2768
Colloid carcinoma arising from IPMN of pancreas: imaging features and differentiation with ductal adenocarcinoma from IPMN1Changhai Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
N/A
Objective
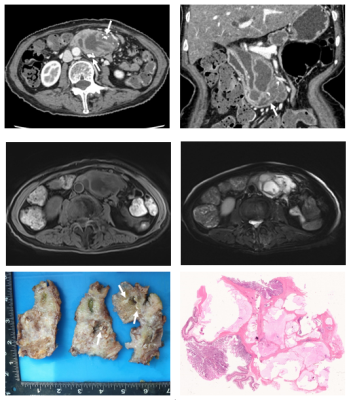
To explore the imaging features of colloid carcinoma arising from intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of pancreas and differentiate with ductal adenocarcinoma from IPMN, correlation with pathological findings.Methods
Retrospective analysis of 24 patients of pathologically confirmed colloid carcinoma with clinical manifestations, imaging features and pathological data from November 2013 to January 2020. As a control group, 30 patients of ductal adenocarcinoma arising from IPMN who were confirmed by pathology at the same time were selected. CT and MRI features of two group were blindly analyzed, including the lesions location, type, size, component, density or signal, enhancement pattern, calcification, dilation and size of the main pancreatic duct (MPD), parenchymal atrophy of pancreas, fistula formation. The Chi-square test or Fisher's exact probability was used to compare the imaging features between the two groups.Results
16 cases located in the head of pancreas, 7 case located in the body and tail of pancreas, and 1 cases diffused in the pancreas. 22 cases had mass formation, the mass size was 21 ~ 190 mm (median 54.5 mm). 19 cases of solid-cystic, 4 cases of cystic and 1 cases of solid. Thick wall and internal separation with mild enhancement. 5 cases of high signal on T1WI. 13 cases with calcification and 2 cases with gas in the mass. The size of MPD was 5~34 mm (mean 12.6 mm). 21 cases of pancreatic parenchymal atrophy. 8 cases of fistula formation. The mass size of IPMN with colloid carcinoma of 54.5 (29.25) mm was significantly greater than the IPMN with ductal adenocarcinoma of 31 (16) mm (P<0.001). IPMN with colloid carcinoma was mainly solid-cystic mass and IPMN with ductal adenocarcinoma was mainly solid mass (P<0.001). IPMN with colloid carcinoma was associated with calcification, fistula formation, high signal on T1WI were more than IPMN with ductal adenocarcinoma (P=0.001、0.031、0.034).Conclusion
IPMN with colloid carcinoma was arising from intestinal type of IPMN. Compared with IPMN with ductal adenocarcinoma, the solid-cystic mass, calcification, fistula formation and high signal on T1WI were all more commonly associated with IPMN with colloid carcinoma. Accurate preoperative diagnosis in important to predict prognosis and clinical management.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Felsenstein M, Noe M, Masica DL, et al. IPMNs with co-occurring invasive cancers: neighbours but not always relatives [J]. Gut, 2018, 67(9): 1652-1662.
[2] Adsay NV, Pierson C, Sarkar F, et al. Colloid (mucinous noncystic) carcinoma of the pancreas [J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2001, 25(1): 26-42.
[3] Yopp AC, Katabi N, Janakos M, et al. Invasive carcinoma arising in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a matched control study with conventional pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [J]. Ann Surg, 2011, 253(5): 968-974.
[4] Jayakrishnan T, Pandya D, Monga D. Colloid Carcinoma of Pancreas in the Setting of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) [J]. Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer, 2019.
[5] Yoon MA, Lee JM, Kim SH, et al. MRI features of pancreatic colloid carcinoma [J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2009, 193(4): W308-W313.
[6] Ren FSCZ. CT features of colloid carcinomas of the pancreas [J]. Chinese Medical Journal, 2010, 123(10): 1329-1332.
[7] Fouladi DF, Raman SP, Hruban RH, et al. Invasive Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms: CT Features of Colloid Carcinoma Versus Tubular Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas [J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2020, 214(5): 1092-1100.
[8] Kobayashi G, Fujita N, Noda Y, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas showing fistula formation into other organs [J]. J Gastroenterol, 2010, 45(10): 1080-1089.
[9] Nagtegaal ID, Odze RD, Klimstra D, et al. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system [J]. Histopathology, 2020, 76(2): 182-188.
[10] Tanaka M, Fernandez-Del CC, Adsay V, et al. International consensus guidelines 2012 for the management of IPMN and MCN of the pancreas [J]. Pancreatology, 2012, 12(3): 183-197.
[11] Escalon JG, Gerst S, Porembka M, et al. Imaging comparison of tubular and colloid pancreatic adenocarcinoma arising from intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm on multidetector CT [J]. Clinical Imaging, 2016, 40(6): 1195-1199.