M., Lipman, Y.: Universal differentiable renderer for implicit neural representations. arXivpreprint arXiv:2003.09852 (2020)
[16] Buoso, S., Stoeck, C.T., Stimm, J., Kozerke, S.: An MRI image-guided left-ventricular shape model embedding local phys-iological coordinates and directions. In: Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 28. p. 2217 (2020)
[17] Buoso, S., Manzoni, A., Alkadhi, H., Plass, A., Quarteroni, A., Kurtcuoglu, V.: Reduced-order modeling ofblood flow for noninvasive functional evaluation of coronary artery disease. Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology 18(6), 1867–1881 (2020)
[18] Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. pp. 234–241. Springer (2015)
[19] Xiahai Zhuang and Juan Shen: Multi-scale patch and multi-modality atlases for whole heart segmentation of MRI, Medical Image Analysis 31: 77-87, (2016)
[20] Xiahai Zhuang: Challenges and Methodologies of Fully Automatic Whole Heart Segmentation: A Review. Journal of Healthcare Engineering 4 (3): 371-407, (2013)
[21] X Zhuang, et al.: Multiatlas whole heart segmentation of CT data using conditional entropy for atlas ranking and selection. Medical physics 42 (7), 3822-3833 (2015)
[22] X Zhuang, et al.: A Registration-Based Propagation Framework for Automatic Whole Heart Segmentation of Cardiac MRI. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 29 (9): 1612-1625, (2010)
[23] O. Bernard, A. Lalande, C. Zotti, F. Cervenansky, et al.: Deep Learning Techniques for Automatic MRI Cardiac Multi-structures Segmentation and Diagnosis: Is the Problem Solved ? in IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 37, no. 11, pp. 2514-2525, (2018)
Figures