Jiang jinghua1, Weiyin Vivian LIu2, Huang Lesheng1, Liu Tianzhu1, Li Hongyi 1, Chen Jun 1, Zhang Wanchun 1, He Tao 1, and Tang Jiahui 1
1Department of Radiology, Guangdong Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhuhai,519000, China, zhuhai, China, 2MR Reaearch,GE healthcare, Beijing,China, China
Synopsis
IVIM,
as a noninvasive tool, has good diagnostic performance in the detection and staging grading
of liver
fibrosis
Introduction
Liver
fibrosis is characterized by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix
(mainly type I collagen). It is a common pathological feature of chronic liver
diseases caused by various etiologies, and can develop into liver dysfunction,
portal hypertension, and even hepatocellular carcinoma, thus increasing
incidence rate and mortality. Early or mid-term liver fibrosis is considered
reversible, as long as timely drug intervention and anti-fibrosis treatment.
Therefore, early detection and accurate staging of liver fibrosis is of great
clinical significance for making correct treatment decisions and evaluating the
prognosis of patients. Liver biopsy is the standard reference index for the
diagnosis and staging of liver fibrosis; however, it is an invasive
examination, and the risk and complications cannot be ignored. Some studies
have shown that IVIM, as a noninvasive examination tool, has good diagnostic
performance for the detection and staging of liver fibrosis [1].Materials and methods
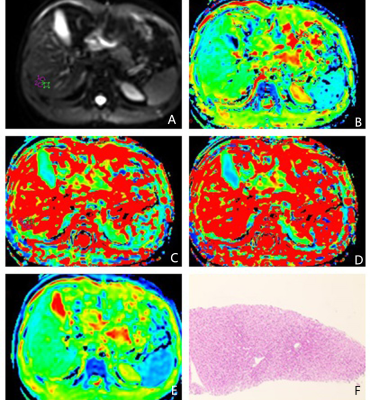
This
study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of our hospital. Six CHB
patients with liver biopsy fibrosis S1(fibrosis stage) and G2 (inflammation grade) results confirmed by liver biopsy were
recruited. Three ROIs (regionsarea of
interest) range
from 80 to 100 mm2 were
placed on S6 and S7 of right liver
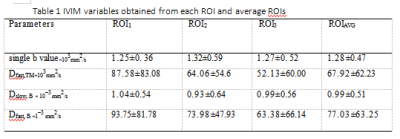
while avoiding obvious vessels. The data of ROI 1,
ROI 2, ROI 3 and ROI-AVE were analyzed to study whether there was correlation
between them. Apparent diffusion coefficient
(ADC) of
single b value 800 s/mm2, ADC of single index standard , perfusion
fraction (f), pseudo-diffusion
coefficient (Dfast),
diffusion coefficient (Dslow) of
IVIM diffusion imaging with 12 b values (0, 25, 50, 75, 100, 150, 200, 300,
400, 500, 600 and 800 s/mm2) were measured for three ROIs and averaged as ROI-AVE using based on both dobble order single
and two-segment
bi-exponential
models and ADC for patients . There were calculated by SPSS21.0 with correlation
(Partial correlation) were analyzed using SPSS21.0 with by after controlling
patients’ sexgender and
age. The potential correlation between singal 800s/mm2DWI-based ADC and IVIM
parameters (ADC, Standand Dslow, Dfast, f using single and bi-exponential model) and
liver function lab indexes (GGT,
AlT, AST, AST/ALT, AFU) [MOU1] were
assessed for the CHB patients.
Result
ROI1/ ROI2,ROI1/ ROI3,ROI2/ ROI3,>0.05,There
was no correlation between ROI1, ROI2
and ROI3.ROI1/
ROIAVG ROI2/ ROIAVG ROI3/ ROIAVG>0.05,There
was no correlation between them.So ROI1,
ROI2, ROI3 and
ROIAVG had no effect on
IVIM and ADC.The
correlations between the standard ADC in S6 (ROI1, ROI2, ROI3
and ROIAVE) of right liver with AFU (P
=0.012), Dslow with AST(P =0.015) and AFU(P =0.007), Dfast
with AST(P =0.044). No significant correlation was found between the remaining
IVIM parameters and laboratory indexes. Discussion:
This
study was aimed to investigate showed the correlation between IVIM model parameters and common laboratory indicators of CHB
in patients with inflammation grade 2 and fibrosis stage 1. The
collected data showed that there was no correlation between ROI1, ROI2, ROI3 , ROIAVG and IVIM . In this our study, the correlation between ROI-AVE and AFU of Dslow (dobble order bi-exponential model) is more obvious than the single b-value ADC.This
correlation between IVIM-based parameters and common laboratory indicators of
CHB in patients with inflammation grade 2 and fibrosis stage 1 that
average ROI-based
measurements is a more reliable discrimination ability of CHB diagnosis.
AFU has a diagnostic value in patients with liver cirrhosis
and acute hepatitis, especially severe hepatitis. Serum
AFU mainly existed in liver tissue., and Serum
AFU its level
would increase
when hepatocytes
was damaged.
The
single b-value ADC measurement can be used to detect liver fibrosis, but can not
be used to reliably distinguish the intermediate stages of fibrosis [2]. In
addition, In
this study, the correlation between ROI-AVE-based and AST of Dslow and AST is
also higher (dobble order single exponential model) than
that of Dfast(dobble order bi-exponential model).[MOU4] The increase of AST reflects the damage of liver
tissue, which AST is
an important indicator of hepatitis progression and increases in reflection of .the
damage of liver tissue.
In this study, the correlation between ROI-AVE and
AST of Dslow(dobble order single exponential model) than that of Dfast(dobble order bi-exponential model).
The
data sample size of this study should be expanded to is small, it is difficult to exclude
the contingency, which is not enough to prove, but and to confirm the
current observation can not consider thatof there is
correlation between IVIM model parameters and common laboratory indicators of CHB
in patients with inflammation grade 2 and fibrosis stage 1. Conclusion
IVIM,
as a noninvasive tool, has good diagnostic performance in the detection and staging grading of liver
fibrosis. However, the
biochemical
test is a more
common
diagnostic method in clinical detection of liver fibrosisdiagnosis and, the
correlation between the twoboth approaches still
needs to expand be examined the relevant sample size, improve and practice
standardized IVIM scheme.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
liver.pdf>.
2. Sandrasegaran, K., et al., Value of diffusion-weighted MRI for assessing liver fibrosis
and cirrhosis.
AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2009. 193(6):
p. 1556-60.