2645
Deep Learning Based ESPIRiT Reconstruction for Highly Accelerated 2D Phase Contrast MRI1Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 4Cardiovascular Institute, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
Synopsis
We propose a novel Deep Learning (DL) based reconstruction framework for accelerated 2D Phase Contrast MRI (PC-MRI) datasets. We extend a previously developed DL method based on ESPIRiT reconstruction for cardiac cine and combine it with a direct Complex Difference estimation approach. We tested the DL methods using retrospectively undersampled 2D PC-MRI data and compared it with conventional Compressed Sensing (CS) reconstruction. Our method outperformed CS and enabled higher acceleration factors up to 8x while maintaining error metrics within a targeted accuracy of ±5%.
Introduction
Phase Contrast MRI (PC-MRI) allows for time-resolved measurements of blood velocity throughout the vasculature. Clinically, these measurements can be used to derive valuable parameters of cardiovascular health and disease, including peak velocity, flow rate, total flow, and pressure gradients. However, one of the main disadvantages of PC-MRI is the extended scan time, which precludes real-time imaging and makes the technique especially susceptible to motion artifacts.1,2One of the most successful techniques, to date, to accelerate PC-MRI data acquisition is Compressed Sensing (CS), wherein the acquisition is accelerated via a pseudorandom undersampling scheme.3 This acquisition produces noise-like artifacts that are later removed using a non-linear reconstruction algorithm that enforces consistency with the acquired data and denoises based on an assumed sparse model of the image.4,5
Nevertheless, generic assumptions of CS sparse models are usually unable to accurately model the complexity of cardiac dynamics. Recently, Deep Learning (DL) based reconstruction frameworks have been demonstrated as an alternative, which aims to learn the sparse model directly from the datasets.6-8 In cardiac cine MR, these novel frameworks have already shown to surpass traditional CS reconstruction techniques by yielding more accurate and faster reconstructions.9
Herein, we present a novel DL-based reconstruction framework that extends a state-of-the-art DL reconstruction framework,9 developed for cardiac cine, to 2D PC-MRI datasets. We extend previously reported results10 and complement them with further measurements to assess the reconstruction accuracy.
The objective of this work was to determine if the proposed DL-based reconstruction framework for retrospectively undersampled 2D PC-MRI could outperform conventional CS reconstructions while maintaining clinically relevant measures of peak velocity (within ±5%) and net flow (within ±5%) when compared to fully-sampled datasets.
Methods
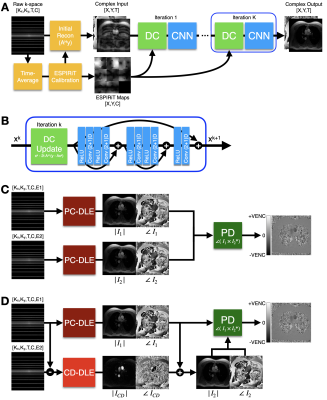
Network architectureThe proposed reconstruction frameworks are presented in Figure 1. First, we adapt the DL-ESPIRiT framework for PC-MRI datasets. DL-ESPIRiT features an Unrolled Network architecture11 that uses an extended ESPIRiT-based12 coil sensitivity model (for robustness against SENSE-related FOV limitations) and (2+1)D convolutions (Fig. 1A). Our first method uses DL-ESPIRiT trained on PC-MRI data (PC-DLE) to reconstruct the flow-encoded images separately before phase difference processing (Fig. 1B).
Second, we leverage previous work5 on accelerated PC-MRI reconstruction and propose the direct reconstruction of the Complex Difference (CD) image. Due to the similarity between the two flow-encoded images, the CD image presents considerably higher sparsity and, thus, should result in higher attainable acceleration factors. Our second method (Fig. 1C) proposes to use PC-DLE to reconstruct one flow-encoded image and then use another DL-ESPIRiT network trained on CD data (CD-DLE) to reconstruct the CD image. With these two images we can obtain the second flow-encoded image and conduct phase difference processing.
Training
Fully sampled (FS) single-slice 2D PC-MRI pediatric datasets (N=194) were obtained with institutional IRB approval and patient consent. All imaging was performed using either a 1.5T (n=23) or 3.0T (n=171) system (GE Healthcare) and an ECG-gated spoiled gradient echo based sequence. The datasets were randomly divided into training, validation, and testing cohorts with a 155/10/29 split. Data augmentation was applied as described in9 with retrospective accelerations ranging from 5-10x. We trained two networks: PC-DLE and CD-DLE.
Evaluation
We retrospectively undersampled the testing datasets with accelerations ranging 5-10x and reconstructed using: L1-ESPIRiT12 (L1E) with Total Variation regularization, PC-DLE, and CD-DLE. We performed background phase correction by masking regions of static tissue and fitting a second-degree polynomial to subtract background phase offsets from the vessel of interest.13 A region-of-interest (ROI) was drawn for each vessel and we measured mean ROI velocity, peak velocity (mean value of the top 5% of all pixels contained in the ROIs), and total flow for the reconstructed and FS images.
Results
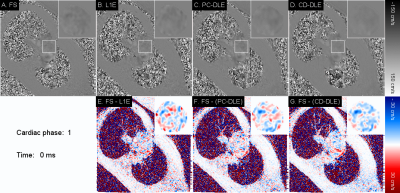
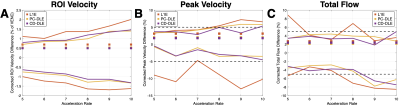
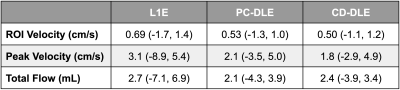
Qualitatively, both PC-DLE and CD-DLE show significantly lower error, especially in time frames with high blood velocity values (Fig. 2). Quantitatively, both DL frameworks outperformed L1E for all measurements (Fig. 3). PC-DLE and CD-DLE showed comparable performance. Errors in the measured total flow and peak velocity were within ±5% for PC-DLE and CD-DLE for accelerations 5-8x, whereas L1E only achieved this for total flow for accelerations of 6-7x and peak velocity for 7x acceleration (Fig. 3 and Table 1). Furthermore, linear regression analysis (Fig. 4) showed near identical agreement with correlation coefficients, $$$R^2 > 0.99$$$ for L1E, PC-DLE, and CD-DLE compared to FS.Discussion & Conclusion
PC-DLE and CD-DLE consistently met the ±5% accuracy criteria for ROI velocity, peak velocity, and total flow for acceleration rates ranging from 5-8x, whereas L1E showed inconsistent results in terms of measurement precision across the same accelerations. This inconsistency could be problematic for prospective undersampling where the exact acceleration rate is difficult to control.Consequently, the DL frameworks allow up to 8x acceleration with high accuracy and precision. This increased acceleration could be leveraged to afford increased spatio-temporal resolution or decreased breath-hold durations compared to conventional FS scans.
Future work will focus on pushing the achievable acceleration via training a deeper network and exploring additional data augmentation techniques. We also aim to evaluate the method on prospectively undersampled data.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported, in part, by U01 EB029427 to SSV and support from GE Healthcare to DBE.References
1. Nayak, K.S., Nielsen, J.F., Bernstein, M.A., Markl, M., Gatehouse, P.D., Botnar, R.M., Saloner, D., Lorenz, C., Wen, H., Hu, B.S. and Epstein, F.H., 2015. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance phase contrast imaging. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 17(1), p.71.
2. Markl, M., Frydrychowicz, A., Kozerke, S., Hope, M. and Wieben, O., 2012. 4D flow MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 36(5), pp.1015-1036.
3. Lustig, M., Donoho, D. and Pauly, J.M., 2007. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 58(6), pp.1182-1195.
4. Giese, D., Schaeffter, T. and Kozerke, S., 2013. Highly undersampled phase‐contrast flow measurements using compartment‐based k–t principal component analysis. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 69(2), pp.434-443.
5. Sun, A., Zhao, B., Ma, K., Zhou, Z., He, L., Li, R. and Yuan, C., 2017. Accelerated phase contrast flow imaging with direct complex difference reconstruction. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 77(3), pp.1036-1048.
6. Hammernik, K., Klatzer, T., Kobler, E., Recht, M.P., Sodickson, D.K., Pock, T. and Knoll, F., 2018. Learning a variational network for reconstruction of accelerated MRI data. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 79(6), pp.3055-3071.
7. Aggarwal, H.K., Mani, M.P. and Jacob, M., 2018. MoDL: Model-based deep learning architecture for inverse problems. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 38(2), pp.394-405.
8. Mardani, M., Gong, E., Cheng, J.Y., Vasanawala, S.S., Zaharchuk, G., Xing, L. and Pauly, J.M., 2018. Deep generative adversarial neural networks for compressive sensing MRI. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 38(1), pp.167-179.
9. Sandino CM, Lai P, Vasanawala SS, Cheng JY. Accelerating cardiac cine MRI using a deep learning‐based ESPIRiT reconstruction. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2020 Jul 22.
10. Oscanoa JA, Middione MJ, Sandino CM, Vasanawala SS, Ennis DB. Accelerated 2D Phase Contrast MRI using deep learning-based reconstruction and direct complex difference estimation. SCMR 24th Annual Meeting, Virtual Meeting, 2021. (Accepted)
11. Mardani, M., Sun, Q., Donoho, D., Papyan, V., Monajemi, H., Vasanawala, S. and Pauly, J., 2018. Neural proximal gradient descent for compressive imaging. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (pp. 9573-9583).
12. Uecker, M., Lai, P., Murphy, M.J., Virtue, P., Elad, M., Pauly, J.M., Vasanawala, S.S. and Lustig, M., 2014. ESPIRiT—an eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel MRI: where SENSE meets GRAPPA. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 71(3), pp.990-1001.
13. Lankhaar JW, Hofman MB, Marcus JT, Zwanenburg JJ, Faes TJ, Vonk‐Noordegraaf A. Correction of phase offset errors in main pulmonary artery flow quantification. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2005 Jul;22(1):73-9.
Figures