2769
Value of diffusion tensor imaging quantitative parameter in differentiating cystic pancreatic cancer from solid pseudopapillary neoplasm1School of Medical Imaging, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Department of Radiology, Dalian Friendship Hospital, Dalian, China, 3Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
It is difficult to differentiate the pancreatic ductail adenocinama(PDAC) from solidpseudopapillary tumer of the pancreas(SPTP),due to their similar imaging characteristics,especially in pancreatic cancer sac change occurs.Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a kind of magnetic resonance technology which can image the diffusion of water molecules in living tissues. There was significant difference in DTI quantitative parameters Fractional Aniso (FA) ,Volume ratio Aniso (VRA), Isotropic image(Iso) and T2-weightial trace(T2-T) between PDAC and SPTP. Therefore, DWI derivative sequences may be an effective method to identify PDAC and SPTP.
Introduction
PDAC is the most common malignant tumor of pancreas, which is hypovascular tumor. According to the latest data of the United States, the 5-year survival rate of PDAC is only 5%, which is worthy of the name of "king of cancer" [1]. Due to its special anatomical location and its own biological characteristics, more than 80% of PDAC is found to be advanced, and the chance of radical resection is lost, and the prognosis is extremely poor [1] . Pancreatic cancer with cystic degeneration and necrosis can also be manifested as cystic solid tumor. The tumor can not be enhanced or delayed enhanced by enhanced scanning, which needs to be differentiated from SPTP [2] There are significant differences in invasion, treatment and prognosis between PDAC and SPTP. Correct preoperative diagnosis is of great significance to guide clinical treatment and judge the prognosis of patients. DTI is a kind of magnetic resonance imaging technology for the diffusion of water molecules in living tissues. The theoretical basis is that the water molecules in the tissues have approximate Gaussian distribution, that is, the diffusion of water molecules in different directions is different, also known as anisotropic diffusion. This paper discusses the value of DTI multiple quantitative parameters in the identification of PDAC and SPTP.Purpose
To evaluate the diagnostic value of multiple quantitative parameters of DTI sequence in the differential diagnosis of PDAC and SPTP.Methods
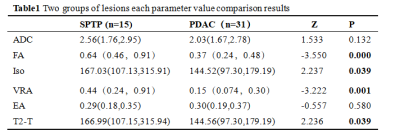
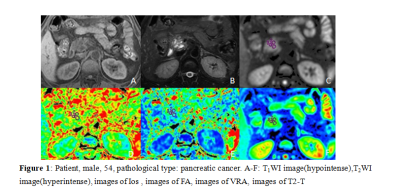
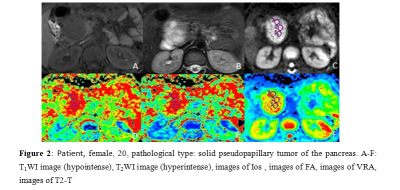
31 cases of PDAC and 15 cases of SPTP were enrolled in our study. Scanning sequence, Tiwi, T2WI, DTI A 1.5T MR scanner (Ge signa hdxt) with phased array coil was used. Scanning sequence and parameters were described in T1WI: TR / TE, 620 ms / 90 ms, matrix, 320 × 192, NEX 1, slice / gap, 6.0 mm/1.5 mm, FOV, 38 cm × 38 cm, scanning time, 17 s; T2WI: TR / TE, 6000 ms / 102 ms, matrix 288 × 224, NEX 3, slice / gap, 6.0 mm/1.5 mm, FOV, 38 cm × 38 cm, scanning time, 17 s. DTI: slice thickness 7mm, layer spacing 2mm, FOV 300mm, matrix 128 × 128, excitation times (nex) = 4, scanning time, 2min5s.Images were transmitted to GE AW 4.6 workstation. DTI quantitative parameter Average DC (ADC), Fractional Aniso (FA), Isotropic image images (Iso), Volume ratio Aniso3 (VRA), Exponential attenuationwere (EA) and T2-weightial trace (T2-T) obtained by functool software.The sequence images were processed by functool software. Two radiologists (observer 1,2) with 5 years' and 10-year MRI diagnosis experience respectively completed the measurement of lesions on the workstation by double-blind method: select the solid part of the lesion and place three circular ROI with an area of about 25-100 mm2, and take the average value( Figure 1, Figure 2). SPSS 26.0 software was used for statistical analysis. Kolmogorov smirov test was used to test whether the parameters were in accordance with normal distribution. Independent sample t test was used for those who conformed, and the mean value was expressed as ± s. The difference was statistically significant if P < 0.05. Mann Whitney rank sum test and m ± s interquartile distance were used for those who did not conform. Receiver operator characteristic curve (ROC curve) was used to analyze the diagnostic efficacy of parameters with statistical difference, and area under curve (AUC), threshold, sensitivity and specificity were obtained.Results
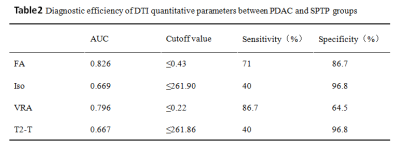
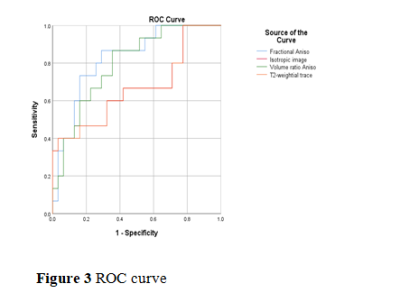
The the value of FA,Iso,VRA,T2-T in PDAC group were significantly smaller than those in STPT group, with statistical significance (P<0.05)(Table1). The AUC were 0.826 for FA(sensitivity71%, specificity 83.6%,Cutoff value ≤0.43) ,0.669 for Iso(sensitivity40%, specificity 96.8%,Cutoff value ≤261.90), 0.796 for VRA(sensitivity86.7%, specificity 64.5%,Cutoff value ≤0.22), 0.667 for T2-T(sensitivity40%, specificity 96.8%,Cutoff value ≤261.86)(Table2, Figure 3).Discussion
Pancreatic cancer often occurs in the elderly. The tumor often has unclear boundary, no capsule, and is invasive. It often leads to dilatation of intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, invasion of blood vessels and adjacent structures, and distant metastasis[2]. SPTP has obvious gender and age tendency, and is prone to young women. Usually SPTP does not cause pancreaticobiliary dilatation. A few large masses located in the head of pancreas can compress the pancreatic duct and bile duct, resulting in mild dilatation. If SPTP appears pancreaticobiliary dilatation, it is related to its growth site and growth mode. If SPTP is located at the head of pancreas and the exogenous growth is not obvious, it may compress the pancreaticobiliary duct and cause the proximal pancreaticobiliary duct dilatation, but the degree is relatively mild, and there is no obvious clinical symptoms[3].There was no significant difference in water molecule diffusion and microcirculation perfusion components between PDAC and SPTP. The pseudopapillary structure formed by tumor cells in pseudopapillary area is a characteristic change of the disease. According to previous studies, SPTP pathological examination showed that tumor cells arranged orderly around the blood vessels with complex structure[4], so the FA and VRA of SPTP were significantly higher than those of SPAC.Conclusion
DTI can be used as an effective way to differentiate PDAC from SPTP, which is of great significance for clinical preoperative diagnosis and prognosis.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010.362(17):1605-1617.
[2] ZHANG Jing,YE Hui—yi.CAl You—quan,et a1.Solid—Pseudopapillary Tumor of Pancreas:MR Imaging features and their correlation with pathological findings,China Hepatobiliary Surg,2009,1007-8118.
[3] ZHANG Jian-ke, ZHANG Yong, HE Peng, Imaging Diagnosis and Pathologic Analysis of Solid Pseudopapillary Tumors of the Pancreas, CHINESE JOURNAL OF CT AND MRI, SEPT.2014,1672 -5131.
[4] ZHANG Jian-ping.NI Jia-lian,LIU Xiao- ming. Diagnosis and treatment of 12 cases of solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas , China Journal of Abdominal Surgery Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery,2011,1003-5591.
Figures