2888
Realistic Simulation of Real-Time Cardiac Cine and First Pass Perfusion on High Performance 0.55T System1Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Biomedical Engineering, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States
Synopsis
We present a realistic cardiac MRI simulation framework, including concomitant effects, off-resonance, realistic coil-array and noise level. The general framework is flexible to different field strengths, sequences, and different motion patterns and ischemia models can be introduced. We demonstrate three usages of the framework, in comparing artifact/noise level at different field strengths, in optimization of real-time 3D trajectories and reconstruction, and capturing myocardial perfusion deficits. Real-time 3D cine and first-pass perfusion with high-resolution whole-heart coverage were tested feasible on a high-performance 0.55T system by simulation.
Introduction
There has been a surge of recent interest in cardiac MRI at lower field strengths, due to reduced off-resonance artifact, reduced B1+ inhomogeneity, relaxed SAR constraints, and improved device safety and compatibility. MRI systems operating at 0.35T (1-3) and 0.55T (4-6) have demonstrated high quality cardiac imaging performance, which suggests that cardiac MRI may be favorable on such high-performance low-field (HPLF) systems.HPLF systems grant substantial new flexibility in terms of k-space trajectory (data sampling) due to reduced off-resonance, but also suffer more greatly from gradient distortions and concomitant fields. These are usually difficult to optimize due to a lack of ground-truth data. We propose a realistic simulation framework to fulfill this unmet need, and to aid in the optimization of data sampling and image reconstruction methods for HPLF cardiac imaging.
We have extended a framework presented by Wang et al. (7) to include concomitant field effects, off-resonance, and use realistic coil sensitivities. We demonstrate three exemplar applications at simulated 0.55 Tesla: evaluation of artifact and noise level; optimization of trajectory and reconstruction; and identification of myocardial perfusion deficit.
Methods
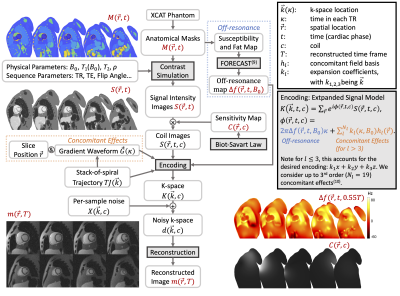
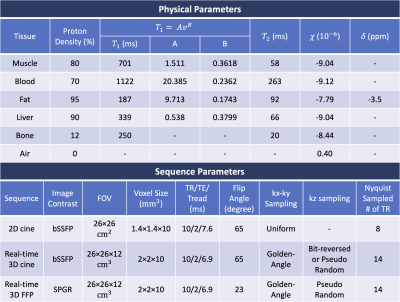
SimulationFigure 1 illustrates the simulation steps. A 1024x1024x180mm3 volume with 1mm isotropic resolution was extracted from the XCAT phantom (8), with cardiac motion sampled at 10ms/frame. The T1, T2 and proton density are used to generate image contrast from steady-state equations, and the susceptibility and chemical shift were used to generate off-resonance maps (9). Table 1 lists physical parameters and sequence parameters used in this study. Coil sensitivities for a 12-channel torso array coil were estimated by Biot-Savart law with realistic coil size and position. K-space was simulated using the expanded signal model (10) to consider concomitant and off-resonance effects, and then realistic levels of complex gaussian noise were added. The trajectory design considered a maximum gradient of 4 G/cm and maximum slew rate of 20 G/cm/msec. We present three exemplar applications:
2D Cine
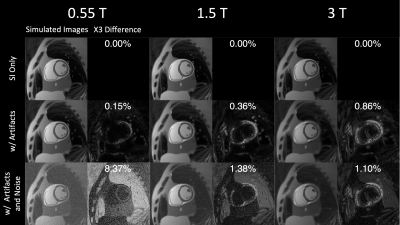
We simulated 2D cine images at 0.55T, 1.5T, and 3T. Concomitant fields, off-resonance, and noise were added to evaluate the dependence of artifact and noise on B0.
Real-Time 3D Cine at 0.55T
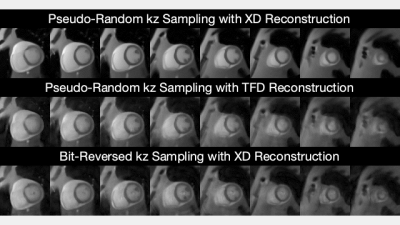
We simulated 3D cine imaging, assuming a 10-second breath-hold and 60/minute heartrate. Golden-angle rotated stack-of-spiral (SOS) sampling was simulated with either bit-reversed sampling or pseudo-random kz order (11). Two constrained reconstructions were implemented. One used temporal finite difference (TFD) and spatial total variation regularizations (12) (TFD reconstruction), and one additionally applied TFD regularization on the cardiac phase dimension (extra dimension (XD) reconstruction). The latter method has been successfully applied to cardiac MRI reconstruction (13-15). Regularization parameters were manually tuned based on experience (12,16).
Real-Time 3D FPP at 0.55T
In myocardial first-pass perfusion (FPP) MRI, there has been increasing interest in obtaining whole-heart, high-resolution images to more accurately estimate ischemia burden and perfusion reserve (16-18). We simulated such acquisition at 0.55T using a real-time 3D SOS sequence, and with an ischemic defect added to the XCAT phantom (19). A measured arterial input function ([Gd]) was used to generate signal intensity curves for myocardium and blood with a contrast agent relaxivity of 3.8L/mmol/s (20). Tissue [Gd] curves for ischemic and normal tissues were estimated with a two-compartment model (21), with ktrans values of 0.2ml/min/g and 0.8ml/min/g, respectively. Forty seconds of data was generated.
Results and Discussion
Figure 2 shows the simulated image artifact level at different field strengths. As B0 increases, concomitant effects reduce, off-resonance effects increase, and SNR increases. The combined concomitant and off-resonance effects are lowest at 0.55T. The off resonance caused by fat largely affects myocardium at 3T, and the common solution is applying fat saturation pulses (not simulated in this study). Note that this simulation is able to capture realistic encoding distortion and may be useful to predict performances of field strengths before building a prototype.Figure 3 compares the simulated 3D RT-MRI images. Pseudorandom kz sampling with XD reconstruction yielded the sharpest and most accurate depiction of endocardial and epicardial contours. Note that the simulation can generate undersamped k-space data and ground-truth images, which could provide insights into trajectory design and reconstruction.
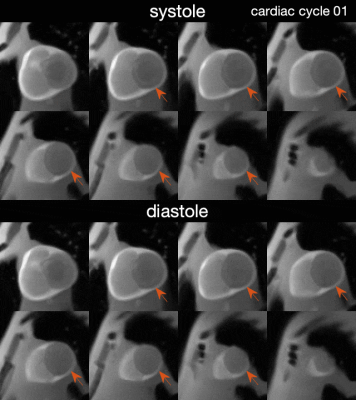
Figure 4 illustrates reconstructed 3D FPP images. Pseudorandom kz sampling with XD reconstruction provided adequate temporal resolution and quality to resolve systole, where the myocardial wall is thick and easy to read for perfusion deficits. Note that the simulation can also produce variation of heart rate, breathing pattern or ischemia pattern to more thoroughly study stress/rest FPP and free-breathing acquisition.
Conclusion
We present a framework for realistic simulation of cardiac MRI at low field strengths, including 0.55 Tesla. Importantly, this work includes concomitant field effects, which have a substantial impact at low field strengths, for off-isocenter imaging, and when using longer non-Cartesian readouts. We demonstrate predictions of real-time 3D cine and 3D FPP performance on a HPLF 0.55T system with stack-of-spiral sampling.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSF #1828763 and NIH R01-HL130494.References
1. Varghese J, Craft J, Crabtree CD, Liu Y, Jin N, Chow K, Ahmad R, Simonetti OP. Assessment of cardiac function, blood flow and myocardial tissue relaxation parameters at 0.35 T. NMR in Biomedicine 2020;33(7):e4317.
2. Rashid S, Han F, Gao Y, Sung K, Cao M, Yang Y, Hu P. Cardiac balanced steady-state free precession MRI at 0.35 T: a comparison study with 1.5 T. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery 2018;8(7):627-636.
3. Simonetti OP, Ahmad R. Low-Field Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging 2017;10(6):e005446.
4. Campbell-Washburn AE, Ramasawmy R, Restivo MC, Bhattacharya I, Basar B, Herzka DA, Hansen MS, Rogers T, Bandettini WP, McGuirt DR, Mancini C, Grodzki D, Schneider R, Majeed W, Bhat H, Xue H, Moss J, Malayeri AA, Jones EC, Koretsky AP, Kellman P, Chen MY, Lederman RJ, Balaban RS. Opportunities in Interventional and Diagnostic Imaging by Using High-Performance Low-Field-Strength MRI. Radiology 2019;293(2):384-393.
5. Restivo MC, Ramasawmy R, Bandettini WP, Herzka DA, Campbell-Washburn AE. Efficient spiral in-out and EPI balanced steady-state free precession cine imaging using a high-performance 0.55T MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2020;84(5):2364-2375.
6. Bandettini WP, Shanbhag SM, Mancini C, McGuirt DR, Kellman P, Xue H, Henry JL, Lowery M, Thein SL, Chen MY, Campbell-Washburn AE. A comparison of cine CMR imaging at 0.55 T and 1.5 T. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2020;22(1):37.
7. Wang X, Lee N, Campbell-Washburn AE, Nayak KS. Realistic Simulation of High-Performance Low Field Cardiac Cine Imaging. 2020; Virtual. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. p 2181.
8. Segars WP, Sturgeon G, Mendonca S, Grimes J, Tsui BM. 4D XCAT phantom for multimodality imaging research. Med Phys 2010;37(9):4902-4915.
9. Zijlstra F, Bouwman JG, Braškutė I, Viergever MA, Seevinck PR. Fast Fourier-based simulation of off-resonance artifacts in steady-state gradient echo MRI applied to metal object localization. Magn Reson Med 2017;78(5):2035-2041.
10. Wilm BJ, Barmet C, Pavan M, Pruessmann KP. Higher order reconstruction for MRI in the presence of spatiotemporal field perturbations. Magn Reson Med 2011;65(6):1690-1701.
11. Zhao Z, Lim Y, Byrd D, Narayanan S, Nayak K. Improved 3D Real-Time MRI of Speech Production. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. in press.
12. Mendes JK, Adluru G, Likhite D, Fair MJ, Gatehouse PD, Tian Y, Pedgaonkar A, Wilson B, DiBella EVR. Quantitative 3D myocardial perfusion with an efficient arterial input function. Magn Reson Med 2020; 83(6):1949-1963.
13. Feng L, Axel L, Chandarana H, Block KT, Sodickson DK, Otazo R. XD-GRASP: Golden-angle radial MRI with reconstruction of extra motion-state dimensions using compressed sensing. Magn Reson Med 2016;75(2):775-788.
14. Han F, Zhou Z, Cao M, Yang Y, Sheng K, Hu P. Respiratory motion-resolved, self-gated 4D-MRI using rotating cartesian k-space (ROCK). Med Phys 2017;44(4):1359-1368.
15. Bustin A, Lima da Cruz G, Jaubert O, Lopez K, Botnar RM, Prieto C. High-dimensionality undersampled patch-based reconstruction (HD-PROST) for accelerated multi-contrast MRI. Magn Reson Med 2019;81(6):3705-3719.
16. Tian Y, Mendes J, Wilson B, Ross A, Ranjan R, DiBella E, Adluru G. Whole-heart, ungated, free-breathing, cardiac-phase-resolved myocardial perfusion MRI by using Continuous Radial Interleaved simultaneous Multi-slice acquisitions at sPoiled steady-state (CRIMP). Magn Reson Med 2020;84(6):3071-3087.
17. Yang Y, Meyer CH, Epstein FH, Kramer CM, Salerno M. Whole-heart spiral simultaneous multi-slice first-pass myocardial perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 2019;81(2):852-862.
18. Anthony Christodoulou NW, Jaime Shaw, Xiaoming Bi, Yibin Xie, Christopher Nguyen, Debiao Li. Respiratory motion compensated Multitasking for 3D myocardial perfusion without breath-holds, ECG, or multiple boluses. 2019; Montréal, Canada. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. p 1175.
19. Veress AI, Segars WP, Tsui BMW, Gullberg GT. Incorporation of a Left Ventricle Finite Element Model Defining Infarction Into the XCAT Imaging Phantom. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2011;30(4):915-927.
20. Campbell-Washburn AE, Herzka DA, Kellman P, Koretsky AP, Balaban RS. Image contrast at 0.55T. 2019; Montréal, Canada. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. p 1214.
21. Tofts PS, Brix G, Buckley DL, Evelhoch JL, Henderson E, Knopp MV, Larsson HB, Lee TY, Mayr NA, Parker GJ, Port RE, Taylor J, Weisskoff RM. Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced T(1)-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: standardized quantities and symbols. J Magn Reson Imaging 1999;10(3):223-232.
22. Kramer CM, Barkhausen J, Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Flamm SD, Kim RJ, Nagel E. Standardized cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) protocols: 2020 update. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2020;22(1):17.
Figures