2775
A Rapid Simultaneously 3D T1/T2* Quantitative Imaging (TXI) in Body within 3 Breath-holds1Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 33. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 4Department of Radiology, the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
Synopsis
Simultaneously multi-parameter quantification is recently a hot research topic for MRI. A series of techniques are available, such as MR fingerprinting, MAGIC and STAGE. This study proposed a rapid and high-quality T1/T2* quantification method, called TXI. The results showed that it can generate high SNR T1 and R2* maps with less motion artifacts, which is superior to the conventional T1 and R2* mapping method. The T1 map is significantly improved with higher measurement consistency among different liver regions than conventional method.
Introduction
Simultaneously multi-parameter quantification is recently hot research topic for MRI. A series of techniques are available recently. MR Fingerprinting is one of the most popular technique in these years, which can generate T1/ T2 maps with high accuracy and consistency(1), while it is not widely available yet. Meanwhile, MAGIC(2) and STAGE(3) techniques could do similar quantification based on traditional method but with relatively faster acquisition, thus have applied in clinical projects recently. While they still need much longer acquisition time than traditional weighted imaging, which is difficult for widely clinical application or for moving organ such as liver and kidney. Although STAGE is based on 3D GRE sequence and could be potentially optimized for body, the B1 inhomogeneity problem cannot be well addressed, which is critical in body region. In this study, we proposed a B1-corrected 3D-GRE sequence method for simultaneously T1/T2* quantitative imaging (TXI) and validate it in liver.Methods
Liver MR scanning was conducted using a 3T MR scanner (MAGNETOM Prisma, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). The acquisition contains two 3D-multi-TE-GRE scans with two different flip angles (degree 3,15) and an additional B1 mapping scan. The imaging parameters were as follows: TR = 5.01ms, TE0/TE6/𝜟TE = 1.05/7.38/1.26 ms, FOV = 393 × 450 mm2, matrix = 222 × 320, slice thickness = 3.5 mm, in-plane acceleration factor = 3, total time 20 seconds for each scan. An additional B1 map sequence was acquired with parameters: TR= 5050ms, TE = 1.83 ms, FOV = 309 × 381mm2, matrix = 52 × 64, slice thickness = 8 mm, total time 10 seconds.The algorithm of TXI method contains 4 steps: 1) R2* was calculated from 2 scans independently by linear fitting the equation: S(FA,TE) = M0(FA) ×exp(-R2* (FA) × TE), where FA denotes flip angle. R2* from different flip angle were added to increase SNR; 2) S(FA,TE=0) were extrapolated by known M0(FA) and R2*(FA) and the equation above; 3)B1 maps were interpolate to the same image size as 3D-GRE scan; 4) S(FA, TE=0) data with different flip angles and interpolated B1 maps were used to calculate T1 map using equation S(FA, TE=0) = M0(FAb1) × sin(FA b1) × (1 – exp(-TR/T1) / (1 – cos(FA b1) × exp(-TR/T1)). Where FA b1 was flip angle corrected by B1 map. The algorithm was implemented in Python 3.5.
Results
The result showed that simultaneously T1 and R2* quantification is feasible within 3 breath-holds, with good mapping SNR and free of motion artifacts when subject could control motion, see Figure 1. The B1 correction can well compensated the signal variation due to B1 field inhomogeneity in liver and showed significant influence on T1 and M0 map, but no influence was found on R2* map. Meanwhile, R2* mapping at two different flip angle showed similar results and their average can well improve SNR and remove motion artifacts. Additional comparison between conventional T1 map (two flip angle and single echo) and the TXI based T1 map (two flip angle and 6 echo) showed that two T1 maps looks similar (Figure 2). ROI analysis based on 6 square 5x5 regions in different liver regions showed that two T1 maps have closed quantitative value, but T1 map of TXI method showed much lower standard deviation among ROIs (TXI: 846.25 ±10.36 ms, conventional: 831.12 ±34.34 ms). The correlation coefficients between ROI means of two T1 maps was 0.47, which is surprising low. TXI method showed higher homogeneity of T1 values in different liver region.Discussion
In this study, we introduced a simultaneously T1/T2* quantification method, namely TXI, with high quality quantitative mapping in liver and fast acquisition speed in 3 breath-holds. The results showed that it may improve SNR and reduce image artifacts of conventional R2* mapping by additional average. For T1 mapping, TXI method could well compensate B1 field inhomogeneity by B1 correction. In addition, the SNR and measurement consistency among different liver regions were significantly improved, which may be due to the usage of multiple echo data. Thus, the TXI method provide a fast and high-quality 3D T1/T2* mapping method in body. In the future, fat saturation method and potential motion among breath-holds will be considered in further development.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Ma D, Gulani V, Seiberlich N, et al.: Magnetic resonance fingerprinting. Nature 2013.
2. Warntjes JBM, Dahlqvist Leinhard O, West J, Lundberg P: Rapid magnetic resonance quantification on the brain: Optimization for clinical usage. Magn Reson Med 2008.
3. Chen Y, Liu S, Wang Y, Kang Y, Haacke EM: STrategically Acquired Gradient Echo (STAGE) imaging, part I: Creating enhanced T1 contrast and standardized susceptibility weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping. Magn Reson Imaging 2018.
Figures
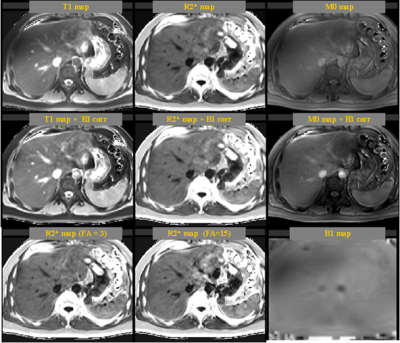
Figure 1. An example of liver simultaneously T1 and R2* mapping. The result showed that without B1 correction, the T1 and M0 maps were significantly influenced by B1 inhomogeneity. B1 correction could significantly improve the image quality.
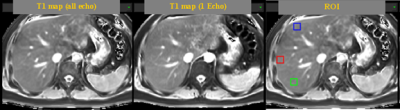
Figure 2. Comparison of T1 mapping by the proposed TXI (based on all echo data) method and conventional method (based on single echo data). The T1 maps from two methods looks similar. ROI analysis were conducted.