2753
The relationship between preperitoneal fat and cardiometabolic risk factors1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2MR Research, Beijing, China
Synopsis
This study assessed the correlation between preperitoneal fat and cardiometabolic risk factors. The results showed that preperitoneal FF and area were associated with specific risk factors, and the correlation coefficient varied by sex. This plays an important role in our further understanding about the association between ectopic fat deposition and cardiometabolic risk factors.
Synopsis
This study assessed the correlation between preperitoneal fat and cardiometabolic risk factors. The results showed that preperitoneal FF and area were associated with specific risk factors, and the correlation coefficient varied by sex. This plays an important role in our further understanding about the association between ectopic fat deposition and cardiometabolic risk factors.Introduction
Previous studies have shown that preperitoneal fat are closely related to type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases [1-2]. Preperitoneal fat compartment is another interesting fat compartment that has not been extensively studied. It may have important value in prevention of cardiometabolic risk factors.Purpose
To assess the relationship between preperitoneal fat and cardiometabolic risk factors.Methods
A total of 320 subjects (148 men and 172 women) were included in the study. In this study, the MRI scanner (GE Medical Systems, Inc., Waukesha, WI, USA) with an eight-channel phased-array body coil was used. IDEAL-IQ sequence parameters were as follows: TR/TE = 6.9 ms/3.0 ms, slice thickness of 10 mm, 200 KHZ bandwidth, FOV = 36 cm×36 cm, matrix = 256 ×160, flip angle = 3 °, NEX = 1, breath holding for less than 24 s. The images were processed using IDEAL Research software provided by the manufacturer to generate water-phase, fat-phase, in-phase, out-phase, along with R2* and FF maps. On the post-processing platform (Intellispace portal, ISP, Philips, Holland), the margins of preperitoneal fat were traced on FF maps (Fig 1). Preperitoneal fat was defined as the fat depot seen anteriorly from the anterior surface of the left lobe of the liver to the linea alba. Preperitoneal fat fraction and area were calculated. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to check the consistency of the two observers. The associations between preperitoneal fat and cardiometabolic risk factors were computed by Spearman test.Results
Patients’ clinical characteristics were shown in Table 1. Two-observer measurement consistency was great (ICC > 0.75) (Table 2). Preperitoneal FF and area were associated with specific risk factors (P<0.05) (Table 3), and the correlation coefficient varied by sex (Table 4).Conclusion
Preperitoneal fat fraction and area were associated with various cardiometabolic risk factors, and the correlation varied by sex.Discussion
This study assessed the correlation between preperitoneal fat and cardiometabolic risk factors. The results showed that preperitoneal FF and area were associated with specific risk factors, and the correlation coefficient varied by sex. This plays an important role in our further understanding about the association between ectopic fat deposition and cardiometabolic risk factors.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Parente DB, Oliveira Neto JA, Brasil PEAA, et al. Preperitoneal fat as a non-invasive marker of increased risk of severe non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;33(2):511-517.
2.Shabestari AA, Bahrami-Motlagh H, Hosseinpanah F, et al. Abdominal fat sonographic measurement compared to anthropometric indices for predicting the presence of coronary artery disease. J Ultrasound Med. 2013;32(11):1957-65.
Figures
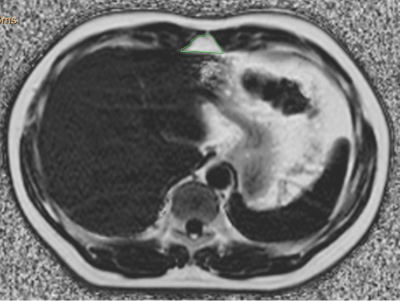
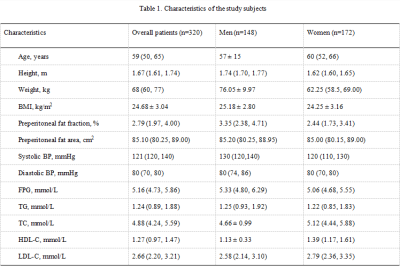
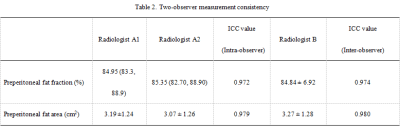
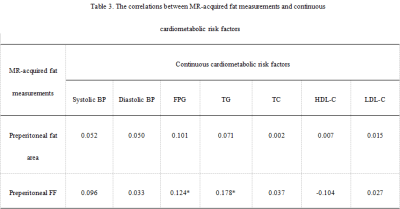
Table 3. The correlations between MR-acquired fat measurements and continuous cardiometabolic risk factors
*P<0.05, **P<0.001.
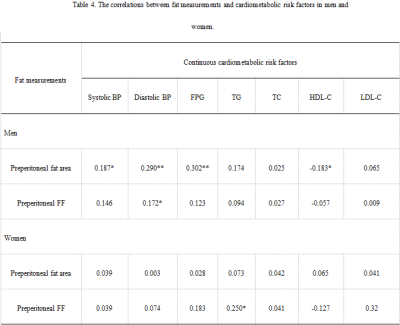
Table 4. The correlations between fat measurements and cardiometabolic risk factors in men and women.
*P<0.05, **P<0.001.